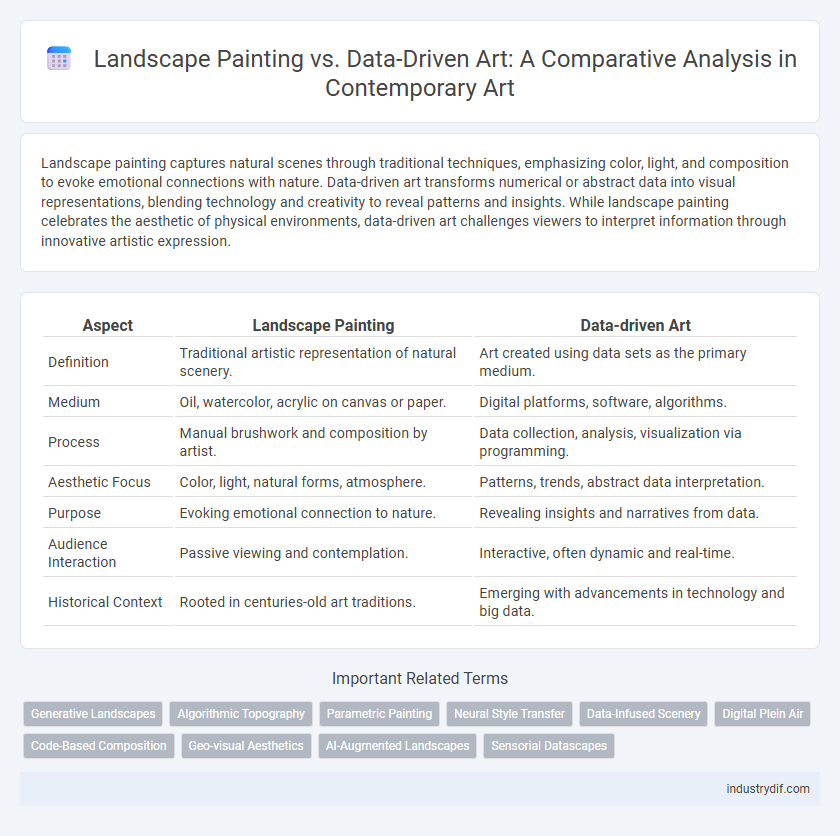
Landscape painting captures natural scenes through traditional techniques, emphasizing color, light, and composition to evoke emotional connections with nature. Data-driven art transforms numerical or abstract data into visual representations, blending technology and creativity to reveal patterns and insights. While landscape painting celebrates the aesthetic of physical environments, data-driven art challenges viewers to interpret information through innovative artistic expression.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Landscape Painting | Data-driven Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional artistic representation of natural scenery. | Art created using data sets as the primary medium. |
| Medium | Oil, watercolor, acrylic on canvas or paper. | Digital platforms, software, algorithms. |
| Process | Manual brushwork and composition by artist. | Data collection, analysis, visualization via programming. |
| Aesthetic Focus | Color, light, natural forms, atmosphere. | Patterns, trends, abstract data interpretation. |
| Purpose | Evoking emotional connection to nature. | Revealing insights and narratives from data. |
| Audience Interaction | Passive viewing and contemplation. | Interactive, often dynamic and real-time. |
| Historical Context | Rooted in centuries-old art traditions. | Emerging with advancements in technology and big data. |
Defining Landscape Painting: Tradition and Techniques
Landscape painting, rooted in centuries of artistic tradition, emphasizes the depiction of natural scenery through techniques such as atmospheric perspective, chiaroscuro, and detailed brushwork to convey depth and realism. This genre often captures the emotional and aesthetic qualities of environments, highlighting elements like light, texture, and spatial composition. Unlike data-driven art, which relies on algorithmic processes and abstract data visualization, landscape painting preserves the classical approach to representing the physical world.
Understanding Data-driven Art: Concepts and Processes
Data-driven art transforms raw datasets into visual narratives, integrating computational algorithms and creative expression to reveal patterns and insights invisible to the naked eye. Unlike traditional landscape painting, which captures natural scenery through brushstrokes and color, data-driven art relies on coding, statistical analysis, and visualization tools to construct dynamic, evolving works. Understanding this process requires familiarity with both data science principles and artistic techniques to interpret and convey complex information aesthetically.
Historical Evolution: From Landscapes to Algorithms
Landscape painting evolved from early Renaissance traditions emphasizing natural beauty and human interaction with environment, capturing serene vistas with meticulous detail. The 20th century introduced data-driven art where algorithms transformed abstract data into visual narratives, marking a paradigm shift from representational forms to computational aesthetics. This historical evolution reflects a transition from manual brushstrokes depicting physical landscapes to algorithmic processes rendering complex digital terrains.
Artistic Intent: Observation vs Computation
Landscape painting captures the natural world through direct observation, emphasizing the artist's personal interpretation of light, color, and atmosphere to evoke emotion and narrative. Data-driven art relies on computational processes and algorithmic analysis, transforming raw data into visual forms that prioritize conceptual frameworks over traditional aesthetic representation. This contrast highlights the shift from subjective perception to objective data manipulation as a fundamental driver of artistic intent in contemporary visual culture.
Materials and Mediums: Canvas vs Digital Platforms
Landscape painting traditionally utilizes natural materials such as oil or acrylic paints on canvas, offering tactile texture and depth through brushstrokes and layering techniques. Data-driven art relies on digital platforms and software tools, enabling dynamic, algorithm-driven visuals that can evolve in real-time or respond to user interactions. The contrast between tangible canvas and intangible digital mediums highlights differing sensory experiences and creative processes within contemporary art practices.
Visual Aesthetics: Nature’s Palette vs Data Visualizations
Landscape painting captures nature's palette through organic forms, rich textures, and vibrant colors that evoke emotional resonance and timeless beauty. Data-driven art transforms numerical information into intricate visualizations, using abstract shapes, patterns, and color gradients to reveal hidden insights and complex relationships. Both art forms harness visual aesthetics to engage viewers, yet landscape art emphasizes natural scenery, while data-driven art highlights analytical depth through design.
Role of Technology in Artistic Production
Landscape painting captures natural scenery through traditional brushwork and color techniques, emphasizing the artist's direct sensory experience. Data-driven art leverages algorithms, sensors, and computational tools to transform vast datasets into dynamic, interactive visualizations. Technology shifts the artistic production process from manual craftsmanship to digital innovation, enabling new forms of expression and audience engagement.
Interpretation and Viewer Engagement
Landscape painting evokes emotional and sensory experiences through detailed natural imagery, inviting viewers to explore themes of beauty and tranquility. Data-driven art relies on algorithmic patterns and information visualization to challenge viewers' perceptions and encourage analytical interpretation. Both forms engage audiences by offering distinct cognitive pathways, blending intuition with data literacy.
Preservation and Longevity: Physical Art vs Digital Artworks
Landscape painting, rooted in traditional media like oil or watercolor, offers tangible preservation methods such as varnishing and controlled storage, ensuring centuries-long durability. In contrast, data-driven art relies on digital formats vulnerable to technological obsolescence, file corruption, and platform dependency, challenging long-term accessibility. Conservation of digital artworks demands continuous migration to new formats and persistent archiving strategies to maintain their integrity and public availability.
The Future of Art: Convergence of Tradition and Innovation
Landscape painting captures the essence of nature through masterful brushwork and timeless techniques, anchoring art in its historical and emotional roots. Data-driven art harnesses algorithms, big data, and interactive technologies to create dynamic, evolving visuals that challenge traditional perceptions of art. The future of art lies in the convergence of traditional landscape aesthetics with innovative, data-infused methods, fostering a hybrid genre that enriches artistic expression and audience engagement.
Related Important Terms
Generative Landscapes
Generative landscapes blend algorithmic processes with artistic expression, creating dynamic, data-driven art that evolves beyond traditional landscape painting's static depiction of nature. These works harness computational techniques and real-time data inputs to produce immersive environments that challenge conventional aesthetics and redefine audience interaction.
Algorithmic Topography
Algorithmic topography in landscape painting redefines traditional depictions by integrating computational algorithms to generate dynamic, data-infused environments. This fusion elevates landscape art beyond static visuals, allowing real-time data influences to shape evolving topographical forms, contrasting the fixed perspectives of classical techniques.
Parametric Painting
Parametric painting in landscape art integrates algorithmic processes to generate dynamic visual compositions based on environmental data, blending traditional aesthetics with computational creativity. This fusion challenges conventional landscape painting by introducing data-driven variability, enabling artists to explore complex spatial patterns and evolving ecosystems through programmable parameters.
Neural Style Transfer
Neural Style Transfer revolutionizes landscape painting by merging traditional scenery with data-driven aesthetics, enabling artists to apply complex computational algorithms that blend content and style from disparate images. This fusion fosters innovative visual expressions where natural landscapes are reinterpreted through the lens of AI, pushing the boundaries of creativity and contemporary art production.
Data-Infused Scenery
Data-infused scenery merges traditional landscape painting techniques with real-time data visualization, creating dynamic artworks that evolve with environmental or social metrics. This fusion transforms static natural scenes into interactive narratives, offering viewers a multidimensional experience of place and time through coded aesthetics.
Digital Plein Air
Digital Plein Air combines the authenticity of traditional landscape painting with the precision of data-driven art by capturing real-time environmental data to enhance naturalistic representations. This fusion allows artists to integrate dynamic atmospheric conditions and geospatial information, creating immersive visual experiences that transcend conventional plein air techniques.
Code-Based Composition
Landscape painting captures natural scenes through traditional brushwork, emphasizing visual aesthetics and emotional expression, while data-driven art uses algorithms and code-based composition to transform complex datasets into layered visual narratives. Code-based art leverages programming languages such as Python, Processing, or JavaScript to generate dynamic, interactive landscapes that evolve based on real-time data inputs, merging computational creativity with environmental themes.
Geo-visual Aesthetics
Landscape painting captures natural scenery through meticulous brushwork and color theory, emphasizing emotional resonance and spatial harmony. Data-driven art leverages geospatial datasets and algorithmic visualization techniques to create dynamic, information-rich compositions that reveal patterns and insights within landscapes.
AI-Augmented Landscapes
AI-augmented landscapes combine traditional landscape painting techniques with data-driven algorithms, enabling artists to generate dynamic, visually complex scenes that reflect real-time environmental data. This fusion of art and technology expands creative possibilities, offering a new dimension where natural aesthetics are enhanced by predictive models and machine learning.
Sensorial Datascapes
Landscape painting captures the natural world through traditional brushstrokes and color theory, evoking emotional and sensorial responses rooted in physical observation. In contrast, data-driven art transforms raw sensorial data from environmental sensors into immersive datas-capes, blending technology and aesthetics to visualize intangible sensory experiences like temperature, sound, and light intensity.
Landscape Painting vs Data-driven Art Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com