Distance education offers flexibility and accessibility by allowing learners to study remotely using digital platforms, making education more inclusive. Immersive learning enhances engagement and retention through interactive experiences such as virtual reality and simulations, providing a hands-on approach. Combining both methods can create a balanced educational environment that maximizes convenience and depth of understanding.
Table of Comparison
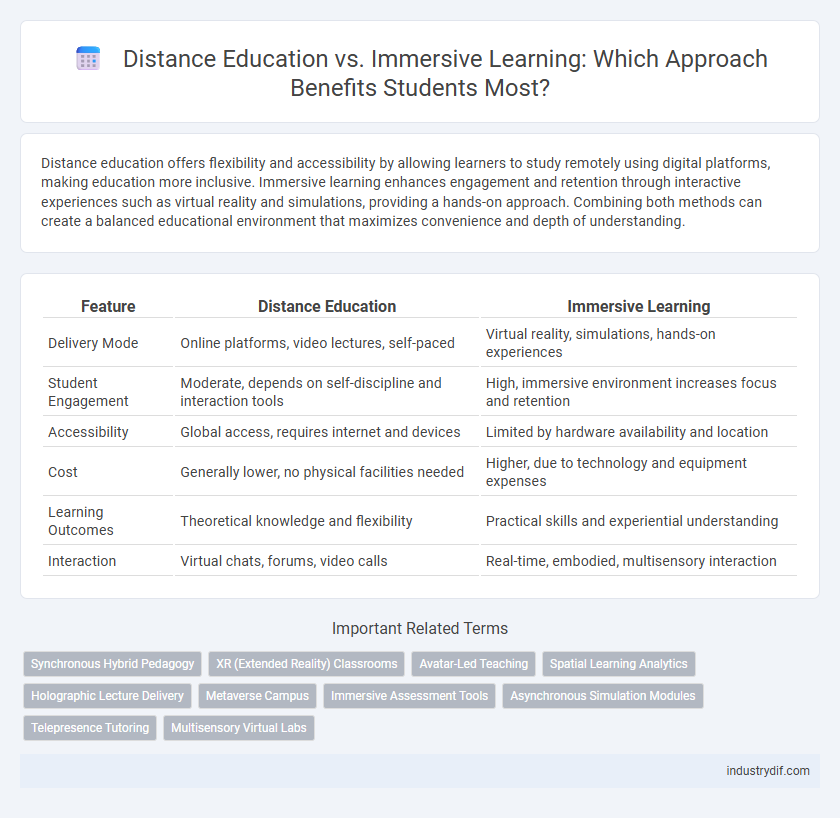
| Feature | Distance Education | Immersive Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Mode | Online platforms, video lectures, self-paced | Virtual reality, simulations, hands-on experiences |
| Student Engagement | Moderate, depends on self-discipline and interaction tools | High, immersive environment increases focus and retention |
| Accessibility | Global access, requires internet and devices | Limited by hardware availability and location |
| Cost | Generally lower, no physical facilities needed | Higher, due to technology and equipment expenses |
| Learning Outcomes | Theoretical knowledge and flexibility | Practical skills and experiential understanding |
| Interaction | Virtual chats, forums, video calls | Real-time, embodied, multisensory interaction |
Defining Distance Education and Immersive Learning
Distance education involves delivering instructional content through digital platforms, enabling students to learn remotely without physical presence in traditional classrooms. Immersive learning integrates virtual reality, augmented reality, or simulation technologies to provide interactive, experiential educational experiences that enhance cognitive engagement and retention. Both approaches leverage modern technology to cater to diverse learning needs, with distance education prioritizing accessibility and immersive learning emphasizing deeper involvement and practical application.
Historical Evolution of Distance Learning
Distance education has evolved from correspondence courses in the 19th century to advanced online learning platforms incorporating multimedia and synchronous technology. Initially reliant on postal services, this mode of learning expanded through radio, television, and eventually the internet, enabling widespread access to education beyond geographic boundaries. Immersive learning, contrasting with traditional distance education, leverages augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to create engaging, interactive experiences that simulate real-world environments.
Technological Foundations of Immersive Learning
Immersive learning leverages advanced technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) to create interactive and engaging educational experiences, surpassing traditional distance education by providing real-time sensory feedback and spatial presence. Key technological foundations include high-performance computing, haptic feedback devices, motion tracking, and AI-driven content adaptation, which collectively enhance cognitive engagement and knowledge retention. These innovations enable personalized, experiential learning environments that foster deeper understanding and skill acquisition compared to conventional video-based or text-based remote education platforms.
Key Differences in Pedagogical Approaches
Distance education leverages digital platforms to deliver content asynchronously, emphasizing self-paced learning and accessibility. Immersive learning employs virtual or augmented reality to create interactive environments that simulate real-world experiences, fostering experiential knowledge. Pedagogically, distance education prioritizes flexibility and autonomy, whereas immersive learning centers on engagement and active participation through experiential scenarios.
Accessibility and Reach: Comparing Both Methods
Distance education leverages digital platforms to provide unparalleled accessibility, enabling learners from remote or underserved areas to access quality education without geographic limitations. Immersive learning, utilizing virtual reality and augmented reality, enhances engagement but requires advanced technology and higher connectivity, potentially limiting reach in low-resource settings. Both methods expand educational opportunities, yet distance education currently offers broader accessibility due to lower infrastructure demands and device versatility.
Student Engagement and Interaction
Distance education often faces challenges in maintaining high levels of student engagement due to limited real-time interaction and reliance on asynchronous content delivery. Immersive learning leverages virtual reality and interactive simulations to create engaging, hands-on experiences that significantly enhance student interaction and motivation. Studies reveal that immersive learning environments increase participation rates by up to 60%, improving knowledge retention and collaborative skills compared to traditional distance learning methods.
Assessment and Feedback Mechanisms
Distance education commonly employs digital quizzes, automated grading systems, and discussion boards to deliver timely feedback and scalable assessment solutions. Immersive learning integrates real-time, interactive simulations and virtual reality environments, allowing for experiential assessments that capture nuanced learner behaviors and skill applications. Effective assessment and feedback mechanisms in both formats enhance learner engagement, motivation, and knowledge retention through tailored, ongoing evaluation.
Costs and Resource Implications
Distance education significantly reduces expenses related to physical infrastructure, commuting, and printed materials, making it a cost-effective option for many institutions and learners. Immersive learning, involving advanced technologies like VR and AR, incurs higher initial setup and maintenance costs but enhances engagement and practical experience. Resource allocation in distance education favors scalable digital platforms, while immersive learning demands specialized equipment and technical support, impacting budget planning and long-term investment.
Scalability and Future Trends
Distance education offers unparalleled scalability by enabling access to learning resources for thousands of students simultaneously across global locations, leveraging cloud-based platforms and asynchronous content delivery. Immersive learning, incorporating virtual and augmented reality technologies, is rapidly advancing to provide highly engaging, interactive experiences that simulate real-world scenarios, though typically at a higher cost and infrastructure demand. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach, combining the scalability of distance education with the depth of immersive experiences, driven by AI personalization and 5G connectivity to enhance accessibility and learner engagement worldwide.
Choosing the Right Model for Institutional Goals
Distance education offers flexibility and scalability, making it ideal for institutions targeting diverse, geographically dispersed learners. Immersive learning enhances engagement and retention through interactive technologies like VR, benefiting institutions prioritizing deep skill acquisition. Selecting the right model depends on aligning the delivery method with specific institutional goals such as accessibility, learner engagement, and desired educational outcomes.
Related Important Terms
Synchronous Hybrid Pedagogy
Synchronous hybrid pedagogy combines real-time interaction with digital tools, enhancing engagement and accessibility in both distance education and immersive learning environments. This approach leverages live video conferencing and interactive platforms to create a cohesive experience that supports diverse learning styles and immediate feedback.
XR (Extended Reality) Classrooms
XR classrooms revolutionize distance education by blending virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) to create immersive, interactive learning environments that enhance student engagement and knowledge retention. Unlike traditional distance education, XR platforms offer real-time simulations, 3D visualization, and spatial learning experiences that replicate in-person instruction while enabling global accessibility.
Avatar-Led Teaching
Avatar-led teaching in distance education leverages virtual avatars to create interactive and personalized learning experiences, enhancing student engagement beyond traditional online methods. Immersive learning environments powered by avatars facilitate real-time collaboration and embodiment, bridging the gap between physical presence and digital education for improved comprehension and retention.
Spatial Learning Analytics
Spatial Learning Analytics enhances Distance Education by tracking learner interactions in virtual environments to optimize engagement and knowledge retention. Immersive Learning leverages 3D simulations and real-time spatial data to provide contextual understanding and personalized feedback, significantly improving educational outcomes.
Holographic Lecture Delivery
Holographic lecture delivery enhances distance education by providing lifelike, three-dimensional projections of instructors, fostering deeper engagement and interaction comparable to immersive learning environments. This technology bridges the gap between remote access and physical presence, transforming traditional virtual classrooms into dynamic, experiential learning spaces.
Metaverse Campus
Metaverse campuses redefine education by integrating immersive learning environments where students engage in interactive 3D virtual worlds, enhancing collaboration and real-time problem-solving beyond traditional distance education platforms. This advanced digital ecosystem leverages VR and AR technologies to simulate campus experiences, offering personalized and experiential learning that drives higher retention and skill acquisition.
Immersive Assessment Tools
Immersive assessment tools in education leverage virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies to create interactive, realistic scenarios that evaluate student performance more effectively than traditional distance education methods. These tools enhance engagement and provide real-time feedback, enabling educators to assess critical thinking and practical skills in a controlled yet dynamic digital environment.
Asynchronous Simulation Modules
Asynchronous simulation modules in distance education enhance learner engagement by allowing flexible, self-paced interaction with complex scenarios, improving knowledge retention and application. These modules offer immersive learning experiences without real-time constraints, supporting diverse learning styles and enabling deeper comprehension through repeated practice and reflection.
Telepresence Tutoring
Telepresence tutoring enhances distance education by enabling real-time, interactive learning experiences that closely replicate classroom environments, leveraging advanced video conferencing and holographic technologies. This immersive approach improves student engagement, comprehension, and personalized feedback, surpassing traditional remote learning methods in effectiveness and connectivity.
Multisensory Virtual Labs
Multisensory virtual labs in immersive learning environments enhance student engagement by simulating hands-on experiments with visual, auditory, and tactile feedback, surpassing the passive experience typical of distance education. These interactive labs foster deeper understanding and skill acquisition by integrating real-time sensory stimuli, which traditional online platforms often lack.
Distance Education vs Immersive Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com