Field trips provide hands-on experiences and direct interaction with educational environments, enhancing student engagement and practical understanding. Virtual fieldwork offers flexibility and accessibility, allowing students to explore remote or otherwise inaccessible locations through digital simulations. Both approaches complement each other by combining physical exploration with technological innovation to deepen learning outcomes.
Table of Comparison
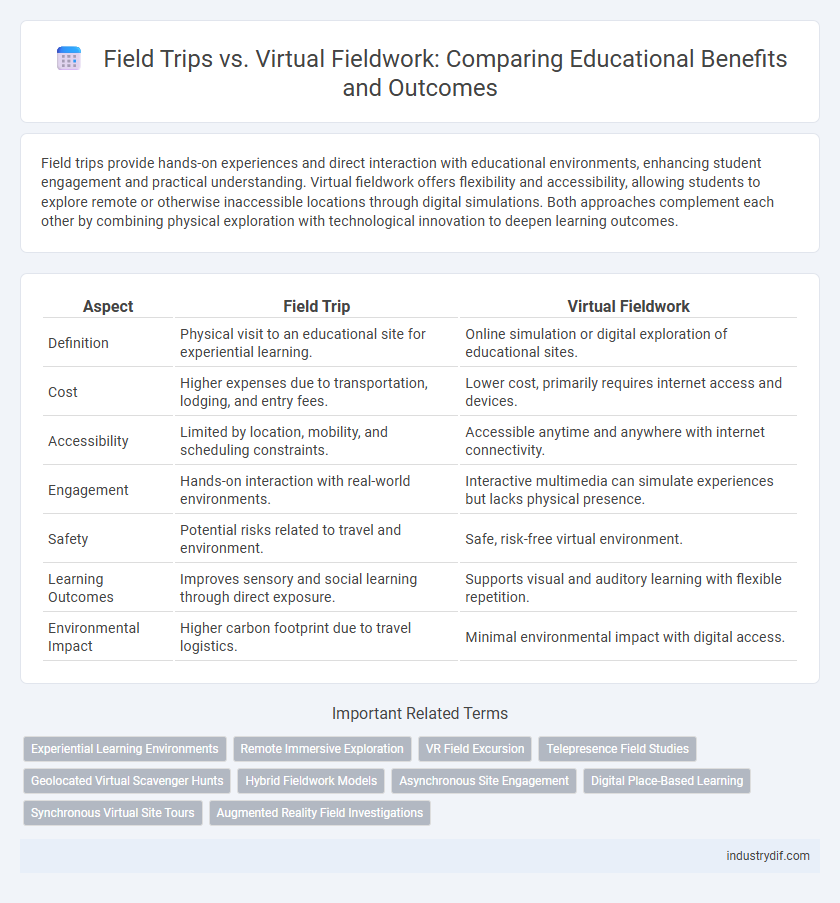
| Aspect | Field Trip | Virtual Fieldwork |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical visit to an educational site for experiential learning. | Online simulation or digital exploration of educational sites. |
| Cost | Higher expenses due to transportation, lodging, and entry fees. | Lower cost, primarily requires internet access and devices. |
| Accessibility | Limited by location, mobility, and scheduling constraints. | Accessible anytime and anywhere with internet connectivity. |
| Engagement | Hands-on interaction with real-world environments. | Interactive multimedia can simulate experiences but lacks physical presence. |
| Safety | Potential risks related to travel and environment. | Safe, risk-free virtual environment. |
| Learning Outcomes | Improves sensory and social learning through direct exposure. | Supports visual and auditory learning with flexible repetition. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint due to travel logistics. | Minimal environmental impact with digital access. |
Defining Field Trips and Virtual Fieldwork
Field trips involve physically visiting locations outside the classroom to provide experiential learning opportunities, allowing students to engage directly with real-world environments and cultural sites. Virtual fieldwork utilizes digital platforms and interactive technologies to simulate these experiences remotely, offering access to diverse environments without geographical or logistical constraints. Both methods enhance student understanding through immersive and contextualized education, though they differ in accessibility and sensory engagement.
Educational Objectives: Comparing Learning Outcomes
Field trips provide experiential learning through direct engagement with real-world environments, enhancing observational skills and contextual understanding. Virtual fieldwork offers interactive simulations that enable access to diverse locations and data sets, promoting analytical thinking and flexibility in learning. Studies show a blend of both methods optimizes retention and critical thinking by combining tactile experience with technology-driven exploration.
Student Engagement: Hands-On vs. Digital Interaction
Field trips provide immersive, hands-on experiences that enhance student engagement through physical interaction with the environment and real-world contexts. Virtual fieldwork leverages digital tools and multimedia resources to simulate these experiences, offering interactive and flexible learning opportunities that can reach diverse learners regardless of location. Both methods significantly impact student engagement, with field trips fostering tactile learning and virtual fieldwork promoting technological fluency and accessibility.
Cost and Resource Considerations
Virtual fieldwork reduces expenses by eliminating travel, accommodation, and meal costs usually associated with traditional field trips, making it a budget-friendly option for educational institutions. Field trips require significant resources including transportation, supervision, and logistical planning, often limiting accessibility for schools with constrained budgets. Investing in digital platforms and VR technology for virtual fieldwork offers scalable, reusable learning experiences while conserving both financial and human resources.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Field Experiences
Field trips provide hands-on experiences but often face physical, financial, and geographic barriers that limit accessibility for students with disabilities or from low-income backgrounds. Virtual fieldwork leverages technology to create inclusive environments, enabling participation regardless of mobility, location, or budget constraints. Enhanced accessibility through virtual platforms promotes equitable learning opportunities and broadens participation in diverse educational settings.
Technological Requirements for Virtual Fieldwork
Virtual fieldwork demands reliable high-speed internet, advanced mobile devices or computers, and specialized software such as virtual reality (VR) platforms or interactive mapping tools. These technological requirements ensure immersive and interactive experiences that closely replicate physical site visits. Proper technical support and user training are essential to maximize engagement and educational outcomes in virtual field environments.
Real-World Exposure vs. Simulated Environments
Field trips provide students with real-world exposure by engaging all their senses in authentic environments, enhancing experiential learning and retention. Virtual fieldwork simulates these settings through immersive technology, offering access to otherwise inaccessible locations and flexible scheduling without physical constraints. Both methods complement each other by balancing hands-on experience with advanced simulation for comprehensive educational outcomes.
Risk Management and Safety Protocols
Field trips require comprehensive risk assessments, including transportation safety, emergency response plans, and student supervision ratios to minimize physical hazards. Virtual fieldwork eliminates travel-related risks and allows controlled, safe access to environments through digital platforms, but demands strict cybersecurity protocols to protect student data. Both approaches necessitate clear safety guidelines, with field trips focusing on real-world contingencies and virtual fieldwork prioritizing technological security measures.
Curriculum Integration Strategies
Field trips and virtual fieldwork both offer unique curriculum integration strategies by connecting classroom concepts with real-world applications. Field trips provide hands-on, sensory-rich experiences that enhance kinesthetic learning and foster direct engagement with the environment, while virtual fieldwork leverages interactive digital tools and multimedia resources to facilitate accessibility and flexible scheduling. Combining these approaches supports diverse learning styles and allows educators to seamlessly align experiential activities with academic standards and learning objectives.
Evaluating the Long-Term Impact on Learners
Field trips provide immersive, hands-on experiences that enhance memory retention and foster social skills through direct interaction with environments and peers. Virtual fieldwork offers scalable access to diverse locations and adaptable learning modules, supporting personalized pacing and repeated engagement for deeper conceptual understanding. Long-term evaluations reveal that combining physical field trips with virtual experiences maximizes knowledge retention, motivation, and critical thinking development in learners.
Related Important Terms
Experiential Learning Environments
Field trips provide immersive, hands-on experiential learning through direct interaction with real-world environments, enhancing sensory engagement and social collaboration. Virtual fieldwork offers flexible, accessible simulations that replicate complex scenarios, enabling students to explore diverse settings and phenomena beyond geographical limitations.
Remote Immersive Exploration
Remote immersive exploration via virtual fieldwork leverages advanced technologies such as VR and 360-degree video to simulate real-world environments, enhancing student engagement and accessibility beyond geographical limitations. Field trips provide hands-on sensory experiences critical for kinesthetic learning, while virtual fieldwork offers scalable, cost-effective opportunities for interactive education in diverse and remote locations.
VR Field Excursion
VR field excursions offer immersive, interactive experiences that replicate real-world environments, enhancing student engagement and accessibility without the logistical challenges of traditional field trips. These virtual fieldwork solutions integrate advanced 3D simulations and real-time data, providing scalable educational opportunities in various subjects such as geography, biology, and history.
Telepresence Field Studies
Telepresence field studies utilize advanced communication technologies to conduct immersive, real-time exploration of remote locations, offering educators and students direct observation opportunities without physical travel. This method reduces costs and environmental impact while maintaining interactive engagement and data collection capabilities similar to traditional field trips.
Geolocated Virtual Scavenger Hunts
Geolocated virtual scavenger hunts enhance education by combining real-world geography with interactive digital experiences, offering immersive learning opportunities beyond traditional field trips. These virtual fieldwork activities enable students to explore diverse locations remotely while developing spatial awareness and critical thinking skills through targeted, location-based challenges.
Hybrid Fieldwork Models
Hybrid fieldwork models combine traditional field trips with virtual fieldwork techniques to enhance experiential learning by providing both hands-on interaction and remote access to diverse environments. This approach optimizes educational outcomes by leveraging augmented reality, live streaming, and interactive digital resources, enabling students to engage with real-world contexts regardless of geographical limitations.
Asynchronous Site Engagement
Asynchronous site engagement in virtual fieldwork allows students to explore educational content and interact with digital resources on their own schedule, enhancing accessibility and flexibility compared to traditional field trips. This method supports diverse learning paces and provides opportunities for repeated site visits without the logistical constraints of physical travel.
Digital Place-Based Learning
Digital place-based learning integrates virtual fieldwork with traditional field trips, leveraging augmented reality and geospatial technologies to enhance student engagement and contextual understanding. This hybrid approach supports experiential education by providing immersive, location-specific content that transcends physical and geographical limitations, promoting accessibility and interactive exploration in diverse learning environments.
Synchronous Virtual Site Tours
Synchronous virtual site tours provide real-time, interactive experiences that enhance student engagement by allowing immediate questions and live guidance from experts, closely replicating the immersive benefits of traditional field trips. This method leverages video conferencing technology to deliver accessible, cost-effective fieldwork opportunities that overcome geographical and logistical barriers inherent in physical site visits.
Augmented Reality Field Investigations
Augmented Reality Field Investigations enhance experiential learning by integrating virtual elements with real-world environments, offering immersive and interactive experiences that surpass traditional field trips in accessibility and engagement. This technology enables students to explore complex concepts and conduct investigations remotely, overcoming geographical and logistical limitations while maintaining high educational value.
Field Trip vs Virtual Fieldwork Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com