Multirole fighters offer versatile combat capabilities, excelling in air-to-air, air-to-ground, and reconnaissance missions with advanced avionics and weapon systems. Loyal wingmen complement these fighters by operating as semi-autonomous drones, extending battlefield awareness and reducing pilot workload while increasing mission survivability. The integration of loyal wingmen with multirole fighters enhances tactical flexibility and force projection in modern defense strategies.
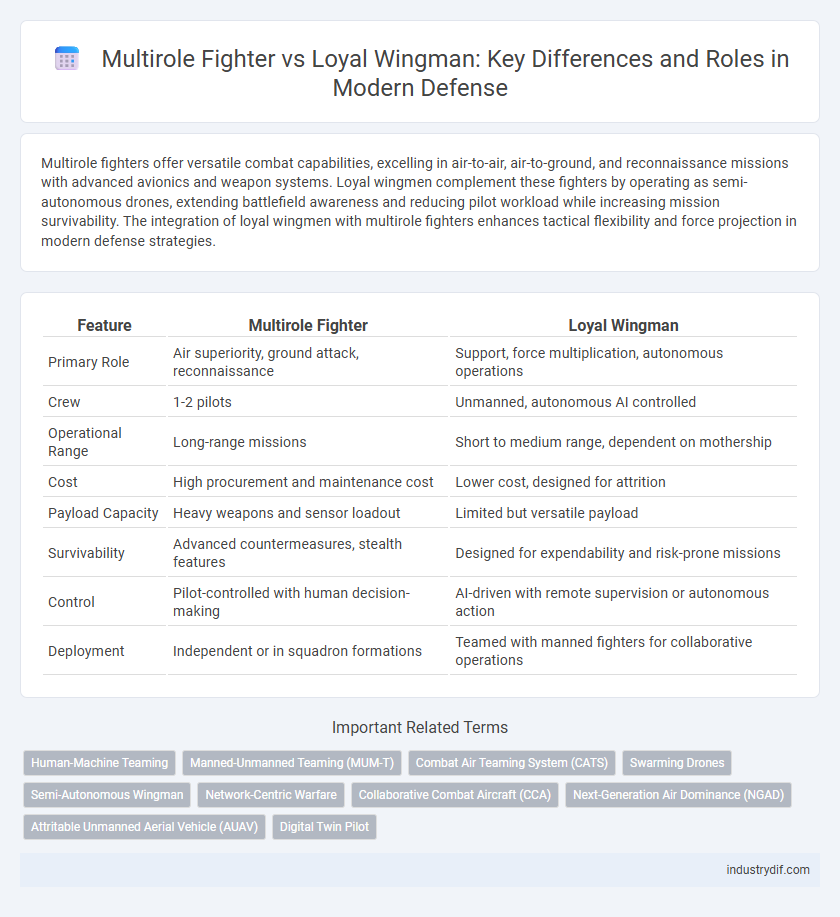
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Multirole Fighter | Loyal Wingman |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Air superiority, ground attack, reconnaissance | Support, force multiplication, autonomous operations |
| Crew | 1-2 pilots | Unmanned, autonomous AI controlled |
| Operational Range | Long-range missions | Short to medium range, dependent on mothership |
| Cost | High procurement and maintenance cost | Lower cost, designed for attrition |
| Payload Capacity | Heavy weapons and sensor loadout | Limited but versatile payload |
| Survivability | Advanced countermeasures, stealth features | Designed for expendability and risk-prone missions |
| Control | Pilot-controlled with human decision-making | AI-driven with remote supervision or autonomous action |
| Deployment | Independent or in squadron formations | Teamed with manned fighters for collaborative operations |
Introduction to Multirole Fighters and Loyal Wingman Concepts
Multirole fighters are advanced combat aircraft designed to perform various missions such as air-to-air combat, ground attack, and reconnaissance, offering versatility on modern battlefields. Loyal Wingman refers to autonomous or semi-autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that operate in coordination with manned fighters, enhancing situational awareness and force multiplication. The integration of loyal wingman UAVs with multirole fighters represents a significant evolution in defense strategy, combining human decision-making with advanced AI capabilities for increased combat effectiveness.
Historical Evolution of Multirole Fighters
Multirole fighters have evolved significantly since the Cold War, transitioning from specialized aircraft like the F-4 Phantom to versatile platforms such as the F-35 Lightning II, capable of air-to-air, air-to-ground, and electronic warfare missions. This evolution reflects advances in avionics, stealth technology, and sensor fusion, enabling modern multirole fighters to perform diverse combat roles with increased effectiveness and adaptability. The emergence of loyal wingman drones complements these manned fighters by providing autonomous reconnaissance, force multiplication, and risk reduction in complex battle environments.
Emergence and Development of the Loyal Wingman Program
The emergence of the Loyal Wingman program marks a strategic shift in multirole fighter operations by integrating autonomous or semi-autonomous drones to enhance mission flexibility and reduce pilot risk. Developed through collaborations between leading defense contractors and military agencies, these unmanned systems are designed to operate alongside piloted fighters, performing complex tasks such as reconnaissance, electronic warfare, and force multiplication. The rapid advancement in artificial intelligence and sensor technology underpins the program's development, enabling loyal wingmen to execute coordinated tactics and extend the operational reach of manned platforms.
Core Capabilities Comparison: Human vs. Autonomous Systems
Multirole fighters excel in adaptability, pilot intuition, and complex decision-making under dynamic combat conditions, leveraging advanced avionics and weapon systems for diverse mission profiles. Loyal Wingman drones provide autonomous swarm capabilities, extended endurance, and real-time data processing, enhancing situational awareness and force multiplication without risking human life. Combining human judgment with autonomous precision offers a synergistic battlefield advantage, optimizing mission success through complementary core capabilities.
Mission Flexibility and Adaptability in Modern Combat
Multirole fighters offer high mission flexibility by seamlessly switching between air-to-air, air-to-ground, and reconnaissance roles, enabling rapid response to diverse combat scenarios. Loyal Wingman drones enhance adaptability by extending operational reach, conducting autonomous missions, and reducing pilot risk while complementing manned aircraft during complex engagements. Combining both platforms optimizes modern combat strategies with versatile firepower and enhanced situational awareness across dynamic battlefield environments.
Cost-Effectiveness and Force Multiplication Analysis
Multirole fighters offer versatile capabilities across air-to-air and air-to-ground missions, but their high procurement and maintenance costs limit fleet size and operational availability. Loyal wingman drones, employing autonomous technology and lower production expenses, enable cost-effective force multiplication by augmenting manned aircraft with enhanced surveillance, target acquisition, and electronic warfare roles. Integrating loyal wingmen with multirole fighters exponentially increases combat effectiveness, reduces pilot risk, and optimizes mission adaptability while maintaining budget constraints.
Integration Challenges: Manned-Unmanned Teaming
Integration challenges in manned-unmanned teaming between multirole fighters and loyal wingman drones primarily involve seamless communication protocols and real-time data sharing to ensure synchronized operations. Advanced sensor fusion and AI-driven decision-making are critical to overcoming latency issues and command autonomy discrepancies. Effective human-machine interface design must address trust and situational awareness to maximize combat effectiveness in complex defense environments.
Operational Scenarios: Synergy and Limitations
Multirole fighters excel in versatility, performing air-to-air combat, ground attack, and reconnaissance, while loyal wingmen enhance mission capabilities by providing autonomous support, electronic warfare, and force multiplication. Their synergy is evident in complex operational scenarios where multirole fighters leverage loyal wingmen for risk reduction and situational awareness, increasing overall mission effectiveness. Limitations arise from reliance on secure communication links and autonomous decision-making constraints in contested environments, which can affect coordination and responsiveness.
Future Trends in Combat Airpower and Collaboration
Multirole fighters remain central to future combat airpower due to their adaptability in executing diverse missions such as air superiority, ground attack, and electronic warfare. Loyal wingman drones are emerging as force multipliers, equipped with advanced AI to operate collaboratively with manned fighters, enhancing situational awareness and survivability. Integrating autonomous wingmen with multirole fighters is expected to revolutionize air combat tactics by enabling seamless data sharing and distributed lethality on the battlefield.
Strategic Implications for Global Defense Forces
Multirole fighters serve as versatile platforms capable of executing air-to-air, air-to-ground, and reconnaissance missions, providing flexible response options for global defense forces. Loyal wingman drones, operating alongside manned aircraft, enhance mission effectiveness by extending sensor range, conducting lethal or non-lethal tasks, and reducing pilot risk in contested environments. The integration of loyal wingman technology reshapes strategic doctrines by optimizing force multiplication, enabling more adaptive and resilient combat formations in modern warfare.
Related Important Terms
Human-Machine Teaming
Multirole fighters leverage pilot expertise combined with advanced avionics for versatile mission profiles, while loyal wingmen operate as autonomous or semi-autonomous drones designed to augment human pilots by enhancing situational awareness and force multiplication. Human-machine teaming in these platforms optimizes combat effectiveness by blending human decision-making with AI-driven tactical support and risk mitigation.
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T)
Multirole fighters equipped with advanced sensors and weaponry collaborate seamlessly with Loyal Wingman drones through Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T), enhancing battlefield situational awareness and force multiplication. This integration allows piloted aircraft to delegate high-risk tasks to autonomous drones, optimizing mission flexibility and survivability in contested environments.
Combat Air Teaming System (CATS)
Multirole fighters deliver versatile combat capabilities across air-to-air and air-to-ground missions, while Loyal Wingman drones extend operational reach and situational awareness within the Combat Air Teaming System (CATS). CATS integrates these platforms to create a networked force multiplier, enhancing mission effectiveness through autonomous coordination and real-time data sharing.
Swarming Drones
Swarming drones deployed alongside multirole fighters enhance mission capabilities by providing overwhelming tactical advantages through coordinated attacks and real-time battlefield intelligence. These autonomous systems act as loyal wingmen, extending the reach and survivability of manned aircraft while executing complex swarm tactics that disrupt enemy defenses and improve target acquisition.
Semi-Autonomous Wingman
Semi-autonomous wingmen in modern defense strategies enhance multirole fighter capabilities by executing complex missions with reduced pilot workload and increased operational flexibility. These intelligent drones leverage AI-driven decision-making and real-time data sharing to act as force multipliers, performing reconnaissance, electronic warfare, and target engagement alongside manned aircraft.
Network-Centric Warfare
Multirole fighters serve as versatile, manned combat platforms capable of executing various missions, while loyal wingmen operate as autonomous or remotely piloted drones designed to extend sensor reach and enhance offensive capabilities. Integration within network-centric warfare allows these systems to share real-time data, enabling collaborative targeting, threat identification, and force multiplication across the battlespace.
Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA)
Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA) like loyal wingmen operate alongside multirole fighters to enhance situational awareness, extend mission range, and provide risk mitigation in high-threat environments. Multirole fighters deliver versatile offensive and defensive capabilities while CCAs execute coordinated tactics, enabling force multiplication and increased battlefield adaptability.
Next-Generation Air Dominance (NGAD)
Next-Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) integrates multirole fighters with loyal wingman drones to enhance mission versatility, survivability, and situational awareness, leveraging advanced AI and stealth technologies. This synergistic pairing enables dynamic force multiplication, allowing manned aircraft to perform complex combat tasks while autonomous wingmen handle high-risk operations and electronic warfare.
Attritable Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (AUAV)
Attritable Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (AUAVs), such as Loyal Wingman drones, offer cost-effective force multiplication and risk reduction compared to traditional multirole fighters by performing high-risk missions with expendable platforms. Integrating AUAVs with manned multirole fighters enhances operational flexibility through coordinated swarm tactics, extended sensor reach, and improved survivability in contested environments.
Digital Twin Pilot
Multirole fighters equipped with advanced avionics leverage Digital Twin Pilot technology to simulate real-time battlefield conditions and pilot responses, boosting mission adaptability and situational awareness. Loyal Wingman drones, integrated with this digital twin framework, extend operational reach and provide autonomous support while maintaining seamless coordination with manned multirole fighter jets.
Multirole Fighter vs Loyal Wingman Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com