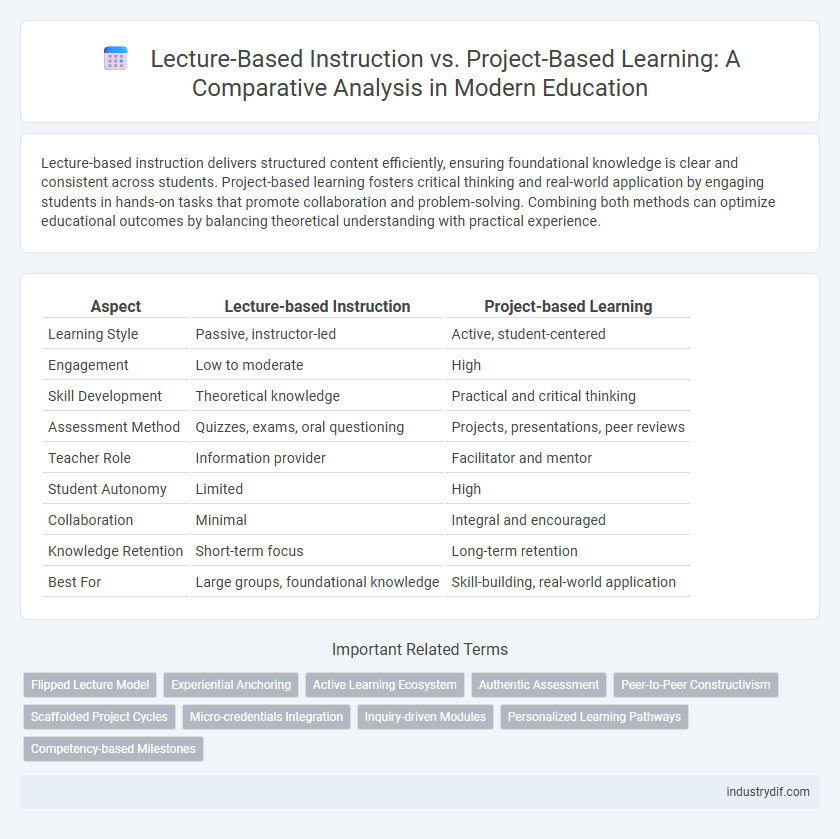
Lecture-based instruction delivers structured content efficiently, ensuring foundational knowledge is clear and consistent across students. Project-based learning fosters critical thinking and real-world application by engaging students in hands-on tasks that promote collaboration and problem-solving. Combining both methods can optimize educational outcomes by balancing theoretical understanding with practical experience.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Lecture-based Instruction | Project-based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Style | Passive, instructor-led | Active, student-centered |
| Engagement | Low to moderate | High |
| Skill Development | Theoretical knowledge | Practical and critical thinking |
| Assessment Method | Quizzes, exams, oral questioning | Projects, presentations, peer reviews |
| Teacher Role | Information provider | Facilitator and mentor |
| Student Autonomy | Limited | High |
| Collaboration | Minimal | Integral and encouraged |
| Knowledge Retention | Short-term focus | Long-term retention |
| Best For | Large groups, foundational knowledge | Skill-building, real-world application |
Overview of Lecture-based Instruction
Lecture-based instruction centers on delivering content through structured presentations, often led by an instructor who guides the curriculum sequentially. This traditional teaching model emphasizes passive learning, where students absorb information primarily via listening and note-taking. Despite critiques, lecture-based methods remain effective for disseminating foundational knowledge and covering extensive material efficiently.
Defining Project-based Learning
Project-based learning (PBL) is an instructional approach that engages students in exploring real-world problems and challenges through hands-on projects. It emphasizes active learning, critical thinking, and collaboration, allowing students to apply knowledge in practical contexts. Unlike lecture-based instruction, PBL fosters deeper understanding by integrating interdisciplinary skills and promoting student-driven inquiry.
Key Principles of Lecture-based Teaching
Lecture-based teaching emphasizes structured content delivery through instructor-led presentations, prioritizing clarity and organization of information. It relies on verbal communication and visual aids to facilitate knowledge transmission and reinforce key concepts. The approach values systematic progression and repetition to ensure comprehension and retention in large or diverse classrooms.
Core Elements of Project-based Learning
Project-based learning emphasizes student-centered inquiry, collaboration, and real-world problem solving, integrating critical thinking and creativity throughout the process. Core elements include authentic projects that engage learners, sustained inquiry enabling deep exploration of topics, and reflection to solidify understanding and skills. Unlike lecture-based instruction focused on content delivery, project-based learning fosters active engagement and practical application of knowledge.
Pedagogical Objectives Compared
Lecture-based instruction centers on delivering structured content to develop foundational knowledge and cognitive understanding, prioritizing information retention and comprehension skills aligned with standardized curricula. Project-based learning emphasizes active student engagement through real-world problem-solving tasks, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and application of interdisciplinary knowledge aimed at deeper conceptual mastery. Pedagogical objectives for lecture-based approaches often target passive absorption of facts, whereas project-based methods cultivate practical skills and learner autonomy essential for lifelong learning.
Student Engagement and Participation
Lecture-based instruction often results in passive student engagement as learners primarily receive information without active involvement. Project-based learning significantly increases student participation by encouraging hands-on collaboration, critical thinking, and real-world problem-solving. This method fosters deeper understanding and retention through immersive and interactive educational experiences.
Assessment Methods in Both Approaches
Assessment methods in lecture-based instruction primarily rely on standardized tests, quizzes, and written exams that emphasize memorization and understanding of theoretical concepts. Project-based learning assessment incorporates performance-based evaluations, portfolios, peer reviews, and presentations to measure critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and practical application of knowledge. Both approaches benefit from formative assessments, but project-based learning provides a more comprehensive assessment of student competencies through real-world tasks and collaborative efforts.
Challenges and Limitations
Lecture-based instruction often limits student engagement and critical thinking due to its passive learning structure, leading to reduced information retention and motivation. Project-based learning faces challenges in time management, resource allocation, and assessment consistency, which can hinder effective implementation in diverse classroom settings. Both methods require careful adaptation to address individual learning needs and balance curriculum demands with practical application.
Best Practices for Hybrid Models
Hybrid models that combine lecture-based instruction with project-based learning optimize student engagement and knowledge retention by balancing direct content delivery with hands-on application. Incorporating frequent formative assessments and collaborative projects within lecture sessions enhances critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills. Integrating technology platforms such as learning management systems and virtual labs supports seamless transitions between theoretical concepts and practical experiences, fostering a dynamic and adaptive educational environment.
Trends and Future Directions in Instruction
Lecture-based instruction remains prevalent due to its scalability and efficiency in delivering foundational knowledge across diverse subjects. Project-based learning gains momentum as educators emphasize critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills vital for 21st-century careers. Emerging trends indicate a blended approach leveraging digital tools to personalize learning experiences and foster deeper engagement through interactive, student-centered projects.
Related Important Terms
Flipped Lecture Model
The Flipped Lecture Model transforms traditional education by delivering instructional content outside the classroom and utilizing in-class time for interactive, project-based learning activities, enhancing student engagement and comprehension. This approach maximizes active learning opportunities and fosters critical thinking skills by encouraging students to apply theoretical knowledge in practical, collaborative projects.
Experiential Anchoring
Lecture-based instruction often provides foundational knowledge through structured content delivery, while project-based learning emphasizes experiential anchoring by actively engaging students in real-world problem-solving tasks that enhance critical thinking and retention. Studies reveal that experiential anchoring in project-based learning fosters deeper understanding and long-term knowledge retention compared to passive information reception in lecture formats.
Active Learning Ecosystem
Lecture-based instruction often limits student engagement to passive information absorption, whereas project-based learning fosters an active learning ecosystem by promoting critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem solving. Integrating project-based methodologies within educational frameworks enhances cognitive skills and cultivates a deeper understanding of subject matter through experiential participation.
Authentic Assessment
Lecture-based instruction typically emphasizes memorization and recall, making authentic assessment challenging due to its reliance on standardized tests. Project-based learning incorporates authentic assessment by evaluating students' application of knowledge through real-world projects, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Peer-to-Peer Constructivism
Lecture-based instruction often centers on knowledge transmission from teacher to student, limiting interactive engagement, whereas project-based learning fosters peer-to-peer constructivism by encouraging collaborative problem-solving and knowledge construction. Research shows that peer interactions in project-based settings enhance critical thinking, deeper understanding, and retention of educational content.
Scaffolded Project Cycles
Lecture-based instruction emphasizes direct transmission of knowledge through structured presentations, whereas project-based learning centers on scaffolded project cycles that gradually build student skills by integrating complex tasks with ongoing support and reflection. Scaffolded project cycles enhance deep learning by breaking projects into manageable phases, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and practical application of concepts in real-world contexts.
Micro-credentials Integration
Lecture-based instruction provides foundational knowledge efficiently, while project-based learning enhances practical skills and critical thinking, making micro-credentials integration more effective by validating real-world competencies and improving learner engagement. Micro-credentials aligned with project outcomes offer targeted recognition, bridging theoretical understanding from lectures with hands-on application in diverse educational settings.
Inquiry-driven Modules
Inquiry-driven modules in lecture-based instruction emphasize structured content delivery followed by targeted questioning to reinforce comprehension, while project-based learning integrates inquiry into hands-on experiences, fostering deeper critical thinking and problem-solving skills through real-world applications. Research shows that students engaged in inquiry-driven project-based learning demonstrate higher retention rates and improved ability to transfer knowledge compared to traditional lecture formats.
Personalized Learning Pathways
Lecture-based instruction delivers foundational knowledge through structured presentations, while project-based learning fosters personalized learning pathways by allowing students to engage with real-world problems tailored to their interests and skill levels. This approach enhances learner autonomy and adaptability, promoting deeper understanding and critical thinking within individualized educational journeys.
Competency-based Milestones
Lecture-based instruction emphasizes knowledge acquisition through structured content delivery, while project-based learning fosters practical application by engaging students in real-world challenges; competency-based milestones in both methods ensure measurable skill development. Tracking competency achievement in project-based learning often leads to deeper mastery and retention compared to traditional lecture-based models.
Lecture-based Instruction vs Project-based Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com