Wholesale involves selling large quantities of products at lower prices to retailers or businesses, focusing on volume and efficiency. Community commerce prioritizes local connections and shared values, fostering trust through direct relationships between buyers and sellers. While wholesale maximizes scale and distribution, community commerce emphasizes personalized experiences and supporting local economies.
Table of Comparison
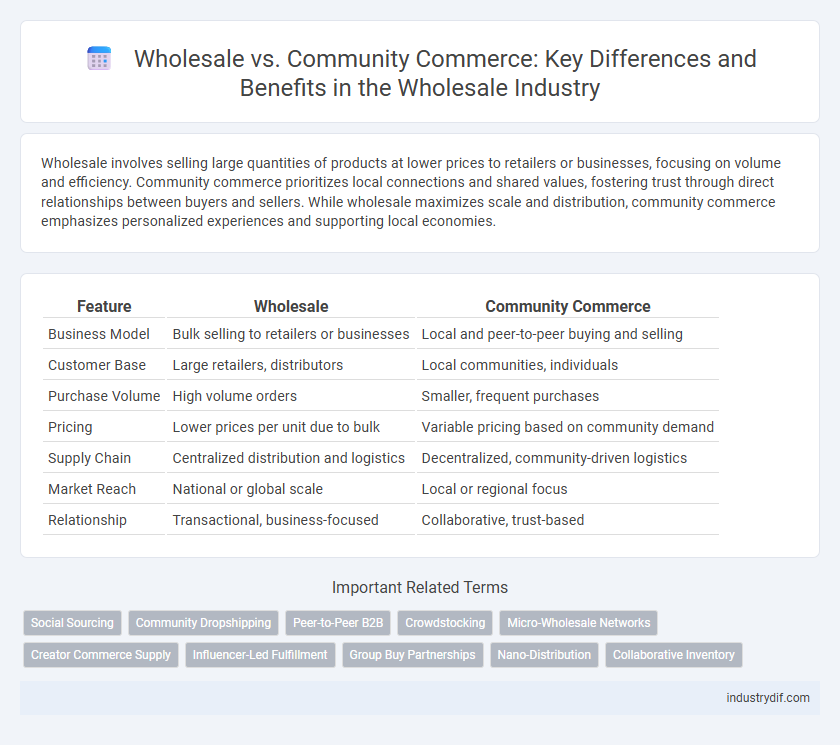
| Feature | Wholesale | Community Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Bulk selling to retailers or businesses | Local and peer-to-peer buying and selling |
| Customer Base | Large retailers, distributors | Local communities, individuals |
| Purchase Volume | High volume orders | Smaller, frequent purchases |
| Pricing | Lower prices per unit due to bulk | Variable pricing based on community demand |
| Supply Chain | Centralized distribution and logistics | Decentralized, community-driven logistics |
| Market Reach | National or global scale | Local or regional focus |
| Relationship | Transactional, business-focused | Collaborative, trust-based |
Understanding Wholesale: Definition and Key Features
Wholesale involves selling goods in large quantities at lower prices to retailers or businesses for resale, emphasizing bulk transactions and volume discounts. Key features include supply chain efficiency, centralized inventory management, and reduced per-unit cost, enabling competitive pricing for downstream sellers. This model contrasts with community commerce, which focuses on local engagement and smaller, personalized transactions.
What is Community Commerce?
Community commerce is a business model that emphasizes direct engagement and collaboration between buyers and sellers within a specific community or network. Unlike traditional wholesale, which relies on large-scale transactions between manufacturers and retailers, community commerce fosters personalized relationships, shared values, and localized economic growth. This approach enhances trust, supports small businesses, and strengthens social connections, driving sustainable commerce at a grassroots level.
Core Differences Between Wholesale and Community Commerce
Wholesale involves selling large quantities of goods to retailers or businesses at discounted prices, emphasizing bulk transactions and supply chain efficiency. Community commerce centers around localized buying and selling within a specific group, fostering trust, engagement, and personalized experiences over volume-driven sales. The core differences lie in target audiences, transaction scale, and the focus on relationship-building versus distribution reach.
Supply Chain Dynamics in Wholesale vs Community Commerce
Wholesale supply chains emphasize large-scale procurement and centralized distribution, optimizing inventory turnover through bulk transactions with manufacturers and retailers. Community commerce supply chains prioritize localized sourcing and direct engagement with smaller vendors, enhancing agility and fostering close-knit supplier relationships. Variations in logistics, order frequency, and demand forecasting highlight the distinct operational strategies between wholesale and community commerce models.
Pricing Strategies in Wholesale Compared to Community Commerce
Wholesale pricing strategies prioritize bulk discounts and tiered pricing to attract large-volume buyers, enabling lower per-unit costs and higher profit margins. Community commerce emphasizes personalized pricing and dynamic adjustments based on local demand and consumer engagement, fostering loyalty and tailored value. Price transparency and flexible negotiation models differentiate wholesale approaches from the community-centric pricing tactics, highlighting efficiency versus relational value.
Customer Relationships: Transactional vs Community-Driven
Wholesale operations typically maintain transactional customer relationships centered on bulk purchases and price negotiations, prioritizing efficiency and volume over personalized interaction. Community commerce, by contrast, fosters community-driven relationships, emphasizing engagement, shared values, and long-term loyalty through interactive platforms and social connections. This shift from transactional to relational strategies enhances customer retention and promotes brand advocacy within niche markets.
Technology’s Role in Wholesale and Community Commerce
Technology transforms wholesale by streamlining supply chains through advanced inventory management systems, real-time data analytics, and automated ordering platforms that increase efficiency and reduce costs. In community commerce, technology fosters localized interactions via social media, mobile apps, and digital marketplaces that enhance buyer-seller trust and facilitate personalized experiences. The integration of AI-driven insights and blockchain for transparency further distinguishes wholesale's scalability from community commerce's focus on trust and engagement.
Scalability and Growth Potential: Wholesale vs Community Commerce
Wholesale offers significant scalability by enabling businesses to distribute large quantities of products to multiple retailers, maximizing market reach and accelerating growth potential. Community commerce relies on localized, trust-based interactions, which may limit rapid expansion but foster strong customer loyalty and niche market penetration. Businesses aiming for broad market dominance often prioritize wholesale, while those focusing on sustainable, community-driven growth may prefer community commerce models.
Pros and Cons of Wholesale and Community Commerce Models
Wholesale offers bulk purchasing advantages, lower per-unit costs, and streamlined supply chains, making it ideal for large-scale operations. Community commerce fosters local engagement, personalized customer experiences, and stronger brand loyalty but may face scalability challenges and limited market reach. Wholesale excels in efficiency and cost savings, whereas community commerce emphasizes relationship-building and niche market focus.
Future Trends: Wholesale and Community Commerce Evolution
Future trends in wholesale highlight the integration of community commerce to foster localized networks that enhance customer engagement and trust. Digital platforms leveraging AI and blockchain are enabling more transparent, efficient supply chains while supporting community-driven purchasing behaviors. The evolution points to hybrid models combining bulk buying power with personalized, socially-connected commerce experiences to drive sustainability and resilience.
Related Important Terms
Social Sourcing
Wholesale relies on direct bulk purchasing from manufacturers to supply retailers efficiently, while community commerce leverages social sourcing by engaging networks of consumers and influencers to drive product discovery and group buying. Social sourcing enhances community engagement and trust, creating organic demand that complements traditional wholesale distribution strategies.
Community Dropshipping
Community dropshipping integrates social networks and direct consumer engagement, enabling wholesalers to leverage localized trust and personalized marketing that traditional wholesale models often lack. This approach enhances product visibility and accelerates fulfillment by tapping into community-driven demand without the overhead of inventory management.
Peer-to-Peer B2B
Wholesale relies on centralized distributors to supply products in bulk to retailers, while Community Commerce emphasizes Peer-to-Peer B2B transactions that enable direct connections between businesses, fostering trust and localized trade networks. Peer-to-Peer B2B models reduce intermediaries, lower costs, and enhance collaboration by leveraging digital platforms tailored for business communities.
Crowdstocking
Wholesale channels leverage bulk purchasing and direct supplier relationships to optimize inventory management, while community commerce emphasizes localized, trust-based transactions supported by crowdstocking mechanisms that aggregate small orders into significant demand pools. Crowdstocking enables community members to collaboratively fund and stock products, reducing friction and enhancing supply chain efficiency compared to traditional wholesale distribution.
Micro-Wholesale Networks
Micro-wholesale networks bridge the gap between traditional wholesale and community commerce by enabling localized, small-scale bulk purchasing that leverages community trust and personalized service. These networks optimize supply chains for niche markets, enhance inventory turnover, and foster resilient economic ecosystems through decentralized distribution models and direct supplier-to-retailer relationships.
Creator Commerce Supply
Wholesale involves bulk selling of products to retailers or distributors, enabling large-scale inventory movement and consistent supply chain management. Community Commerce, centered on Creator Commerce Supply, leverages individual creators and influencers to distribute products directly to niche audiences, fostering stronger brand loyalty and personalized customer engagement.
Influencer-Led Fulfillment
Wholesale relies on large-scale bulk distribution through established supply chains, whereas community commerce leverages influencer-led fulfillment to create personalized and trust-driven purchasing experiences. Influencers act as key intermediaries who directly connect brands with niche audiences, enhancing engagement and driving higher conversion rates through authentic recommendations within community networks.
Group Buy Partnerships
Group buy partnerships in wholesale leverage collective purchasing power to reduce costs and increase product accessibility, enabling suppliers to optimize inventory turnover and enhance profit margins. Community commerce, by contrast, emphasizes direct consumer engagement and local collaboration, creating niche markets but often lacking the scale efficiencies found in wholesale group buys.
Nano-Distribution
Nano-distribution in wholesale leverages hyper-local networks to connect small-scale producers directly with niche customer bases, enhancing efficiency and reducing intermediaries. Community commerce emphasizes localized, trust-driven transactions, whereas wholesale nano-distribution scales this model by integrating technology to optimize supply chains and improve real-time inventory management.
Collaborative Inventory
Wholesale traditionally relies on bulk purchasing and centralized inventory control to maximize cost efficiency, while community commerce emphasizes collaborative inventory sharing among local businesses to reduce stockouts and increase product variety. This collaborative inventory approach in community commerce enhances supply chain resilience and fosters stronger partnerships within the local ecosystem.
Wholesale vs Community Commerce Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com