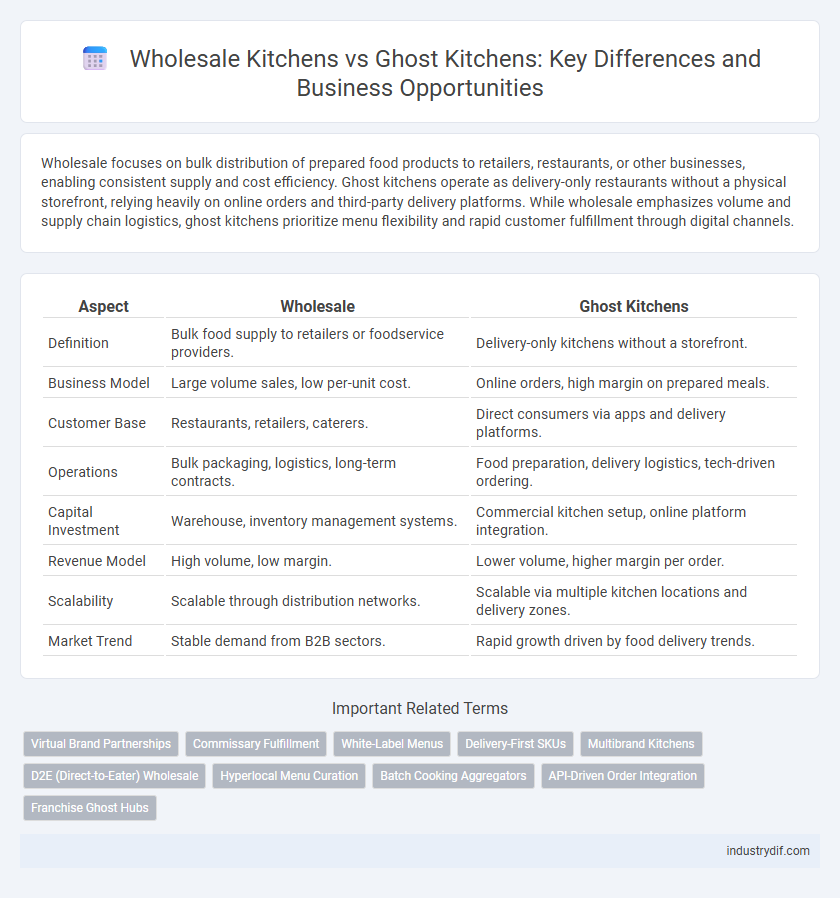
Wholesale focuses on bulk distribution of prepared food products to retailers, restaurants, or other businesses, enabling consistent supply and cost efficiency. Ghost kitchens operate as delivery-only restaurants without a physical storefront, relying heavily on online orders and third-party delivery platforms. While wholesale emphasizes volume and supply chain logistics, ghost kitchens prioritize menu flexibility and rapid customer fulfillment through digital channels.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Wholesale | Ghost Kitchens |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bulk food supply to retailers or foodservice providers. | Delivery-only kitchens without a storefront. |
| Business Model | Large volume sales, low per-unit cost. | Online orders, high margin on prepared meals. |
| Customer Base | Restaurants, retailers, caterers. | Direct consumers via apps and delivery platforms. |
| Operations | Bulk packaging, logistics, long-term contracts. | Food preparation, delivery logistics, tech-driven ordering. |
| Capital Investment | Warehouse, inventory management systems. | Commercial kitchen setup, online platform integration. |
| Revenue Model | High volume, low margin. | Lower volume, higher margin per order. |
| Scalability | Scalable through distribution networks. | Scalable via multiple kitchen locations and delivery zones. |
| Market Trend | Stable demand from B2B sectors. | Rapid growth driven by food delivery trends. |
Understanding Wholesale in the Food Industry
Wholesale in the food industry involves the bulk distribution of food products from producers to retailers, restaurants, and other businesses, emphasizing volume sales and cost efficiency. Unlike ghost kitchens that focus on virtual restaurant operations and direct-to-consumer delivery, wholesale prioritizes supply chain logistics and large-scale inventory management to meet diverse client demands. Efficient wholesale operations ensure consistent food quality, regulatory compliance, and timely delivery to maintain strong business relationships across the foodservice sector.
What Are Ghost Kitchens?
Ghost kitchens are delivery-only food production facilities that operate without a traditional storefront, enabling restaurants to expand their reach through online orders and third-party delivery services. Unlike wholesale operations, which supply bulk food products to retailers and food service providers, ghost kitchens focus on preparing and distributing ready-to-eat meals directly to consumers. These kitchens leverage technology and flexible kitchen space to reduce overhead costs while meeting growing demand for convenience and contactless delivery.
Key Differences Between Wholesale and Ghost Kitchens
Wholesale involves supplying bulk food products or ingredients directly to businesses such as restaurants, retailers, or catering services, emphasizing large-scale inventory management and distribution efficiency. Ghost kitchens operate as delivery-only food service facilities without a traditional storefront, focusing on preparing meals for online orders through digital platforms. Key differences include wholesale's role in product supply chain versus ghost kitchens' emphasis on on-demand food preparation and delivery logistics.
Supply Chain Dynamics in Wholesale and Ghost Kitchens
Wholesale supply chains emphasize large-volume procurement, streamlined inventory management, and bulk distribution networks to ensure consistent product availability for diverse clients. Ghost kitchens rely on agile supply chains with rapid replenishment cycles, localized sourcing, and integrated technology platforms to meet fluctuating demand from delivery-only operations. Both models require robust logistics coordination, but wholesale prioritizes scale efficiency while ghost kitchens focus on speed and flexibility in supply management.
Revenue Models: Wholesale vs. Ghost Kitchens
Wholesale revenue models generate consistent cash flow through bulk sales to retailers, leveraging economies of scale and long-term contracts. Ghost kitchens optimize revenue by minimizing overhead, utilizing delivery platforms to reach customers directly, and scaling rapidly with flexible kitchen spaces. Both models prioritize operational efficiency but differ in customer engagement and revenue predictability.
Operational Efficiency: Comparing Wholesale and Ghost Kitchens
Wholesale operations streamline supply chains by leveraging bulk purchasing and centralized distribution, reducing per-unit costs and minimizing inventory waste. Ghost kitchens optimize operational efficiency by focusing solely on food preparation and delivery, eliminating expenses related to front-of-house services and dining space maintenance. While wholesale emphasizes large-scale production and broad distribution channels, ghost kitchens prioritize agility and speed in fulfilling direct-to-consumer delivery orders.
Scalability and Growth Opportunities
Wholesale models enable rapid scalability by leveraging existing production capacities and established distribution networks, facilitating consistent supply to multiple retail locations. Ghost kitchens offer flexible growth opportunities through virtual brands and delivery-only services, minimizing overhead costs and expanding market reach without the constraints of physical storefronts. Both strategies provide scalable solutions tailored to different market demands, with wholesale focusing on volume and distribution, while ghost kitchens capitalize on delivery efficiency and digital marketing.
Technology Integration in Wholesale and Ghost Kitchens
Technology integration in wholesale enables efficient inventory management, real-time order tracking, and seamless supplier communication through advanced software platforms. Ghost kitchens leverage cloud-based kitchen management systems and AI-driven analytics to optimize food preparation and delivery logistics without the need for a traditional front-of-house setup. Both sectors utilize IoT devices and automation, but wholesale focuses on supply chain synchronization while ghost kitchens emphasize dynamic operational scalability and data-driven customer insights.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Wholesale operations must comply with strict food safety regulations, labeling requirements, and distribution licenses enforced by agencies such as the FDA and USDA. Ghost kitchens face unique regulatory challenges, including zoning laws, health inspections, and compliance with delivery service protocols. Both models require adherence to sanitation standards and proper documentation to ensure consumer safety and avoid legal penalties.
Future Trends: Wholesale and Ghost Kitchen Synergies
Wholesale and ghost kitchens are converging as future foodservice trends forecast increased collaboration for optimized supply chains and faster market responsiveness. Data-driven inventory management in wholesale supports ghost kitchens' demand for agility and scalability, minimizing waste and improving profit margins. Integrating wholesale distribution networks and ghost kitchen operations enables seamless product innovation and expands geographic reach through digital ordering platforms.
Related Important Terms
Virtual Brand Partnerships
Wholesale distribution enables virtual brand partnerships to scale by supplying bulk ingredients and products to ghost kitchens, supporting operational efficiency and menu diversity. Ghost kitchens leverage these wholesale partnerships to rapidly test and expand virtual brands without the overhead of traditional restaurant infrastructure.
Commissary Fulfillment
Commissary fulfillment in wholesale provides centralized kitchen space and bulk ingredient storage, enabling efficient large-scale food production without the overhead of traditional restaurant setups. Ghost kitchens leverage commissary fulfillment to streamline meal prep and delivery logistics, reducing costs and scaling operations for multiple virtual brands simultaneously.
White-Label Menus
Wholesale models offer scalable distribution of white-label menus, enabling food brands to supply multiple ghost kitchens without compromising consistency or increasing operational costs. Ghost kitchens leverage these pre-developed white-label menus to rapidly expand their delivery portfolio, optimizing market reach while maintaining brand neutrality and streamlined inventory management.
Delivery-First SKUs
Wholesale operations prioritize bulk production and distribution of delivery-first SKUs to multiple retailers, ensuring consistent volume and supply chain efficiency. Ghost kitchens focus exclusively on delivery with SKU optimization tailored for direct-to-consumer orders, leveraging data-driven menu engineering to enhance speed and reduce overhead costs.
Multibrand Kitchens
Multibrand kitchens leverage wholesale supply chains to optimize inventory costs and streamline meal production across various culinary brands under one roof, enhancing operational efficiency compared to standalone ghost kitchens. By integrating wholesale purchasing, multibrand kitchens reduce ingredient expenses and improve scalability, driving higher profit margins and consistent product quality in a competitive food delivery market.
D2E (Direct-to-Eater) Wholesale
Direct-to-Eater (D2E) wholesale streamlines the supply chain by delivering bulk food products directly from producers to consumers, bypassing traditional intermediaries and ghost kitchens that primarily serve as virtual food preparation spaces. This approach enhances freshness, reduces costs, and offers scalable distribution for restaurants and food brands aiming to expand their reach without the operational complexities of managing ghost kitchen infrastructure.
Hyperlocal Menu Curation
Wholesale enables hyperlocal menu curation by providing bulk ingredients tailored to regional tastes, ensuring freshness and cost efficiency for restaurants. Ghost kitchens leverage this model to rapidly adapt menus based on local demand data, optimizing inventory and minimizing waste.
Batch Cooking Aggregators
Batch cooking aggregators streamline wholesale operations by consolidating prepared meals from multiple ghost kitchens, enhancing distribution efficiency and reducing per-unit costs. This model leverages centralized production and bulk purchasing advantages, contrasting traditional wholesale methods that rely on separate suppliers and fragmented logistics.
API-Driven Order Integration
API-driven order integration enables seamless real-time connectivity between wholesale suppliers and ghost kitchens, streamlining inventory management, order processing, and delivery schedules. Leveraging robust APIs reduces manual errors, accelerates fulfillment, and enhances operational efficiency in the rapidly evolving foodservice supply chain.
Franchise Ghost Hubs
Franchise Ghost Hubs revolutionize wholesale by providing centralized kitchens that streamline large-scale food production and distribution without traditional storefront costs. These hubs enhance operational efficiency and scalability for wholesale businesses by leveraging shared kitchen resources and optimized delivery logistics.
Wholesale vs Ghost Kitchens Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com