Irrigation delivers water broadly across fields but often results in significant water loss due to evaporation and runoff, reducing efficiency. Drip fertigation combines precise water application with targeted nutrient delivery directly to plant roots, enhancing nutrient uptake and conserving water. This method improves crop yields and reduces resource waste, making it a more sustainable choice for modern agriculture.
Table of Comparison
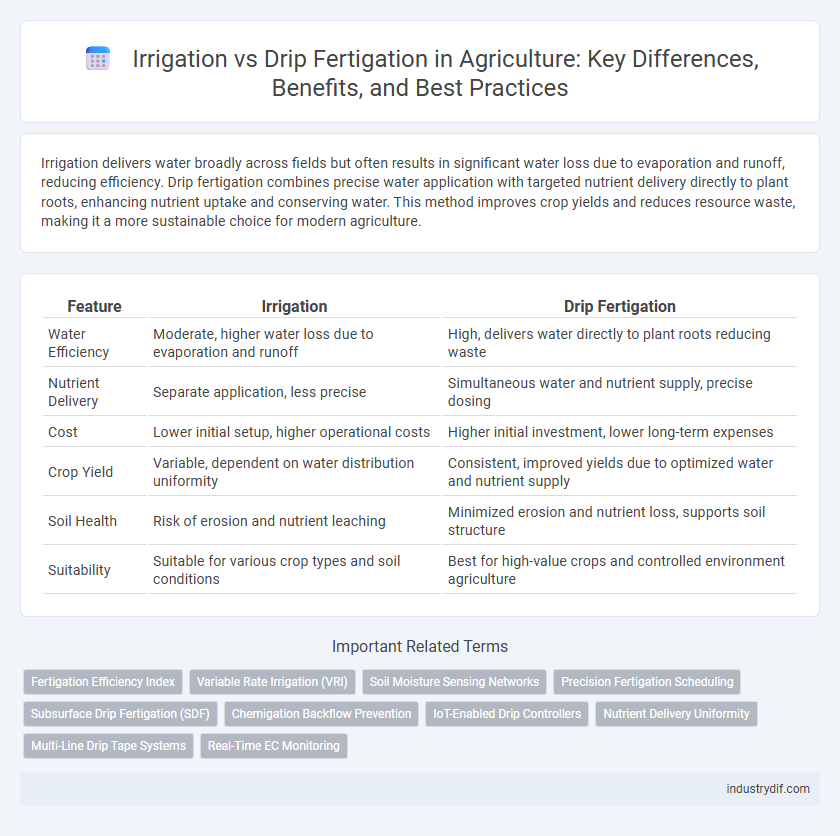
| Feature | Irrigation | Drip Fertigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | Moderate, higher water loss due to evaporation and runoff | High, delivers water directly to plant roots reducing waste |
| Nutrient Delivery | Separate application, less precise | Simultaneous water and nutrient supply, precise dosing |
| Cost | Lower initial setup, higher operational costs | Higher initial investment, lower long-term expenses |
| Crop Yield | Variable, dependent on water distribution uniformity | Consistent, improved yields due to optimized water and nutrient supply |
| Soil Health | Risk of erosion and nutrient leaching | Minimized erosion and nutrient loss, supports soil structure |
| Suitability | Suitable for various crop types and soil conditions | Best for high-value crops and controlled environment agriculture |
Overview of Irrigation and Drip Fertigation
Irrigation is the general practice of supplying water to crops using methods such as surface, sprinkler, or sub-surface irrigation to support plant growth and improve yield. Drip fertigation combines drip irrigation with the precise application of fertilizers directly to the root zone, enhancing nutrient use efficiency and reducing water consumption. This targeted approach promotes healthier crop development, minimizes nutrient runoff, and maximizes agricultural productivity.
Key Differences Between Irrigation and Drip Fertigation
Irrigation primarily delivers water uniformly across farmland, while drip fertigation precisely supplies water combined with nutrients directly to the plant roots. Drip fertigation enhances nutrient uptake efficiency and reduces water wastage compared to traditional irrigation methods. The key differences lie in application method, resource use efficiency, and impact on crop yield and soil health.
Benefits of Traditional Irrigation Systems
Traditional irrigation systems provide widespread water distribution suitable for large-scale farms, ensuring soil moisture levels are maintained for diverse crop types. These methods often require lower initial investment and simpler technology, making them accessible to small and medium farmers. The consistent water application supports rapid crop growth, which can lead to higher yields in regions with abundant water resources.
Advantages of Drip Fertigation Technology
Drip fertigation technology enhances nutrient efficiency by delivering water and fertilizers directly to the root zone, reducing wastage and improving crop yield. This method conserves water by minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional irrigation techniques. Precise nutrient application also helps in reducing soil salinity and environmental pollution, promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Water Efficiency: Irrigation vs Drip Fertigation
Drip fertigation delivers water and nutrients directly to the root zone, achieving up to 90% water use efficiency compared to traditional irrigation methods that often lose 30-50% of water through evaporation and runoff. This precise application reduces water waste and supports sustainable agriculture by minimizing irrigation frequency and volume. Optimizing water efficiency through drip fertigation enhances crop yield while conserving valuable water resources in water-scarce regions.
Nutrient Management in Drip Fertigation
Drip fertigation enhances nutrient management by delivering precise amounts of water-soluble fertilizers directly to the root zone, reducing nutrient loss and improving uptake efficiency compared to traditional irrigation. This method allows for controlled, frequent applications tailored to crop growth stages, optimizing nutrient availability and minimizing leaching or runoff. Improved nutrient use efficiency in drip fertigation supports higher yields and sustainable resource management in agricultural production.
Cost Implications and Return on Investment
Irrigation systems generally have lower initial costs but higher water and fertilizer usage, leading to increased operational expenses over time. Drip fertigation, although involving higher upfront investment in specialized equipment and installation, enhances water-use efficiency and precise nutrient delivery, significantly boosting crop yields and reducing input costs. This optimized resource management results in a faster return on investment and greater long-term profitability for farmers.
Suitability for Different Crop Types
Irrigation methods vary in suitability depending on crop type, with traditional flood or sprinkler irrigation best suited for large-scale field crops like wheat, maize, and rice due to their broad water distribution needs. Drip fertigation targets row crops, vegetables, and high-value fruits by delivering precise water and nutrients directly to the root zone, enhancing growth and reducing resource waste. Crops sensitive to soil moisture levels, such as tomatoes and strawberries, benefit significantly from the controlled environment provided by drip fertigation systems.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Irrigation methods significantly influence environmental sustainability in agriculture, with drip fertigation offering a more efficient nutrient and water delivery system that minimizes runoff and soil erosion compared to traditional irrigation. Drip fertigation reduces groundwater contamination by optimizing fertilizer application, decreasing nutrient leaching and greenhouse gas emissions associated with over-fertilization. Studies indicate that drip fertigation enhances water use efficiency by up to 40% and lowers the carbon footprint of crop production, promoting eco-friendly farming practices.
Adoption Trends and Future Outlook in Agriculture
Drip fertigation shows a significant rise in adoption due to its precision in water and nutrient delivery, enhancing crop yields and resource efficiency compared to traditional irrigation methods. Recent agricultural surveys indicate a growing preference for drip fertigation systems in arid and semi-arid regions, driven by increasing water scarcity and the demand for sustainable farming practices. Future outlooks predict continued expansion of drip fertigation adoption, supported by advancements in automation technology and government policies promoting water conservation.
Related Important Terms
Fertigation Efficiency Index
Drip fertigation enhances water and nutrient use by delivering precise amounts directly to the root zone, significantly increasing the Fertigation Efficiency Index compared to traditional irrigation methods. This optimized nutrient delivery reduces wastage and boosts crop yield, making fertigation a more sustainable and cost-effective agricultural practice.
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI)
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI) technology optimizes water distribution by applying precise amounts tailored to specific field zones, enhancing crop yield and water efficiency compared to uniform irrigation methods. Drip fertigation integrated with VRI further refines nutrient delivery, reducing runoff and improving nutrient uptake by targeting root zones with variable nutrient concentrations.
Soil Moisture Sensing Networks
Soil moisture sensing networks provide precise data that enhance irrigation efficiency by optimizing water distribution, reducing wastage, and improving crop yield. In drip fertigation systems, these networks enable targeted nutrient delivery directly to root zones, ensuring balanced soil moisture and nutrient levels, which promotes sustainable agriculture practices.
Precision Fertigation Scheduling
Precision fertigation scheduling using drip systems enhances nutrient delivery accuracy by aligning water and fertilizer applications directly with crop growth stages, minimizing nutrient runoff and maximizing uptake efficiency. This targeted approach contrasts with traditional irrigation methods by optimizing resource use, boosting crop yields, and reducing environmental impact through precise timing and dosage control.
Subsurface Drip Fertigation (SDF)
Subsurface Drip Fertigation (SDF) enhances water use efficiency by delivering nutrients directly to the root zone through buried drip lines, minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional irrigation methods. SDF promotes higher crop yields and optimizes fertilizer uptake, reducing environmental impact and operational costs in precision agriculture systems.
Chemigation Backflow Prevention
Chemigation backflow prevention is critical in irrigation systems to avoid contamination of groundwater by chemicals and fertilizers, ensuring environmental safety and compliance with regulatory standards. Drip fertigation systems offer precise nutrient delivery combined with effective backflow prevention devices, reducing the risk of chemical backflow compared to traditional irrigation methods.
IoT-Enabled Drip Controllers
IoT-enabled drip controllers optimize water and nutrient delivery by precisely regulating irrigation schedules and fertilizer concentrations, enhancing crop yield and reducing resource wastage compared to traditional irrigation methods. These smart systems leverage real-time sensor data and remote management capabilities to adapt to soil moisture levels and environmental conditions, promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
Nutrient Delivery Uniformity
Drip fertigation provides superior nutrient delivery uniformity by combining irrigation and fertilization directly at the root zone, ensuring consistent nutrient availability and reducing wastage. In contrast, traditional irrigation methods often result in uneven nutrient distribution, leading to suboptimal crop growth and increased fertilizer runoff.
Multi-Line Drip Tape Systems
Multi-line drip tape systems in irrigation deliver precise water and nutrient application directly to the root zone, enhancing crop yields and reducing waste compared to traditional irrigation methods. These systems optimize fertigation efficiency by enabling uniform distribution of fertilizers with minimal runoff and improved soil moisture management.
Real-Time EC Monitoring
Real-time EC monitoring in drip fertigation systems enables precise control over nutrient delivery by continuously measuring electrical conductivity levels, optimizing water and fertilizer use efficiency. In contrast, traditional irrigation lacks this dynamic adjustment capability, often resulting in nutrient runoff and suboptimal crop growth.
Irrigation vs Drip fertigation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com