Wholesale offers businesses the advantage of purchasing products in bulk at lower prices, enabling rapid inventory turnover and minimized risk. Private label allows companies to create unique branded products, fostering customer loyalty and higher profit margins through exclusive offerings. Choosing between wholesale and private label depends on a company's goals for brand identity, control over product quality, and scalability.
Table of Comparison
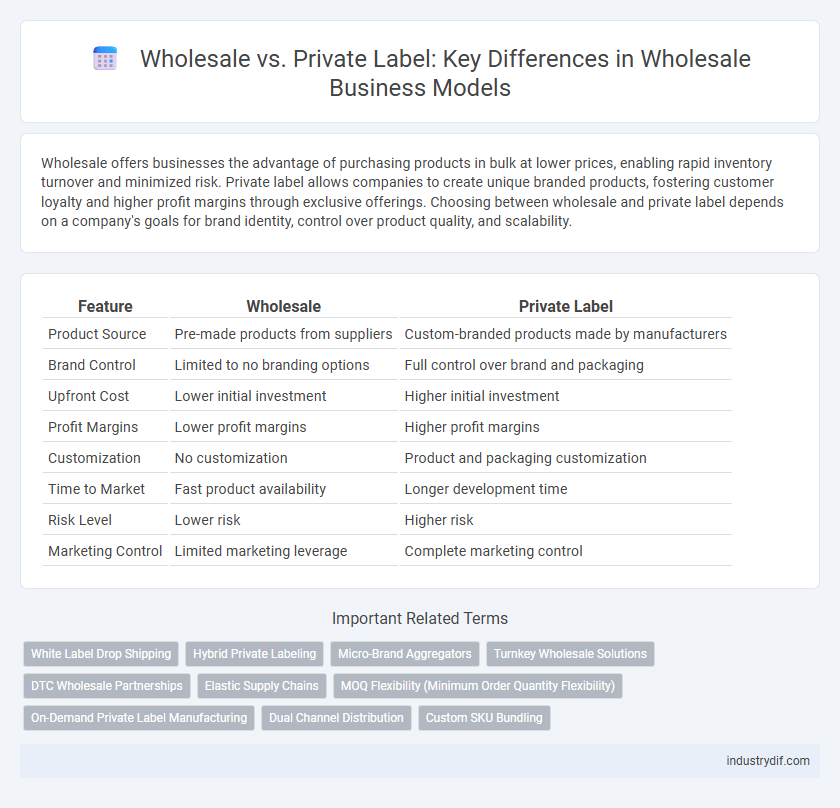
| Feature | Wholesale | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Product Source | Pre-made products from suppliers | Custom-branded products made by manufacturers |
| Brand Control | Limited to no branding options | Full control over brand and packaging |
| Upfront Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher initial investment |
| Profit Margins | Lower profit margins | Higher profit margins |
| Customization | No customization | Product and packaging customization |
| Time to Market | Fast product availability | Longer development time |
| Risk Level | Lower risk | Higher risk |
| Marketing Control | Limited marketing leverage | Complete marketing control |
Introduction to Wholesale and Private Label
Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of products directly from manufacturers or distributors at discounted rates, allowing retailers to resell them under the original brand. Private label refers to products manufactured by third parties but sold under a retailer's own brand, offering greater control over branding and product specifications. Both strategies are essential in retail, with wholesale emphasizing volume and established brands, while private label focuses on customization and brand exclusivity.
Key Differences Between Wholesale and Private Label
Wholesale involves purchasing pre-made products in bulk from manufacturers or distributors at a lower cost to resell them directly, while private label entails creating unique products branded under a retailer's name with control over design, packaging, and specifications. Wholesale offers faster market entry with lower upfront investment, whereas private label requires higher initial costs but provides greater brand differentiation and profit margins. Key differences include ownership of the product brand, customization options, pricing strategies, and long-term scalability potential.
Pros and Cons of Wholesale
Wholesale offers the advantage of lower upfront costs and faster market entry since products are ready-made and available in bulk. However, limited control over branding and product differentiation can restrict competitive positioning and profit margins. Relying on existing product lines may also reduce flexibility in customizing offerings to specific customer needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private Label
Private label products offer wholesalers higher profit margins and greater brand control compared to generic wholesale items, enabling tailored marketing strategies and customer loyalty building. However, private label requires significant upfront investment in product development, branding, and quality assurance, posing risks if the product fails to gain market traction. This contrasts with wholesale models that focus on selling existing brands with lower financial risk but limited differentiation opportunities.
Profit Margins: Wholesale vs Private Label
Wholesale offers lower profit margins typically ranging from 10% to 30% due to bulk purchasing and established brand pricing, while private label products can yield higher margins of 40% to 60% by eliminating brand royalties and allowing for customized pricing strategies. Private label businesses benefit from greater control over product costs, packaging, and branding, which directly impacts profitability and market positioning. Wholesale relies on volume sales with lower per-unit profits, whereas private labeling leverages unique product identity to command premium pricing and enhanced customer loyalty.
Branding Opportunities in Wholesale vs Private Label
Wholesale offers branding opportunities by allowing retailers to sell established products with recognized brand names, leveraging existing market presence and customer trust. Private label provides greater control over branding, enabling businesses to design unique products and develop exclusive brand identity tailored to target audiences. Choosing between wholesale and private label depends on whether the priority is leveraging well-known brands or creating differentiated, proprietary brand experiences.
Supply Chain and Inventory Management
Wholesale offers streamlined supply chain processes by purchasing bulk products directly from manufacturers, reducing lead times and simplifying inventory management through consistent product availability. Private label requires more complex coordination, including product development, branding, and quality control, which can extend supply chain timelines and increase inventory risks. Effective inventory management in private labeling demands precise demand forecasting and supplier collaboration to avoid overstock or stockouts.
Scalability and Growth Potential
Wholesale offers immediate access to established brands with lower upfront costs, enabling faster inventory turnover and scalable sales channels through existing demand. Private label provides greater control over product differentiation and brand identity, fostering long-term growth potential by building unique customer loyalty and higher profit margins. Scalability in wholesale depends on supplier relationships and market trends, while private label scalability hinges on marketing strategy and production capacity.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Wholesale offers established brand recognition and faster market entry by purchasing products in bulk from manufacturers, while private label allows full control over branding and product customization, enhancing long-term profit margins. Evaluating factors such as initial investment, control over product quality, and scalability helps determine the best model for your business strategy. Businesses with strong marketing capabilities may benefit from private labeling, whereas those seeking quicker inventory turnover might prefer wholesale.
Wholesale vs Private Label: Industry Trends and Future Outlook
Wholesale involves purchasing bulk products from manufacturers or distributors to resell them under the original brand, enabling faster market entry and lower upfront costs. Private label requires creating custom-branded products, offering higher profit margins and control over branding but demands greater investment in design and marketing. Industry trends indicate growing preference for private label due to consumer demand for unique products, while wholesale remains a viable option for businesses prioritizing speed and lower risk, with future outlook favoring hybrid models combining both approaches.
Related Important Terms
White Label Drop Shipping
White label drop shipping allows retailers to sell products under their own brand without managing inventory, streamlining the supply chain compared to traditional wholesale purchasing. This model enhances scalability and brand control while minimizing upfront investment and storage costs.
Hybrid Private Labeling
Hybrid private labeling combines the scalability of wholesale distribution with the customization of private label products, enabling retailers to offer unique merchandise without the full investment of traditional private labeling. This approach maximizes brand differentiation while leveraging established supply chains for cost-efficiency and faster market entry.
Micro-Brand Aggregators
Micro-brand aggregators specialize in acquiring and scaling niche wholesale brands, leveraging established customer bases and unique product offerings to optimize distribution channels and market reach. Unlike private label models, which create products from scratch, micro-brand aggregators focus on consolidating diverse wholesale portfolios to enhance competitive advantage and operational efficiency.
Turnkey Wholesale Solutions
Turnkey wholesale solutions streamline inventory management, packaging, and distribution, enabling businesses to scale rapidly without the complexities of product development inherent in private label strategies. These solutions offer ready-to-sell products with established demand, reducing time-to-market and minimizing risk compared to the customization and branding efforts required for private label ventures.
DTC Wholesale Partnerships
Wholesale partnerships enable brands to scale distribution rapidly by supplying large retailers and e-commerce platforms, whereas private label focuses on producing products exclusively for a single retailer's brand. DTC wholesale partnerships combine direct consumer insights with broad market reach, optimizing inventory turnover and enhancing brand visibility without sacrificing control over product quality.
Elastic Supply Chains
Wholesale leverages established elastic supply chains to scale inventory rapidly and respond to market demand fluctuations with flexibility, whereas private label often requires more rigid supply chain management due to brand-specific production and quality control. Elastic supply chains in wholesale enable cost-effective bulk purchasing and faster replenishment cycles, optimizing operational efficiency and market responsiveness.
MOQ Flexibility (Minimum Order Quantity Flexibility)
Wholesale offers greater MOQ flexibility, allowing businesses to purchase larger quantities at discounted rates without strict minimums tied to branding. Private label typically requires higher MOQs to justify custom packaging and product personalization costs, making wholesale more adaptable for smaller or variable order sizes.
On-Demand Private Label Manufacturing
On-demand private label manufacturing offers wholesale buyers greater flexibility by producing customized products only as needed, significantly reducing inventory costs and enhancing market responsiveness. This approach leverages advanced production technologies to deliver tailored goods quickly, contrasting with traditional wholesale models that require bulk ordering and stockholding.
Dual Channel Distribution
Wholesale allows businesses to distribute products through multiple retail channels simultaneously, maximizing market reach and inventory turnover. Private label focuses on exclusive branding but often limits distribution to a single channel, reducing the ability to leverage dual channel distribution strategies effectively.
Custom SKU Bundling
Wholesale offers ready-made products in bulk with standard SKUs, enabling faster inventory turnover and predictable costs, while private label allows custom SKU bundling tailored to brand-specific needs, enhancing differentiation and customer loyalty. Custom SKU bundling in private label supports unique product combinations and packaging, optimizing market positioning compared to the uniform offerings in wholesale distribution.
Wholesale vs Private Label Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com