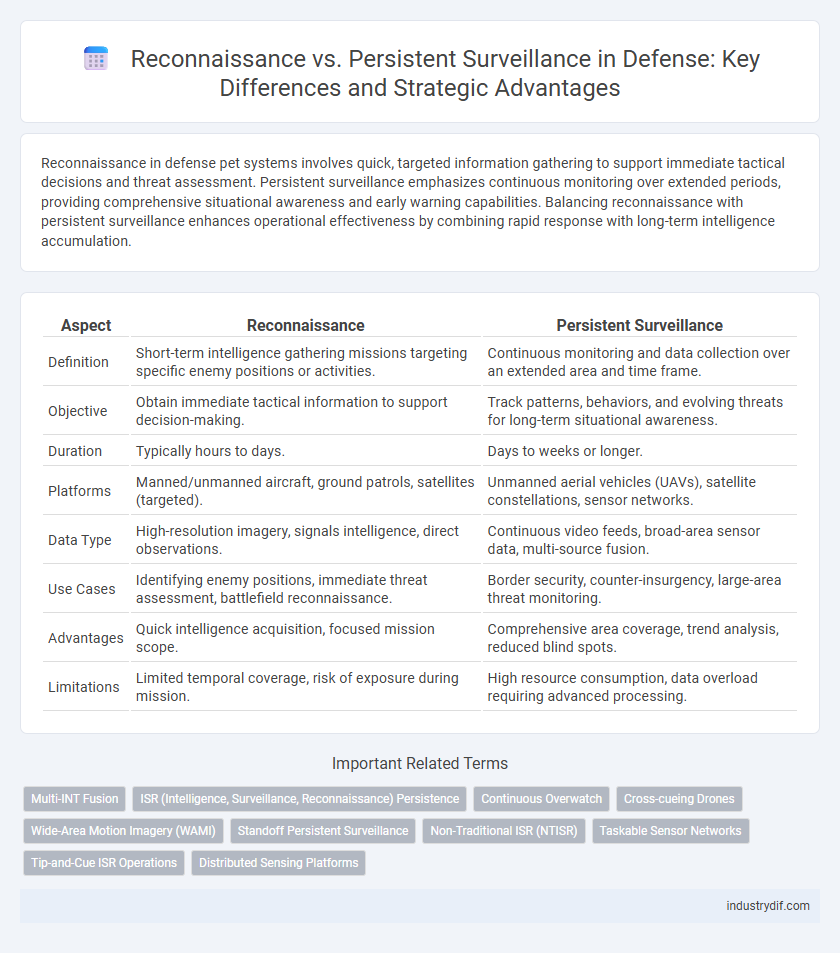
Reconnaissance in defense pet systems involves quick, targeted information gathering to support immediate tactical decisions and threat assessment. Persistent surveillance emphasizes continuous monitoring over extended periods, providing comprehensive situational awareness and early warning capabilities. Balancing reconnaissance with persistent surveillance enhances operational effectiveness by combining rapid response with long-term intelligence accumulation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reconnaissance | Persistent Surveillance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term intelligence gathering missions targeting specific enemy positions or activities. | Continuous monitoring and data collection over an extended area and time frame. |
| Objective | Obtain immediate tactical information to support decision-making. | Track patterns, behaviors, and evolving threats for long-term situational awareness. |
| Duration | Typically hours to days. | Days to weeks or longer. |
| Platforms | Manned/unmanned aircraft, ground patrols, satellites (targeted). | Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), satellite constellations, sensor networks. |
| Data Type | High-resolution imagery, signals intelligence, direct observations. | Continuous video feeds, broad-area sensor data, multi-source fusion. |
| Use Cases | Identifying enemy positions, immediate threat assessment, battlefield reconnaissance. | Border security, counter-insurgency, large-area threat monitoring. |
| Advantages | Quick intelligence acquisition, focused mission scope. | Comprehensive area coverage, trend analysis, reduced blind spots. |
| Limitations | Limited temporal coverage, risk of exposure during mission. | High resource consumption, data overload requiring advanced processing. |
Understanding Reconnaissance in Defense Operations
Reconnaissance in defense operations involves the targeted collection of tactical information through short-term, mission-specific efforts to assess enemy positions, capabilities, and activities. It emphasizes rapid deployment and flexibility to support immediate decision-making and battlefield awareness. Unlike persistent surveillance, reconnaissance prioritizes precision and adaptability over continuous, long-duration monitoring.
Defining Persistent Surveillance in Military Context
Persistent surveillance in a military context refers to the continuous, long-duration monitoring of an area to detect, track, and analyze enemy movements and activities over time. Unlike reconnaissance, which is typically short-term and mission-specific, persistent surveillance employs advanced sensors, unmanned aerial systems, and real-time data analytics to maintain an ongoing situational awareness. This capability enables commanders to make informed decisions, anticipate threats, and coordinate operations with higher precision and timeliness.
Key Objectives: Reconnaissance vs Persistent Surveillance
Reconnaissance focuses on gathering specific, time-sensitive information about enemy positions, movements, and capabilities to support immediate tactical decisions. Persistent surveillance aims to maintain continuous observation over a designated area to detect patterns, track targets, and provide comprehensive situational awareness. Key objectives of reconnaissance include rapid, targeted intelligence collection, while persistent surveillance prioritizes long-duration monitoring and data accumulation for strategic analysis.
Methods and Technologies Employed
Reconnaissance relies on targeted, short-duration missions using manned aircraft, drones, or satellite imaging to gather specific intelligence quickly. Persistent surveillance employs continuous monitoring through advanced sensor networks, including UAV swarms, ground-based radars, and high-resolution electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) systems to maintain real-time situational awareness. Integration of artificial intelligence and edge computing enhances data processing speed and accuracy in both methods, enabling timely threat detection and decision-making.
Duration and Coverage: Temporal Differences
Reconnaissance missions typically focus on short-term, high-intensity information collection over targeted areas, delivering immediate battlefield intelligence. Persistent surveillance provides continuous monitoring across extensive regions, enabling long-term situational awareness and trend analysis. The temporal advantage of persistent surveillance lies in its ability to maintain uninterrupted observation, while reconnaissance emphasizes temporal precision and rapid data acquisition.
Data Collection and Intelligence Integration
Reconnaissance involves targeted data collection through brief, mission-specific operations, providing real-time intelligence that supports immediate tactical decisions. Persistent surveillance continuously gathers extensive data across wider areas over extended periods, enabling comprehensive pattern analysis and threat detection. Intelligence integration synthesizes information from both reconnaissance and persistent surveillance platforms, enhancing situational awareness and enabling more effective strategic planning.
Tactical Applications in Battlefield Scenarios
Reconnaissance missions provide real-time intelligence by deploying specialized units or drones for quick, targeted information gathering in dynamic battlefield scenarios. Persistent surveillance employs continuous monitoring systems such as drones, satellites, or ground sensors to maintain an ongoing operational picture, enhancing situational awareness over extended periods. Tactical applications benefit from reconnaissance for immediate threat assessment while persistent surveillance supports long-term strategic decision-making and force protection.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Approach
Reconnaissance offers rapid, targeted data collection ideal for tactical decision-making but is limited by shorter mission durations and vulnerability to enemy detection. Persistent surveillance provides continuous monitoring over extended periods, enhancing situational awareness and threat detection, though it requires substantial resource commitment and may generate excessive data for timely analysis. Balancing the immediacy of reconnaissance with the comprehensive scope of persistent surveillance optimizes defense intelligence capabilities.
Evolving Trends in Surveillance and Reconnaissance
Evolving trends in defense emphasize the integration of reconnaissance and persistent surveillance to enhance situational awareness and threat detection. Reconnaissance focuses on targeted, short-term data collection using UAVs and satellite assets, while persistent surveillance leverages continuous monitoring through advanced sensor networks and AI-driven analytics to provide real-time intelligence. Emerging technologies such as machine learning, multi-source data fusion, and autonomous platforms are revolutionizing the precision, scope, and responsiveness of both surveillance and reconnaissance operations.
Strategic Impact on Modern Defense Planning
Reconnaissance provides targeted, real-time intelligence by gathering specific information on enemy positions and movements, enabling rapid tactical decision-making in dynamic combat environments. Persistent surveillance delivers continuous, wide-area monitoring through advanced sensor networks and unmanned systems, offering comprehensive situational awareness critical for long-term strategic defense planning. Integrating reconnaissance with persistent surveillance enhances force readiness and operational adaptability, directly influencing modern defense strategies by optimizing resource allocation and threat response.
Related Important Terms
Multi-INT Fusion
Reconnaissance operations rely on targeted, short-term data collection using specialized platforms, whereas persistent surveillance emphasizes continuous, wide-area monitoring often supported by autonomous systems. Multi-INT fusion integrates signals intelligence (SIGINT), imagery intelligence (IMINT), and human intelligence (HUMINT) to enhance situational awareness, enabling more precise threat detection and decision-making in both reconnaissance and persistent surveillance missions.
ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance) Persistence
Reconnaissance provides targeted, time-limited intelligence gathering missions, while persistent surveillance offers continuous, long-duration monitoring crucial for real-time situational awareness in ISR operations. Persistent ISR enhances decision-making by maintaining uninterrupted data streams, enabling rapid response to emerging threats and dynamic battlefield conditions.
Continuous Overwatch
Continuous overwatch through persistent surveillance employs advanced sensor networks and real-time data analytics to maintain uninterrupted situational awareness over a target area, enhancing threat detection beyond the intermittent snapshots provided by traditional reconnaissance missions. This sustained visibility supports proactive decision-making and rapid response, crucial for battlefield dominance and force protection in dynamic operational environments.
Cross-cueing Drones
Cross-cueing drones enhance the effectiveness of reconnaissance and persistent surveillance by enabling real-time data sharing and coordinated target identification across multiple platforms. This integration improves situational awareness, reduces response time, and increases mission success rates in defense operations.
Wide-Area Motion Imagery (WAMI)
Wide-Area Motion Imagery (WAMI) enables persistent surveillance by continuously capturing high-resolution video across extensive geographic areas, allowing real-time tracking of multiple moving targets. In contrast, reconnaissance typically involves targeted, time-limited data collection focused on specific locations or objectives rather than continuous monitoring.
Standoff Persistent Surveillance
Standoff Persistent Surveillance enables continuous monitoring of hostile territories using long-range sensors and unmanned aerial systems, minimizing risks to personnel while maintaining real-time intelligence gathering. Unlike traditional reconnaissance, which is often time-limited and closer to enemy lines, standoff surveillance provides extended situational awareness by leveraging satellite imagery, radar systems, and advanced ISR platforms.
Non-Traditional ISR (NTISR)
Non-Traditional ISR (NTISR) leverages advanced sensor fusion and machine learning algorithms to enhance reconnaissance by providing timely, adaptive intelligence without continuous presence. Persistent surveillance emphasizes continuous data collection over extended periods, enabling comprehensive situational awareness but often demanding significant resources compared to NTISR's targeted, mission-specific capabilities.
Taskable Sensor Networks
Taskable sensor networks in reconnaissance enable real-time, adaptive data collection focused on specific targets, enhancing situational awareness with precise, on-demand intelligence. Persistent surveillance utilizes continuous, wide-area monitoring through fixed or mobile sensors, providing long-term pattern analysis and threat detection but with less flexibility compared to taskable systems.
Tip-and-Cue ISR Operations
Reconnaissance missions provide targeted intelligence gathering on specific threats or areas of interest, enabling rapid decision-making in dynamic combat environments. Persistent surveillance maintains continuous observation over broader regions, using tip-and-cue ISR operations to efficiently allocate reconnaissance assets based on real-time threat detection and cueing information.
Distributed Sensing Platforms
Distributed sensing platforms enhance reconnaissance by providing real-time, multi-angle data collection across vast operational areas, enabling rapid threat detection and situational awareness. Persistent surveillance extends this capability by continuously monitoring targets over extended periods, leveraging networked sensors for sustained intelligence gathering and improved decision-making accuracy.
Reconnaissance vs Persistent surveillance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com