Border security primarily focuses on physical protection measures such as surveillance, checkpoints, and patrols to prevent unauthorized access and threats at national boundaries. Cognitive security addresses the protection of information, mental integrity, and resilience against psychological manipulation, misinformation, and cyber threats that aim to influence or disrupt decision-making processes. Both forms of security are crucial for comprehensive defense, combining tangible barriers with strategies to safeguard intellectual and informational domains.
Table of Comparison
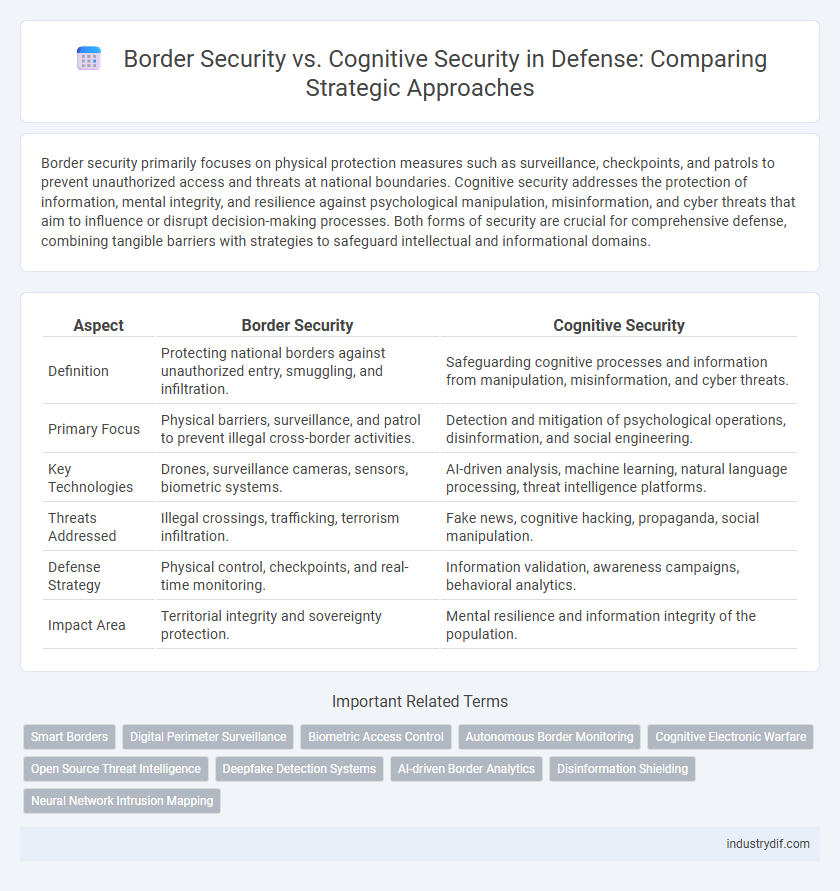
| Aspect | Border Security | Cognitive Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protecting national borders against unauthorized entry, smuggling, and infiltration. | Safeguarding cognitive processes and information from manipulation, misinformation, and cyber threats. |
| Primary Focus | Physical barriers, surveillance, and patrol to prevent illegal cross-border activities. | Detection and mitigation of psychological operations, disinformation, and social engineering. |
| Key Technologies | Drones, surveillance cameras, sensors, biometric systems. | AI-driven analysis, machine learning, natural language processing, threat intelligence platforms. |
| Threats Addressed | Illegal crossings, trafficking, terrorism infiltration. | Fake news, cognitive hacking, propaganda, social manipulation. |
| Defense Strategy | Physical control, checkpoints, and real-time monitoring. | Information validation, awareness campaigns, behavioral analytics. |
| Impact Area | Territorial integrity and sovereignty protection. | Mental resilience and information integrity of the population. |
Introduction to Border Security and Cognitive Security
Border security involves the protection of national frontiers through surveillance, control of immigration, and prevention of illegal crossings, utilizing technologies like drones, sensors, and biometric systems. Cognitive security addresses the protection of societal beliefs, perceptions, and information integrity from manipulation through misinformation, disinformation, and cyber threats. Both domains are critical in defense strategies, with border security focusing on physical barriers and cognitive security emphasizing the safeguarding of information ecosystems.
Evolving Threats: Physical vs Cognitive Domains
Evolving threats to defense encompass both physical border security challenges, such as unauthorized crossings and smuggling, and cognitive security risks, including misinformation campaigns and cyber influence operations. Physical domain threats demand enhanced surveillance technologies and rapid response teams to safeguard territorial integrity, while cognitive threats require sophisticated AI-driven monitoring and counter-propaganda strategies to protect public perception and national decision-making processes. Integrating defense systems across these domains is crucial to address the multifaceted nature of modern security threats effectively.
Core Principles of Border Security
Border security fundamentally relies on physical barriers, surveillance systems, and rapid response protocols to prevent unauthorized crossings and protect national sovereignty. Core principles include risk assessment, layered defense strategies, and the integration of technology such as biometric identification and sensor networks. Ensuring situational awareness and interoperability among agencies enhances threat detection and response efficiency along national borders.
Fundamentals of Cognitive Security
Fundamentals of cognitive security involve protecting the human decision-making process from manipulation, misinformation, and psychological threats that can undermine national defense. Unlike traditional border security, which focuses on physical barriers and surveillance technologies, cognitive security addresses the integrity of information and perception among military personnel and the public. Implementing cognitive security strategies enhances resilience against influence operations, social engineering, and cyber-based psychological attacks that target cognitive vulnerabilities.
Overlapping Objectives: Where Border and Cognitive Security Intersect
Border security and cognitive security intersect in protecting national sovereignty by preventing unauthorized access and mitigating disinformation campaigns that threaten social stability. Both domains utilize advanced surveillance technologies, such as AI-driven analytics and biometric verification, to identify and counteract threats originating from hostile actors. Integrated strategies enhance resilience by addressing physical breaches alongside psychological manipulation, ensuring comprehensive defense against multifaceted security challenges.
Technological Innovations Shaping Security Strategies
Technological innovations such as AI-driven surveillance systems and biometric authentication are revolutionizing border security by enabling real-time threat detection and rapid response capabilities. Cognitive security leverages advanced machine learning algorithms to identify and mitigate cyber threats by analyzing behavioral patterns and intent, enhancing the protection of critical defense infrastructure. Integrating these technologies creates a multi-layered security framework that strengthens both physical borders and information domains against evolving threats.
Policy Frameworks and International Collaboration
Effective border security policies integrate cognitive security measures to address emerging hybrid threats such as misinformation and cyber espionage. International collaboration through multilateral frameworks, including INTERPOL and NATO, enhances the sharing of intelligence and standardizes protocols for countering cross-border cognitive attacks. Policy frameworks must evolve to encompass both physical and cognitive dimensions, ensuring coordinated defense strategies that protect national sovereignty and uphold global security norms.
Challenges and Limitations in Implementation
Border security faces challenges such as vast geographic expanses, limited technological infrastructure, and the high cost of deploying advanced surveillance systems. Cognitive security encounters limitations in accurately interpreting complex human behavior, mitigating misinformation, and ensuring privacy without compromising defense objectives. Both domains struggle with integrating real-time data analytics while balancing ethical concerns and resource constraints.
Future Trends in Border and Cognitive Security
Future trends in border security emphasize the integration of AI-driven surveillance systems and biometric authentication to enhance real-time threat detection and identity verification. Cognitive security leverages machine learning algorithms to anticipate and mitigate cyber threats by analyzing behavioral patterns and adapting to evolving attack vectors. The convergence of these technologies promises a holistic defense framework that strengthens national security through proactive, intelligent threat management.
Comparative Analysis: Synergies and Trade-offs
Border security and cognitive security both play critical roles in national defense, with border security focusing on physical infrastructure, surveillance technologies, and personnel to prevent unauthorized entry and protect territorial integrity. Cognitive security emphasizes protecting the information environment, countering misinformation, and safeguarding decision-making processes from psychological manipulation or cyber threats. Integrating these domains reveals synergies in intelligence sharing and threat detection but also trade-offs in resource allocation and prioritizing tactical versus psychological defense strategies.
Related Important Terms
Smart Borders
Smart border technologies integrate advanced sensors, AI-driven analytics, and biometric authentication to enhance border security by enabling real-time threat detection and streamlined immigration processes. Cognitive security systems complement these technologies by employing machine learning algorithms to predict and counter cyber threats targeting critical border infrastructure, ensuring comprehensive protection of national frontiers.
Digital Perimeter Surveillance
Digital perimeter surveillance integrates advanced sensors and AI-driven analytics to enhance border security by detecting and mitigating physical threats in real-time. Cognitive security complements this by protecting the integrity of surveillance data from cyberattacks, ensuring reliable threat assessment and response along digital borders.
Biometric Access Control
Biometric access control enhances border security by providing precise identification methods such as fingerprint, facial recognition, and iris scans, reducing unauthorized entries and improving threat detection. Cognitive security integrates behavioral biometrics and AI-driven analytics to anticipate and mitigate insider threats, ensuring robust protection of sensitive defense infrastructure.
Autonomous Border Monitoring
Autonomous border monitoring leverages AI-powered sensors and drones to enhance border security by detecting and responding to physical threats in real-time, reducing human error and operational costs. Integration of cognitive security systems enables the analysis of behavioral patterns and cyber threats, providing a comprehensive defense framework against both tangible breaches and digital infiltrations.
Cognitive Electronic Warfare
Cognitive Electronic Warfare enhances border security by leveraging AI-driven signal processing to detect and counteract adversaries' cognitive tactics, disrupting decision-making processes through advanced electromagnetic spectrum manipulation. Integrating cognitive security frameworks with traditional physical border defenses optimizes threat identification and response, ensuring proactive mitigation of hybrid warfare strategies.
Open Source Threat Intelligence
Border security leverages Open Source Threat Intelligence (OSTI) to detect and mitigate physical threats at geographic boundaries, employing geographic information systems and surveillance data for real-time threat identification. Cognitive security uses OSTI to safeguard human decision-making processes by analyzing social media, cyber threat forums, and psychological operations, enhancing situational awareness and countering misinformation campaigns.
Deepfake Detection Systems
Deepfake detection systems play a vital role in border security by identifying manipulated digital content that could be used for identity fraud or intelligence deception at cross-border checkpoints. Integrating cognitive security measures enhances the ability to analyze behavioral and contextual cues, strengthening defenses against sophisticated deepfake threats targeting national borders.
AI-driven Border Analytics
AI-driven Border Analytics enhances border security by integrating real-time data from sensors, cameras, and biometric systems to detect and prevent unauthorized crossings efficiently. Cognitive security complements this by analyzing behavioral patterns and potential threats, leveraging machine learning algorithms to predict and mitigate security risks before they materialize.
Disinformation Shielding
Border security ensures the physical protection of national boundaries, while cognitive security targets the prevention of disinformation campaigns that manipulate public perception and destabilize democratic processes. Effective disinformation shielding involves advanced AI-driven detection systems and strategic communication frameworks to counteract false narratives and safeguard societal trust.
Neural Network Intrusion Mapping
Neural Network Intrusion Mapping enhances border security by identifying and predicting unauthorized access patterns through advanced machine learning algorithms. Integrating cognitive security techniques enables real-time threat analysis and adaptive response, maximizing defense efficacy against evolving cyber and physical threats.
Border security vs Cognitive security Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com