Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) offer superior firepower, heavy armor, and battlefield presence, making them critical for direct combat roles. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) enhance operational flexibility by providing remote-controlled or autonomous capabilities, reducing risk to personnel in high-threat environments. Integrating UGCVs alongside MBTs can optimize force effectiveness by combining human decision-making with advanced robotics technology.
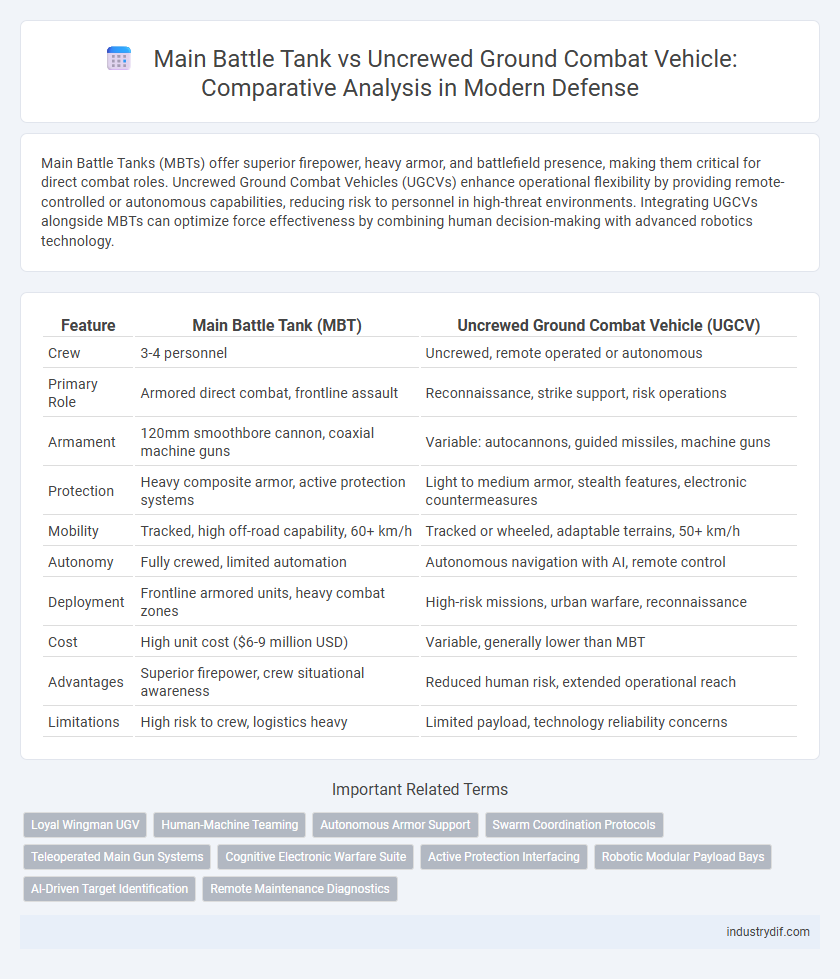
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Main Battle Tank (MBT) | Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicle (UGCV) |
|---|---|---|
| Crew | 3-4 personnel | Uncrewed, remote operated or autonomous |
| Primary Role | Armored direct combat, frontline assault | Reconnaissance, strike support, risk operations |
| Armament | 120mm smoothbore cannon, coaxial machine guns | Variable: autocannons, guided missiles, machine guns |
| Protection | Heavy composite armor, active protection systems | Light to medium armor, stealth features, electronic countermeasures |
| Mobility | Tracked, high off-road capability, 60+ km/h | Tracked or wheeled, adaptable terrains, 50+ km/h |
| Autonomy | Fully crewed, limited automation | Autonomous navigation with AI, remote control |
| Deployment | Frontline armored units, heavy combat zones | High-risk missions, urban warfare, reconnaissance |
| Cost | High unit cost ($6-9 million USD) | Variable, generally lower than MBT |
| Advantages | Superior firepower, crew situational awareness | Reduced human risk, extended operational reach |
| Limitations | High risk to crew, logistics heavy | Limited payload, technology reliability concerns |
Introduction to Main Battle Tanks and Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) serve as heavily armored and highly mobile armored fighting vehicles designed to engage enemy forces with powerful armament, including large-caliber main guns and advanced targeting systems. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) represent a new frontier in military technology, featuring remote or autonomous operation capabilities designed to reduce soldier risk while performing reconnaissance, fire support, or combat missions. The integration of UGCVs alongside traditional MBTs is reshaping battlefield dynamics through enhanced situational awareness and force multiplication.
Evolution of Armored Warfare Technologies
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) have evolved with enhanced armor composites, advanced targeting systems, and increased firepower to maintain battlefield superiority. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) integrate autonomous navigation, AI-driven threat detection, and remote operation capabilities, representing a paradigm shift in armored warfare technology. The ongoing fusion of MBT robustness with UGCV automation drives the future evolution of armored combat platforms.
Design Characteristics: Manned vs Uncrewed Platforms
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) feature heavily armored, crew-operated designs with integrated weapon systems and advanced targeting capabilities, emphasizing crew protection and battlefield situational awareness. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) prioritize modularity, remote operation, and lower profiles, enabling deployment in high-risk environments without endangering personnel. The contrast in design characteristics highlights trade-offs between human decision-making and autonomous system endurance in modern ground combat platforms.
Firepower and Weapon Systems Comparison
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) feature heavily armored turreted cannons typically ranging from 120mm to 125mm smoothbore guns capable of firing a variety of ammunition types including APFSDS, HEAT, and guided missiles, providing versatile and high-impact firepower. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) often rely on modular weapon systems with remote-operated machine guns, autocannons between 20mm to 50mm, and sometimes integrated missile launchers, emphasizing precision engagement and reduced crew risk. While MBTs prioritize raw destructive power and durability in direct combat, UGCVs leverage advanced targeting systems and networked sensors for flexible, multi-domain battlefield roles with scalable firepower.
Survivability and Protection Technologies
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) incorporate advanced composite armor and active protection systems, such as Trophy and Arena, to defend against anti-tank guided missiles and kinetic penetrators, ensuring high crew survivability on the battlefield. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) leverage layered armor combined with sensor fusion and electronic countermeasures to mitigate threats without endangering personnel, enhancing mission persistence in contested environments. Both platforms integrate reactive armor and electromagnetic jamming technologies, but UGCVs benefit from reduced risk exposure, allowing for more aggressive operational tactics in high-threat scenarios.
Battlefield Roles and Operational Applications
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) serve as heavily armored firepower platforms for direct frontline engagement and force projection, excelling in combined arms operations and urban combat. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) provide enhanced reconnaissance, risk reduction for personnel, and flexible mission adaptability in high-threat environments through remote or autonomous operation. MBTs dominate traditional armored warfare roles, while UGCVs supplement battlefield awareness, force multiplication, and asymmetric conflict scenarios.
Mobility, Endurance, and Logistics
Main Battle Tanks exhibit superior mobility with advanced suspension systems and powerful engines enabling rapid maneuvering across diverse terrains, while Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) benefit from smaller footprints and modular designs for agile reconnaissance and support roles. In terms of endurance, MBTs rely on robust fuel capacity and armored protection to sustain prolonged frontline operations, whereas UGCVs leverage efficient power management and autonomous navigation to extend mission duration without crew fatigue. Logistics for MBTs demand extensive supply chains for fuel, ammunition, and maintenance, contrasted by UGCVs' streamlined resupply needs and potential for remote diagnostics, reducing the logistical footprint in contested environments.
Command, Control, and Communication Capabilities
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) integrate advanced command, control, and communication (C3) systems enabling real-time battlefield data sharing, target acquisition, and coordination with infantry and aerial support. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) leverage autonomous navigation and encrypted communication links to conduct remote operations, reducing risk to personnel while maintaining connectivity with command centers. The synergy of MBT C3 networks with UGCV remote control frameworks enhances situational awareness and force multiplier effects in modern combat environments.
Future Trends in Ground Combat Vehicles
Future trends in ground combat vehicles emphasize increased autonomy and network-centric warfare capabilities, with Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) offering enhanced reconnaissance and risk reduction compared to Main Battle Tanks (MBTs). Advances in AI-driven targeting systems, modular armor, and hybrid powertrains are accelerating UGCV development, enabling them to operate alongside or independently from manned MBTs. Integration of these technologies aims to improve battlefield survivability, situational awareness, and operational flexibility in evolving combat scenarios.
Strategic Implications for Modern Defense Forces
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) continue to symbolize armored warfare with unmatched firepower, armor, and battlefield presence, while Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) introduce enhanced operational flexibility and reduced risk to personnel. Integration of UGCVs offers modern defense forces opportunities for remote reconnaissance, autonomous targeting, and force multiplication in complex combat environments. The strategic balance involves optimizing MBT lethality alongside UGCV adaptability to maintain combat superiority and ensure mission success in evolving warfare scenarios.
Related Important Terms
Loyal Wingman UGV
The Loyal Wingman uncrewed ground combat vehicle (UGV) enhances main battle tank (MBT) operations by providing autonomous reconnaissance, target acquisition, and force multiplication without risking crew lives. Equipped with advanced sensors and networked communication systems, the Loyal Wingman UGV extends battlefield awareness and supports coordinated maneuvers, complementing the firepower and armor protection of traditional MBTs.
Human-Machine Teaming
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) leverage heavily armored firepower and crewed tactical decision-making, while Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) enhance battlefield adaptability through autonomous targeting and remote operation. Human-machine teaming integrates MBTs' situational awareness with UGCVs' sensor data, optimizing combat effectiveness and reducing risk to personnel.
Autonomous Armor Support
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) provide heavily armored firepower with crew-operated precision, while Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) offer autonomous armor support through advanced AI-driven targeting and reconnaissance capabilities. Integration of UGCVs enhances battlefield scalability and reduces human risk by complementing MBTs with automated threat detection and rapid response systems.
Swarm Coordination Protocols
Main Battle Tanks utilize advanced swarm coordination protocols that enable real-time data sharing and synchronized maneuvers among multiple units, enhancing battlefield dominance through collective targeting and threat response. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles employ decentralized swarm algorithms allowing autonomous decision-making and adaptive formation changes, increasing operational resilience and reducing human risk in complex combat environments.
Teleoperated Main Gun Systems
Main Battle Tanks equipped with teleoperated main gun systems offer enhanced crew protection by allowing operators to control weaponry remotely from within armored compartments. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles leverage these teleoperated technologies to increase battlefield versatility and reduce human casualties during high-risk engagements.
Cognitive Electronic Warfare Suite
The Main Battle Tank integrates advanced armor and firepower with evolving cognitive electronic warfare suites designed to detect, analyze, and counteract enemy signals in real-time. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles enhance battlefield adaptability by leveraging AI-driven cognitive electronic warfare systems that autonomously disrupt adversary communications and electronic threats while maintaining stealth and operational endurance.
Active Protection Interfacing
Main Battle Tanks employ integrated Active Protection Systems (APS) with advanced radar and countermeasure deployment, enhancing survivability against anti-tank guided missiles and rocket-propelled grenades. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles leverage networked APS interfaces allowing real-time threat detection and automated defensive responses, improving battlefield adaptability without risking crew safety.
Robotic Modular Payload Bays
Main Battle Tanks leverage heavily armored, crew-operated platforms designed for direct combat engagement, whereas Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles prioritize robotic modular payload bays enabling rapid sensor and weapon system reconfiguration to adapt mission-specific requirements. Robotic modular payload bays enhance operational flexibility by supporting diverse payload integration such as reconnaissance drones, anti-tank missiles, and electronic warfare packages, significantly extending battlefield versatility and reducing crew risk.
AI-Driven Target Identification
AI-driven target identification in main battle tanks enhances threat detection through advanced sensor fusion and deep learning algorithms, allowing precise engagement in complex combat environments. Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicles leverage autonomous AI systems for rapid target recognition and real-time decision-making, reducing operator risk and increasing battlefield efficiency.
Remote Maintenance Diagnostics
Main battle tanks typically require on-site maintenance by skilled crews, whereas uncrewed ground combat vehicles (UGCVs) integrate advanced remote maintenance diagnostics that enable real-time fault detection, predictive analytics, and remote system updates, significantly reducing downtime and operational risk. The use of IoT sensors and AI-driven diagnostic platforms in UGCVs enhances battlefield readiness by providing continuous health monitoring and automated troubleshooting, which contrasts with the traditionally manual inspection processes in main battle tanks.
Main Battle Tank vs Uncrewed Ground Combat Vehicle Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com