The Green Revolution introduced high-yield crop varieties and intensive use of fertilizers and irrigation, significantly boosting agricultural productivity in the 20th century. Smart Farming leverages digital technologies such as AI, IoT, and precision agriculture to optimize resource use, increase efficiency, and reduce environmental impact. While the Green Revolution laid the foundation for modern agriculture, Smart Farming represents an evolution toward sustainable and data-driven farming practices.
Table of Comparison
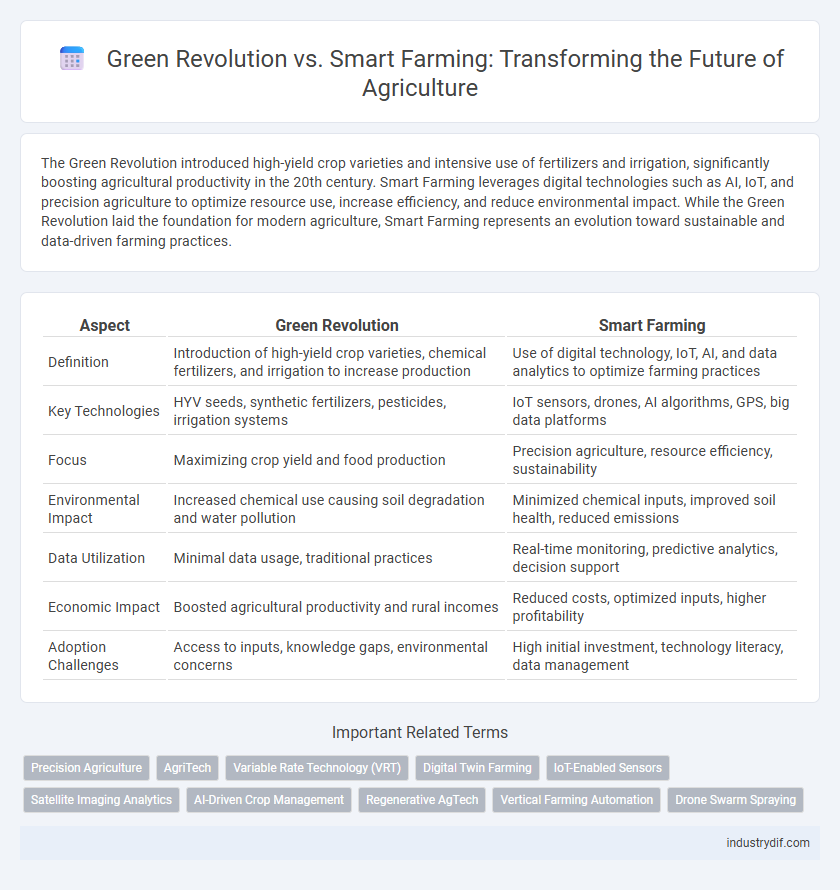
| Aspect | Green Revolution | Smart Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Introduction of high-yield crop varieties, chemical fertilizers, and irrigation to increase production | Use of digital technology, IoT, AI, and data analytics to optimize farming practices |
| Key Technologies | HYV seeds, synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, irrigation systems | IoT sensors, drones, AI algorithms, GPS, big data platforms |
| Focus | Maximizing crop yield and food production | Precision agriculture, resource efficiency, sustainability |
| Environmental Impact | Increased chemical use causing soil degradation and water pollution | Minimized chemical inputs, improved soil health, reduced emissions |
| Data Utilization | Minimal data usage, traditional practices | Real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, decision support |
| Economic Impact | Boosted agricultural productivity and rural incomes | Reduced costs, optimized inputs, higher profitability |
| Adoption Challenges | Access to inputs, knowledge gaps, environmental concerns | High initial investment, technology literacy, data management |
Introduction to the Green Revolution and Smart Farming
The Green Revolution marked a significant increase in agricultural productivity through high-yield crop varieties, chemical fertilizers, and irrigation techniques during the mid-20th century. Smart Farming leverages advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, GPS mapping, and data analytics to optimize resource use and enhance crop management in real time. Both approaches aim to boost food production but differ fundamentally in their methods, with the Green Revolution relying on traditional inputs and Smart Farming focusing on digital innovation.
Key Innovations: Green Revolution vs Smart Farming
The Green Revolution introduced high-yielding variety seeds, chemical fertilizers, and irrigation techniques that significantly increased crop production in the mid-20th century. Smart Farming leverages advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, drones, and AI-driven data analytics to optimize resource use and enhance precision in agriculture. These innovations shift the focus from quantity-focused methods to sustainable, data-driven practices that improve yield and minimize environmental impact.
Impact on Crop Yields and Productivity
The Green Revolution significantly increased crop yields through high-yield varieties, chemical fertilizers, and irrigation, leading to substantial productivity gains in the mid-20th century. Smart Farming integrates advanced technologies like IoT sensors, AI, and precision agriculture to optimize input use, monitor crop health in real-time, and improve decision-making, resulting in enhanced productivity and sustainable yield improvements. While the Green Revolution boosted food production rapidly, Smart Farming aims to increase efficiency and resilience in crop yields amid climate change challenges.
Technological Advancements Shaping Agriculture
The Green Revolution introduced high-yield crop varieties and chemical fertilizers that significantly boosted agricultural productivity in the mid-20th century. Smart farming leverages advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, drones, and AI-driven data analytics to optimize resource use and enhance crop management precision. These technological advancements continue to revolutionize agriculture by improving efficiency, sustainability, and food security.
Sustainability: Environmental and Economic Perspectives
The Green Revolution significantly boosted crop yields through high-yield varieties and chemical inputs, yet it often led to soil degradation and water resource depletion, raising environmental sustainability concerns. Smart farming integrates precision agriculture technologies such as IoT sensors, drones, and data analytics to optimize resource use, reduce chemical inputs, and enhance crop productivity, promoting long-term ecological balance. Economically, smart farming reduces input costs and improves yield predictability, supporting sustainable farming profitability compared to the traditional practices of the Green Revolution.
Resource Utilization and Efficiency
The Green Revolution significantly increased crop yields through high-yield varieties and chemical inputs but often led to resource depletion and environmental strain. Smart farming leverages precision agriculture technologies like IoT sensors, drones, and AI to optimize water usage, fertilizer application, and energy efficiency. This digital approach enhances sustainability by reducing waste and improving resource utilization in modern agricultural practices.
Role of Data and Precision Agriculture
The Green Revolution significantly increased crop yields through improved seed varieties and chemical inputs, but lacked real-time data utilization. Smart Farming leverages advanced data analytics, IoT sensors, and precision agriculture techniques to optimize resource use, enhance crop health monitoring, and improve decision-making accuracy. This data-driven approach enables precise application of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, reducing waste and increasing sustainability compared to traditional Green Revolution methods.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
The Green Revolution significantly increased crop yields through high-yield varieties, synthetic fertilizers, and irrigation, but faced challenges such as environmental degradation, soil fertility loss, and limited accessibility for smallholder farmers. Smart farming leverages precision agriculture technologies, IoT, and data analytics to optimize resource use and sustainability, yet it is constrained by high initial costs, technological complexity, and the digital divide in rural areas. Both approaches struggle with scalability and adapting to diverse agro-ecological zones, necessitating integrated solutions for future agricultural productivity and resilience.
Future Trends in Agricultural Development
The future of agricultural development is marked by a transition from the Green Revolution's emphasis on high-yield crop varieties and chemical inputs to Smart Farming, which leverages precision agriculture technologies, IoT sensors, and data analytics for optimized resource use and sustainable practices. Innovations such as AI-driven crop monitoring, drone-based soil analysis, and automated irrigation systems are set to enhance productivity while minimizing environmental impact. Smart Farming's integration of real-time data and machine learning models represents a significant leap forward in achieving global food security and climate resilience.
Conclusion: Integrating Tradition and Technology
Integrating traditional Green Revolution practices with Smart Farming technologies enhances agricultural productivity and sustainability by combining proven crop improvement methods with precision data analytics. This fusion optimizes resource use, improves crop resilience, and reduces environmental impact, supporting global food security. Embracing both approaches ensures a balanced strategy that addresses modern agricultural challenges effectively.
Related Important Terms
Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture, a core component of smart farming, leverages GPS technology, IoT sensors, and big data analytics to optimize crop yield and resource use efficiency compared to the Green Revolution's reliance on high-yield seeds and chemical inputs. This data-driven approach enhances soil health monitoring, irrigation management, and pest control with real-time insights, improving sustainability and reducing environmental impact.
AgriTech
The Green Revolution introduced high-yield crop varieties and chemical fertilizers, significantly boosting agricultural productivity during the mid-20th century. Modern Smart Farming leverages AgriTech innovations such as IoT sensors, AI-driven data analytics, and precision irrigation systems to optimize crop management and enhance sustainable resource use.
Variable Rate Technology (VRT)
Variable Rate Technology (VRT) revolutionized agriculture during the Green Revolution by enabling precise input application based on spatial variability within fields, significantly improving crop yields and resource efficiency. In smart farming, VRT is integrated with IoT sensors, GPS, and data analytics to optimize fertilizer, pesticide, and irrigation application in real-time, enhancing sustainability and reducing environmental impact.
Digital Twin Farming
Digital Twin Farming integrates real-time data from sensors, drones, and satellite imagery to create precise virtual models of agricultural fields, enabling predictive analytics and optimized crop management beyond the scope of the Green Revolution's traditional mechanization and chemical inputs. This smart farming technology enhances resource efficiency, reduces environmental impact, and supports sustainable intensification by simulating multiple scenarios for irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
IoT-Enabled Sensors
IoT-enabled sensors in Smart Farming provide real-time data on soil moisture, crop health, and weather conditions, enabling precise resource management that significantly improves yield and sustainability compared to the Green Revolution's reliance on high-yield crop varieties and chemical inputs. Integrating IoT technology enhances decision-making through continuous monitoring and predictive analytics, driving efficient water usage and reducing environmental impact in modern agricultural practices.
Satellite Imaging Analytics
Satellite imaging analytics revolutionizes agriculture by enhancing crop monitoring, yield prediction, and resource management beyond the traditional Green Revolution's reliance on high-yield varieties and chemical inputs. Integrating remote sensing data with smart farming technologies enables precise, real-time decision-making that optimizes irrigation, pest control, and soil health for sustainable agricultural productivity.
AI-Driven Crop Management
AI-driven crop management in smart farming leverages machine learning algorithms and real-time data from satellite imagery, soil sensors, and weather forecasts to optimize planting schedules, irrigation, and pest control, significantly improving yield efficiency compared to the Green Revolution's reliance on chemical inputs and mechanization. This precision agriculture approach reduces resource wastage and environmental impact while enhancing crop resilience and productivity through tailored, data-driven decisions.
Regenerative AgTech
Green Revolution introduced high-yield varieties and chemical inputs that boosted agricultural productivity but often degraded soil health, while Smart Farming integrates Regenerative AgTech practices like precision irrigation, soil microbiome management, and carbon sequestration to enhance sustainability and resilience. These advanced technologies support ecosystem restoration, optimize input use, and promote long-term soil fertility critical for climate-smart agriculture and food security.
Vertical Farming Automation
Vertical farming automation significantly enhances resource efficiency and crop yield, positioning itself as a modern evolution beyond the Green Revolution's traditional methods. Integrating IoT sensors, AI-driven climate control, and robotics in vertical farms optimizes plant growth cycles, reduces water usage by up to 90%, and enables year-round production in urban environments.
Drone Swarm Spraying
Drone swarm spraying in smart farming leverages autonomous drones equipped with precision sensors to apply pesticides and fertilizers efficiently, reducing chemical use and minimizing environmental impact. This technology surpasses the Green Revolution's conventional mechanized approaches by enabling targeted crop management and real-time data analysis for optimized agricultural productivity.
Green Revolution vs Smart Farming Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com