Supply chain management in defense pet focuses on coordinating complex networks of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to ensure timely delivery of critical components and materials. Additive manufacturing logistics streamline production by enabling on-demand fabrication of parts directly at or near the point of use, reducing dependency on traditional supply chains and minimizing lead times. This shift enhances operational flexibility and resilience in mission-critical environments where rapid response and customization are paramount.
Table of Comparison
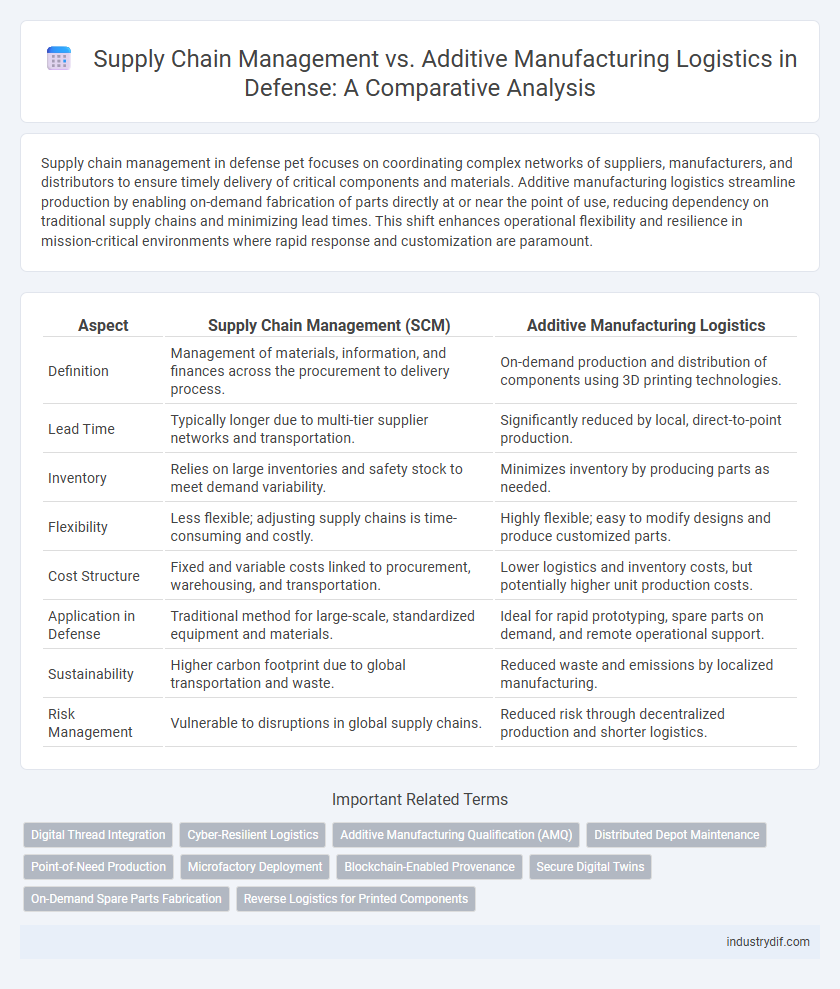
| Aspect | Supply Chain Management (SCM) | Additive Manufacturing Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management of materials, information, and finances across the procurement to delivery process. | On-demand production and distribution of components using 3D printing technologies. |
| Lead Time | Typically longer due to multi-tier supplier networks and transportation. | Significantly reduced by local, direct-to-point production. |
| Inventory | Relies on large inventories and safety stock to meet demand variability. | Minimizes inventory by producing parts as needed. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; adjusting supply chains is time-consuming and costly. | Highly flexible; easy to modify designs and produce customized parts. |
| Cost Structure | Fixed and variable costs linked to procurement, warehousing, and transportation. | Lower logistics and inventory costs, but potentially higher unit production costs. |
| Application in Defense | Traditional method for large-scale, standardized equipment and materials. | Ideal for rapid prototyping, spare parts on demand, and remote operational support. |
| Sustainability | Higher carbon footprint due to global transportation and waste. | Reduced waste and emissions by localized manufacturing. |
| Risk Management | Vulnerable to disruptions in global supply chains. | Reduced risk through decentralized production and shorter logistics. |
Overview of Defense Supply Chain Management
Defense supply chain management integrates procurement, production, and distribution to ensure timely delivery of critical military equipment and materials. Traditional supply chains emphasize centralized manufacturing and extensive transportation networks, while additive manufacturing logistics enable on-demand, localized production that reduces lead times and inventory costs. Leveraging advanced technologies and real-time data analytics enhances resilience and responsiveness in complex defense operations.
Introduction to Additive Manufacturing in Defense Logistics
Additive manufacturing in defense logistics revolutionizes supply chain management by enabling on-demand production of critical components, reducing dependency on traditional inventory and lengthy procurement cycles. This technology improves operational readiness by allowing rapid prototyping and localized manufacturing, minimizing delays caused by complex global supply chains. Enhanced flexibility and reduced logistical footprints are pivotal advantages, streamlining maintenance and repair processes in military operations.
Comparative Analysis: Traditional vs. Additive Manufacturing Supply Chains
Traditional supply chain management in defense relies heavily on long lead times, extensive inventory, and complex multi-tier supplier networks, which often result in higher costs and slower response to urgent demands. Additive manufacturing logistics streamline production by enabling on-demand, decentralized manufacturing, reducing inventory requirements and shortening delivery times for critical components. Comparative analysis reveals that additive manufacturing enhances agility, lowers logistical footprints, and improves supply chain resilience compared to conventional defense supply chains.
Impact of Additive Manufacturing on Military Logistics
Additive manufacturing significantly reduces dependency on traditional supply chains by enabling on-demand, decentralized production of critical military components directly in the field. This technology minimizes inventory requirements and shortens lead times, enhancing operational readiness and mission flexibility. Incorporating 3D printing into military logistics improves resilience against supply chain disruptions and decreases transportation costs associated with conventional manufacturing methods.
Inventory Optimization Through Additive Manufacturing
Inventory optimization through additive manufacturing in defense supply chain management reduces excess stock and enhances readiness by enabling on-demand production of critical components. This approach minimizes storage costs and mitigates risks of obsolescence while ensuring rapid replenishment in dynamic operational environments. Integrating additive manufacturing logistics streamlines inventory by transforming traditional supply chain dependencies into agile, localized production capabilities.
Lead Time Reduction: Conventional vs. Additive Approaches
Lead time reduction in defense supply chain management significantly varies between conventional manufacturing and additive manufacturing logistics. Conventional methods rely on complex, multi-tiered supplier networks and lengthy transportation routes, often resulting in extended lead times spanning weeks or months. Additive manufacturing streamlines production by enabling on-demand, localized fabrication of parts, drastically cutting lead times to hours or days and enhancing operational readiness in critical defense scenarios.
Risk Mitigation in Defense Supply Chains
Defense supply chains face significant risks from geopolitical instability, cyber threats, and natural disasters, making risk mitigation critical. Additive manufacturing logistics reduce dependency on extended supply chains by enabling on-demand, localized production of critical components, minimizing delays and vulnerabilities. Effective supply chain management integrates predictive analytics and real-time monitoring to identify disruptions early and coordinate rapid responses, ensuring operational continuity in defense missions.
Cost Efficiency in Additive Manufacturing Logistics
Additive manufacturing logistics significantly reduces supply chain costs by minimizing inventory needs and enabling on-demand production of defense components, cutting storage and transportation expenses. The technology streamlines procurement processes and lowers material waste, directly contributing to improved cost efficiency in military supply chains. Optimized additive manufacturing logistics also enhances the responsiveness and agility of defense operations, reducing downtime and associated logistical overhead.
Security and Reliability in Sensitive Defense Components
Supply chain management in defense ensures stringent security protocols and traceability for sensitive components, minimizing risks of tampering or counterfeiting throughout the logistics network. Additive manufacturing logistics enhance reliability by enabling on-demand production, reducing dependence on extended supply lines vulnerable to disruption or cyber threats. Integrating both approaches strengthens defense readiness by balancing controlled material sourcing with flexible, secure fabrication capabilities.
Future Trends: Integration of Additive Manufacturing in Defense Supply Chains
The integration of additive manufacturing in defense supply chains is poised to revolutionize logistics by enabling on-demand production of critical components, significantly reducing lead times and inventory costs. Future trends indicate increased adoption of decentralized manufacturing hubs equipped with 3D printing technologies to enhance operational flexibility and responsiveness in combat scenarios. Advanced materials and digital supply chain integration will further optimize maintenance cycles and support rapid deployment capabilities across military operations.
Related Important Terms
Digital Thread Integration
Supply chain management in defense integrates complex procurement networks to ensure timely delivery of critical components, while additive manufacturing logistics leverage on-demand production capabilities to reduce lead times and inventory costs. Digital thread integration enhances both systems by providing seamless data connectivity across design, production, and supply phases, enabling real-time tracking, quality assurance, and adaptive decision-making in defense manufacturing processes.
Cyber-Resilient Logistics
Cyber-resilient logistics in defense supply chain management integrates advanced cybersecurity protocols to protect data integrity and operational continuity, while additive manufacturing logistics leverages decentralized, on-demand production capabilities to reduce supply chain vulnerabilities. Implementing real-time monitoring and blockchain technology enhances transparency and resilience against cyber threats, ensuring secure and efficient delivery of critical defense materials.
Additive Manufacturing Qualification (AMQ)
Additive Manufacturing Qualification (AMQ) ensures that 3D-printed defense components meet strict aerospace and military standards, enabling reliable, on-demand production within secure supply chains. This qualification process enhances logistical efficiency by reducing lead times and minimizing dependence on traditional supply chain vulnerabilities in defense operations.
Distributed Depot Maintenance
Distributed Depot Maintenance enhances Defense supply chain management by integrating Additive Manufacturing logistics, enabling on-demand production of critical spare parts close to the point of need. This approach reduces lead times, lowers inventory costs, and improves operational readiness by minimizing dependency on traditional centralized supply chains.
Point-of-Need Production
Point-of-Need Production in defense supply chain management enhances operational readiness by enabling on-site additive manufacturing, reducing reliance on extended logistics and decreasing lead times for critical spare parts. This approach streamlines maintenance and repair processes, improves inventory management, and supports agile response in dynamic combat environments.
Microfactory Deployment
Microfactory deployment in defense supply chain management enhances rapid production and logistical efficiency by localizing additive manufacturing processes, reducing dependency on extended supply lines and mitigating risks of disruption. Integrating microfactories enables scalable, on-demand fabrication of critical components, optimizing inventory levels and accelerating maintenance and repair operations in dynamic combat environments.
Blockchain-Enabled Provenance
Blockchain-enabled provenance enhances supply chain management in defense by providing immutable records for tracking parts and materials, ensuring authenticity and reducing counterfeit risks. In additive manufacturing logistics, blockchain ensures traceability of digital designs and printed components, enabling secure, real-time validation of production origin and quality compliance.
Secure Digital Twins
Secure digital twins enhance defense supply chain management by providing real-time, accurate replication of logistics assets, enabling proactive risk assessment and rapid response to disruptions. Integrating additive manufacturing logistics with secure digital twins ensures on-demand production and streamlined inventory control, significantly increasing operational resilience and reducing vulnerabilities.
On-Demand Spare Parts Fabrication
On-demand spare parts fabrication through additive manufacturing logistics significantly enhances defense supply chain management by reducing lead times and inventory costs while improving mission readiness. This approach allows for rapid production of critical components at or near the point of need, minimizing dependency on traditional supply chains vulnerable to disruption.
Reverse Logistics for Printed Components
Reverse logistics for printed components in defense supply chain management streamlines the retrieval, inspection, and recycling of additive manufactured parts, significantly reducing waste and costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods. Integrating advanced tracking systems and quality assessment protocols ensures rapid refurbishment or disposal, enhancing overall asset lifecycle efficiency and operational readiness.
Supply chain management vs Additive manufacturing logistics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com