The Administrator typically manages daily operations and ensures organizational policies are followed, focusing on efficiency and workflow. The Chief of Staff acts as a senior advisor and strategist, coordinating between executives and departments to align goals and priorities. While the Administrator handles administrative tasks, the Chief of Staff drives executive decision-making and organizational planning.
Table of Comparison
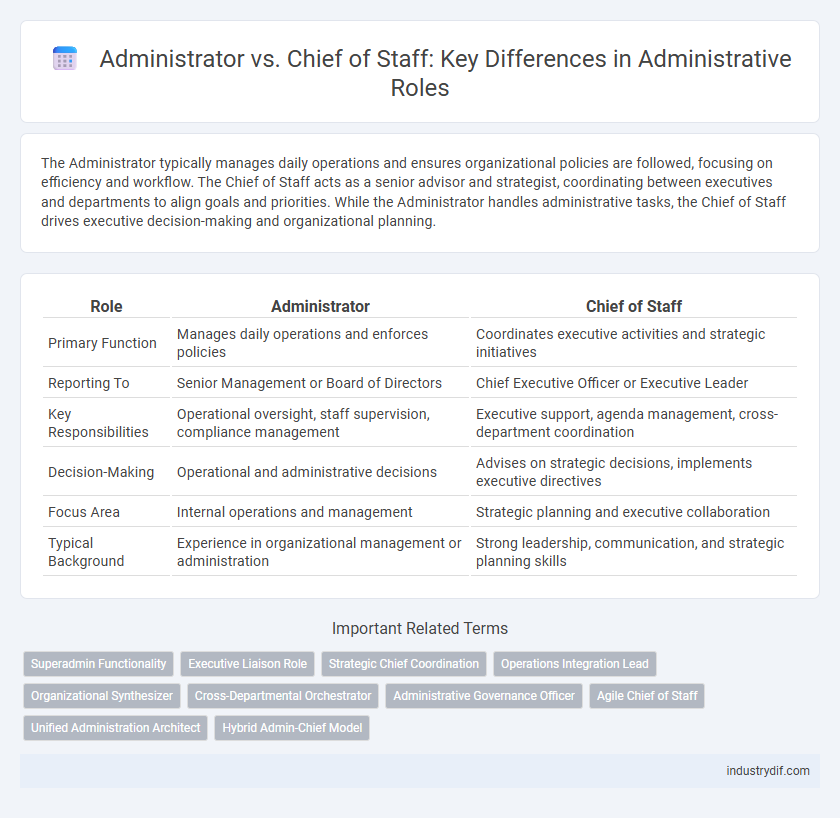
| Role | Administrator | Chief of Staff |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manages daily operations and enforces policies | Coordinates executive activities and strategic initiatives |
| Reporting To | Senior Management or Board of Directors | Chief Executive Officer or Executive Leader |
| Key Responsibilities | Operational oversight, staff supervision, compliance management | Executive support, agenda management, cross-department coordination |
| Decision-Making | Operational and administrative decisions | Advises on strategic decisions, implements executive directives |
| Focus Area | Internal operations and management | Strategic planning and executive collaboration |
| Typical Background | Experience in organizational management or administration | Strong leadership, communication, and strategic planning skills |
Defining the Roles: Administrator vs Chief of Staff
The Administrator oversees organizational operations, focusing on policy implementation, resource management, and compliance with regulations to ensure efficient workflow. The Chief of Staff acts as a strategic partner to senior leadership, coordinating communication, managing priorities, and facilitating decision-making processes. Distinctly, the Administrator handles day-to-day administrative functions, while the Chief of Staff aligns executive goals with operational activities.
Key Responsibilities Compared
An Administrator primarily oversees the daily operations, manages office resources, and ensures compliance with organizational policies to maintain efficiency. A Chief of Staff coordinates executive activities, facilitates strategic planning, and manages communication between leadership and departments to align goals. Both roles require strong organizational skills, but the Chief of Staff emphasizes executive support and high-level decision-making coordination.
Organizational Hierarchy and Reporting Lines
The Administrator typically oversees daily operations and manages departmental functions, reporting directly to the CEO or Board of Directors. The Chief of Staff acts as a key advisor and liaison, coordinating between executive leadership and internal teams to ensure strategic alignment. In organizational hierarchy, the Chief of Staff often holds a more strategic role with broader influence on policy execution, while Administrators handle operational execution within their domains.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
An effective Administrator requires strong organizational skills, proficiency in office management software, and a deep understanding of compliance and regulatory standards. Essential qualifications include a degree in business administration or public administration, alongside experience in scheduling, communication, and resource allocation. The Chief of Staff must demonstrate strategic leadership, exceptional problem-solving abilities, and expertise in coordinating cross-departmental initiatives, often supported by a background in management, political science, or public affairs.
Strategic Influence and Decision-Making
Administrators manage operational functions, ensuring efficient execution of policies and procedures within an organization, while Chiefs of Staff hold a pivotal role in shaping strategic direction and facilitating high-level decision-making processes for executive leaders. The Chief of Staff acts as a key advisor and coordinator, streamlining communication between departments and aligning organizational goals with leadership priorities. Their influence on strategy is profound, often guiding critical decisions that impact the organization's long-term vision and resource allocation.
Day-to-Day Operations and Task Management
Administrators oversee day-to-day operations by managing organizational processes, resource allocation, and routine task execution to ensure operational efficiency. Chiefs of Staff coordinate cross-departmental initiatives, prioritize strategic tasks, and serve as key liaisons between leadership and staff, streamlining communication and decision-making. While Administrators focus on maintaining consistent workflow and operational stability, Chiefs of Staff emphasize managing complex responsibilities and aligning tasks with overarching organizational goals.
Leadership and Team Collaboration
Administrators focus on operational leadership by managing daily activities and ensuring efficient workflow across departments. Chiefs of Staff play a strategic leadership role by coordinating executive priorities and fostering collaboration between leadership teams. Both positions require strong communication skills to align team efforts and drive organizational goals effectively.
Career Pathways and Professional Growth
Administrators often start their careers in specialized operational roles, gaining expertise in organizational management before advancing to senior administrative positions. Chief of Staff roles typically require extensive experience in strategic planning, stakeholder coordination, and leadership within complex environments, often serving as a critical advisor to executive leaders. Professional growth for Administrators centers on mastering administrative systems and processes, while Chiefs of Staff develop broader influence through political acumen, decision-making authority, and high-level organizational impact.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Administrators and Chiefs of Staff often face challenges such as managing complex stakeholder expectations, ensuring seamless communication across departments, and balancing strategic priorities with day-to-day operations. Solutions include implementing robust project management tools, fostering transparent communication channels, and prioritizing tasks based on organizational goals. Leveraging data analytics for performance monitoring also enhances decision-making and resource allocation efficiency.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Organization
Selecting between an Administrator and a Chief of Staff hinges on organizational structure and leadership needs; Administrators typically manage daily operations and enforce policies, while Chiefs of Staff coordinate executive priorities and streamline communication among departments. Assessing the scale of decision-making authority and the complexity of organizational goals ensures alignment with the role that drives efficiency and strategic execution. Clear role definition enhances workflow, accountability, and optimized resource allocation across the organization.
Related Important Terms
Superadmin Functionality
An Administrator manages core system operations, user access, and settings essential for organizational efficiency, while a Chief of Staff oversees strategic coordination and communication across departments. Superadmin functionality grants elevated privileges, enabling comprehensive control over system configurations, user roles, and security protocols beyond standard administrative capabilities.
Executive Liaison Role
The Administrator manages internal operations and ensures seamless coordination across departments, acting as a key executive liaison by facilitating communication between leadership and staff. The Chief of Staff serves as a strategic partner to the executive, prioritizing initiatives and managing high-level stakeholder relationships to enhance organizational alignment and decision-making.
Strategic Chief Coordination
The Administrator primarily manages organizational operations and ensures policy implementation, while the Chief of Staff focuses on strategic chief coordination by streamlining communication and aligning executive priorities across departments. Effective synergy between these roles enhances decision-making efficiency and drives organizational success through coordinated strategic planning.
Operations Integration Lead
The Administrator oversees overall organizational functions, ensuring compliance and resource allocation, while the Chief of Staff acts as the Operations Integration Lead, coordinating cross-departmental initiatives and streamlining communication to optimize workflow efficiency. This role demands expertise in project management, strategic alignment, and real-time problem-solving to unify operations across diverse teams.
Organizational Synthesizer
An Administrator manages day-to-day operations, ensuring organizational processes run efficiently, while a Chief of Staff acts as an organizational synthesizer, integrating cross-departmental efforts and aligning strategic initiatives. This role enhances communication flow, coordinates executive priorities, and translates complex information into actionable plans for cohesive organizational performance.
Cross-Departmental Orchestrator
An Administrator primarily manages departmental operations and ensures compliance with organizational policies, while a Chief of Staff acts as a cross-departmental orchestrator, coordinating strategic initiatives across multiple teams to align resources and priorities. The Chief of Staff leverages interdepartmental communication and project management skills to facilitate collaboration, enhance efficiency, and drive enterprise-wide goals.
Administrative Governance Officer
An Administrative Governance Officer ensures compliance with organizational policies and oversees administrative procedures to maintain operational efficiency. Unlike the Chief of Staff, who manages executive priorities and strategic initiatives, the Administrator focuses on implementing governance frameworks and regulatory adherence within the organization.
Agile Chief of Staff
An Agile Chief of Staff enhances organizational responsiveness by integrating Agile methodologies into executive operations, streamlining decision-making and fostering cross-functional collaboration. Unlike traditional Administrators who focus on routine management and operational tasks, Agile Chiefs of Staff drive strategic adaptability and innovation through iterative planning and continuous feedback loops.
Unified Administration Architect
An Administrator typically manages daily operations and enforces policies within an organization, while a Chief of Staff strategically coordinates executive priorities and facilitates communication across departments. In a Unified Administration Architect framework, the Chief of Staff integrates administrative functions to streamline decision-making and optimize organizational efficiency.
Hybrid Admin-Chief Model
The Hybrid Admin-Chief Model integrates the traditional administrative support role with strategic leadership functions, enabling Administrators to handle both operational tasks and high-level decision-making alongside Chiefs of Staff. This model enhances organizational efficiency by combining administrative expertise with executive coordination, streamlining communication and project management across departments.
Administrator vs Chief of Staff Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com