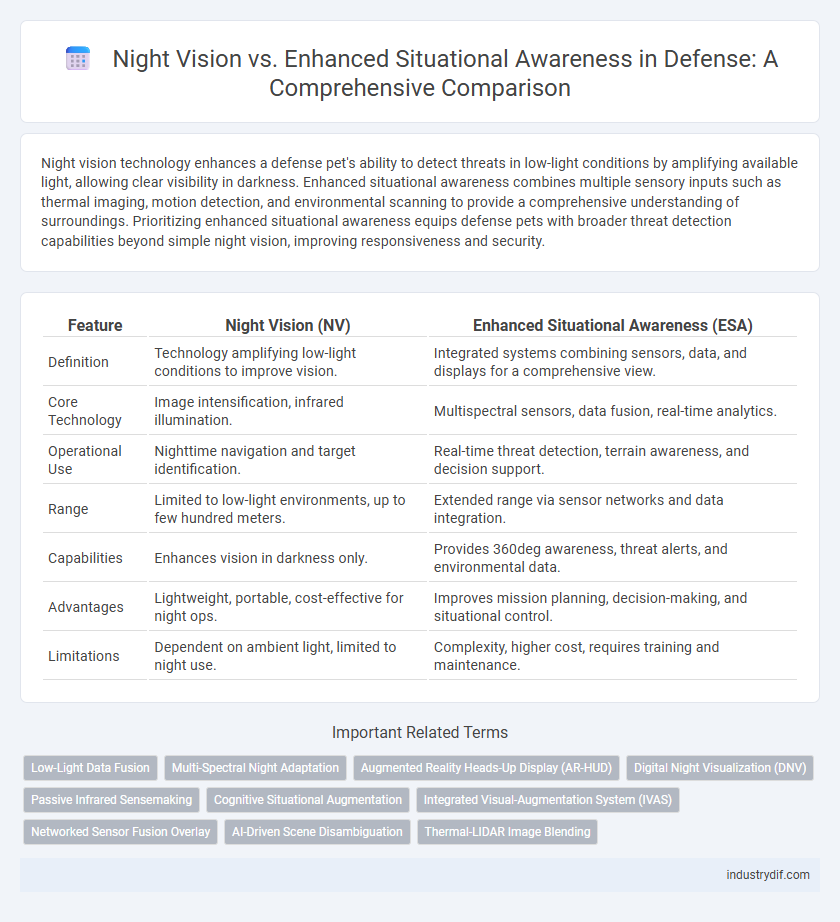
Night vision technology enhances a defense pet's ability to detect threats in low-light conditions by amplifying available light, allowing clear visibility in darkness. Enhanced situational awareness combines multiple sensory inputs such as thermal imaging, motion detection, and environmental scanning to provide a comprehensive understanding of surroundings. Prioritizing enhanced situational awareness equips defense pets with broader threat detection capabilities beyond simple night vision, improving responsiveness and security.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Night Vision (NV) | Enhanced Situational Awareness (ESA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology amplifying low-light conditions to improve vision. | Integrated systems combining sensors, data, and displays for a comprehensive view. |
| Core Technology | Image intensification, infrared illumination. | Multispectral sensors, data fusion, real-time analytics. |
| Operational Use | Nighttime navigation and target identification. | Real-time threat detection, terrain awareness, and decision support. |
| Range | Limited to low-light environments, up to few hundred meters. | Extended range via sensor networks and data integration. |
| Capabilities | Enhances vision in darkness only. | Provides 360deg awareness, threat alerts, and environmental data. |
| Advantages | Lightweight, portable, cost-effective for night ops. | Improves mission planning, decision-making, and situational control. |
| Limitations | Dependent on ambient light, limited to night use. | Complexity, higher cost, requires training and maintenance. |
Night Vision: Core Principles and Technologies
Night vision relies on image intensification and thermal imaging technologies to amplify available light or detect infrared radiation, enabling clear visibility in low-light or no-light conditions. Core components include photomultiplier tubes and infrared sensors that convert photons into visible images, enhancing soldiers' operational effectiveness during nighttime missions. Advances in digital night vision incorporate high-resolution sensors and real-time image processing to improve target detection and situational awareness on the battlefield.
Enhanced Situational Awareness: Definition and Components
Enhanced Situational Awareness (ESA) in defense refers to the comprehensive understanding of the battlefield environment, achieved through the integration of real-time data from multiple sources such as sensors, communication systems, and intelligence feeds. Key components include advanced surveillance technologies, data fusion platforms, and decision-support tools that provide timely, accurate information to military personnel. ESA improves operational effectiveness by enabling proactive threat detection, rapid response, and coordinated mission execution beyond the capabilities of traditional night vision devices.
Comparing Image Intensification vs Multi-Sensor Fusion
Image intensification amplifies available light to produce clear night vision images, excelling in low-light conditions but limited by environmental factors like fog or smoke. Multi-sensor fusion integrates data from infrared, thermal, and other sensors to provide a comprehensive situational picture, enhancing target detection and identification beyond the capabilities of single technology systems. Combining these technologies in defense operations significantly improves situational awareness, enabling faster decision-making and greater mission success in complex environments.
Key Applications in Modern Battlefield Operations
Night vision technology enables military personnel to operate effectively in low-light conditions by amplifying ambient light or using infrared imaging, essential for covert reconnaissance, navigation, and target detection. Enhanced situational awareness integrates data from multiple sensors, real-time communication systems, and AI-driven analytics to provide comprehensive battlefield intelligence, significantly improving decision-making and threat response. Key applications include urban warfare, special operations, and surveillance missions where rapid threat assessment and operational coordination are critical for mission success.
Limitations and Challenges of Night Vision Devices
Night vision devices (NVDs) face significant limitations such as reduced effectiveness in environments with insufficient ambient light or adverse weather conditions like fog and rain. They often provide a narrow field of view and depth perception issues, impeding comprehensive situational awareness. High power consumption and vulnerability to bright lights also challenge their reliability in continuous tactical operations.
Advancements in Heads-Up Display Systems
Modern heads-up display (HUD) systems in defense have significantly enhanced night vision capabilities, integrating thermal imaging and augmented reality to provide soldiers with improved target identification and threat detection during low-light operations. These advancements enable real-time data overlay, such as navigational routes, enemy positions, and system diagnostics, directly on the visor, allowing for quicker decision-making and reduced cognitive load. Enhanced situational awareness through advanced HUDs improves operational effectiveness and survivability in complex combat environments.
Integration with Tactical Communication Networks
Night vision technology enhances soldier effectiveness by providing clear visibility in low-light conditions through infrared and image intensification sensors, improving target acquisition and navigation. Enhanced situational awareness systems integrate data from multiple sensors, including night vision devices, with real-time tactical communication networks to deliver comprehensive battlefield information to command units and individual troops. This integration facilitates rapid decision-making, precise coordination, and seamless information sharing across units, crucial for modern combat operations.
Threat Detection and Target Identification Capabilities
Night vision technology amplifies available light to enhance threat detection in low-light conditions, providing clear imagery critical for identifying potential threats at night. Enhanced situational awareness integrates multiple sensor inputs such as infrared, thermal imaging, and radar data to offer comprehensive target identification and real-time battlefield intelligence. Combining night vision with advanced situational awareness systems significantly improves operational effectiveness by increasing detection range, accuracy, and response time against diverse security threats.
Human Factors: Cognitive Load and User Training
Night vision technology enhances situational awareness by amplifying low-light environments, but it can increase cognitive load due to the limited field of view and image distortion. Enhanced situational awareness systems integrate multiple data sources, reducing cognitive strain by presenting consolidated, clear information, thereby improving decision-making speed and accuracy. User training is critical in both technologies to ensure operators can interpret visual data effectively and manage cognitive demands under high-stress defense scenarios.
Future Trends in Defense Optical Systems
Future trends in defense optical systems emphasize the integration of night vision technologies with enhanced situational awareness features, leveraging multispectral imaging and AI-driven analytics to improve target detection and threat assessment under low-light conditions. Advances in sensor fusion combine thermal, infrared, and low-light sensors to deliver comprehensive battlefield visibility, enabling real-time decision making and reducing operator fatigue. Enhanced situational awareness coupled with next-generation night vision devices supports autonomous vehicle navigation and augmented reality interfaces, reshaping tactical operations in complex environments.
Related Important Terms
Low-Light Data Fusion
Low-light data fusion integrates multiple sensor inputs such as infrared, thermal imaging, and image intensification to provide comprehensive night vision capabilities, significantly enhancing situational awareness in defense operations. This fusion technology enables real-time threat detection and identification in low-visibility environments, surpassing traditional night vision devices that rely solely on single-spectrum imagery.
Multi-Spectral Night Adaptation
Multi-spectral night adaptation integrates infrared, thermal, and low-light imaging technologies to surpass conventional night vision, providing enhanced situational awareness in complex combat environments. This fusion of spectral data enables precise threat detection, target identification, and navigation under varied lighting and weather conditions, optimizing defense operations during night missions.
Augmented Reality Heads-Up Display (AR-HUD)
The Augmented Reality Heads-Up Display (AR-HUD) integrates advanced night vision technology with real-time data overlays, significantly enhancing situational awareness by providing soldiers with critical information in low-light environments. This fusion enables rapid decision-making and threat detection, surpassing traditional night vision devices by delivering a comprehensive battlefield perspective through augmented reality.
Digital Night Visualization (DNV)
Digital Night Visualization (DNV) technology in defense systems significantly improves situational awareness by providing high-resolution, real-time imaging in low-light and no-light conditions, surpassing traditional night vision devices. Unlike analog night vision, DNV integrates advanced sensors and image processing algorithms to enhance target detection, identification, and threat assessment, thereby increasing operational effectiveness and soldier safety during nighttime missions.
Passive Infrared Sensemaking
Passive infrared sensemaking enhances night vision by detecting thermal signatures without emitting light, enabling covert operations and reducing detection risk. This technology improves enhanced situational awareness by providing precise heat-based imagery, critical for identifying threats in low-visibility defense environments.
Cognitive Situational Augmentation
Cognitive Situational Augmentation (CSA) enhances traditional night vision by integrating real-time data analytics and AI-driven threat recognition, significantly improving decision-making accuracy in low-light combat scenarios. This advanced approach surpasses basic image enhancement by providing operators with predictive insights and situational context, thereby elevating overall mission effectiveness and safety.
Integrated Visual-Augmentation System (IVAS)
The Integrated Visual-Augmentation System (IVAS) revolutionizes defense capabilities by combining advanced night vision with enhanced situational awareness, enabling soldiers to detect threats in low-light environments while maintaining real-time battlefield data overlays. This fusion of thermal imaging, augmented reality, and GPS integration provides tactical superiority through improved target acquisition, navigation, and communication under diverse combat conditions.
Networked Sensor Fusion Overlay
Networked sensor fusion overlay integrates data from multiple night vision devices and enhanced situational awareness systems to provide comprehensive real-time battlefield intelligence. This fusion significantly improves target detection accuracy, reduces operator fatigue, and enhances decision-making by creating a cohesive, multi-spectral visual representation of the environment.
AI-Driven Scene Disambiguation
AI-driven scene disambiguation in night vision systems significantly enhances situational awareness by accurately distinguishing between threats and non-threats in low-light environments. This advanced technology processes complex visual data in real time, enabling faster decision-making and reducing the risk of misidentification during defense operations.
Thermal-LIDAR Image Blending
Thermal-LIDAR image blending integrates thermal imaging's heat signature detection with LiDAR's precise spatial mapping to enhance situational awareness in defense operations, enabling superior target identification and navigation in low visibility conditions. This fusion technology outperforms traditional night vision by providing clear, real-time 3D environmental data regardless of lighting, smoke, or camouflage interference.
Night Vision vs Enhanced Situational Awareness Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com