Degree programs offer comprehensive, in-depth education spanning several years, providing a broad foundation in a specific field with formal accreditation and recognized qualifications. Nanodegree programs focus on targeted, skill-specific training delivered in a shorter time frame, designed to quickly enhance employability and practical knowledge in emerging technologies. Choosing between the two depends on career goals, time commitment, and the need for formal credentials versus specialized skills.
Table of Comparison
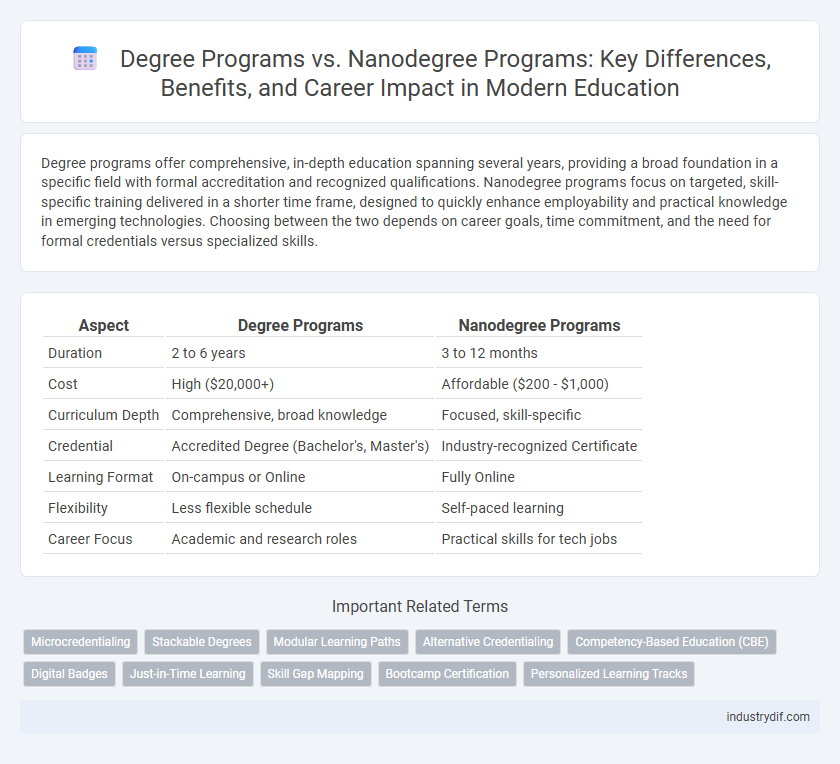
| Aspect | Degree Programs | Nanodegree Programs |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 2 to 6 years | 3 to 12 months |
| Cost | High ($20,000+) | Affordable ($200 - $1,000) |
| Curriculum Depth | Comprehensive, broad knowledge | Focused, skill-specific |
| Credential | Accredited Degree (Bachelor's, Master's) | Industry-recognized Certificate |
| Learning Format | On-campus or Online | Fully Online |
| Flexibility | Less flexible schedule | Self-paced learning |
| Career Focus | Academic and research roles | Practical skills for tech jobs |
Definition of Degree Programs
Degree programs are formal, comprehensive academic courses offered by universities and colleges, typically leading to a bachelor's, master's, or doctoral degree. These programs encompass a structured curriculum that includes general education, major-specific courses, and electives, spanning several years of full-time study. Designed to provide in-depth knowledge and critical thinking skills, degree programs often require completion of credit hours, internships, and a thesis or capstone project.
Overview of Nanodegree Programs
Nanodegree programs offer specialized, industry-relevant skills in a condensed format, often developed in partnership with leading technology companies. These programs focus on practical, project-based learning designed to enhance employability in fields like data science, programming, and artificial intelligence. Unlike traditional degree programs, Nanodegrees provide flexible schedules and real-world experience tailored for rapid career advancement.
Curriculum Structure Comparison
Degree programs typically offer a comprehensive curriculum spanning multiple disciplines, integrating theoretical foundations with practical applications over several years, ensuring a broad academic experience. Nanodegree programs focus on specialized skill sets through concise, project-based modules designed for rapid mastery and immediate industry relevance, often completed within months. The modular structure of nanodegrees allows flexible, targeted learning compared to the rigid, credit-based progression in traditional degree programs.
Duration and Flexibility
Degree programs typically span three to six years and follow a fixed academic calendar, requiring full-time commitment and structured coursework. Nanodegree programs offer significantly shorter durations, often ranging from a few weeks to six months, designed for flexibility with self-paced learning modules that accommodate working professionals. This contrast makes nanodegrees ideal for skill-specific, accelerated education, while degree programs provide comprehensive, in-depth academic training.
Accreditation and Recognition
Degree programs typically offer accreditation from regional or national educational authorities, ensuring widespread recognition and transferability of credits across institutions and employers. Nanodegree programs, often developed in partnership with industry leaders, provide specialized, career-focused skills but usually lack formal accreditation, limiting their academic recognition. Employers increasingly value nanodegree credentials for practical expertise, though traditional degree accreditation remains crucial for advanced education paths and professional licensing.
Cost and Financial Investment
Degree programs typically require a substantial financial investment, often ranging from $20,000 to over $100,000 depending on the institution and field of study, while nanodegree programs usually cost between $200 and $2,000, offering a more affordable alternative. Nanodegree programs focus on skill-specific training with shorter durations, reducing opportunity costs compared to traditional degrees that often take multiple years to complete. Students seeking cost-effective education with targeted outcomes often prefer nanodegrees due to lower tuition fees and minimal ancillary expenses such as housing and textbooks.
Career Outcomes and Employability
Degree programs often provide comprehensive theoretical knowledge and a broad educational foundation, enhancing long-term career prospects across various industries. Nanodegree programs emphasize practical, skill-based training tailored to specific job roles, resulting in faster employability and relevance in rapidly evolving tech fields. Employers increasingly value nanodegree credentials for demonstrating up-to-date competencies and project-based experience critical for immediate job performance.
Admission Requirements
Degree programs typically mandate high school diplomas, standardized test scores, and formal application processes, reflecting their rigorous admission standards. Nanodegree programs offer flexible entry criteria, often requiring only foundational skills or prior knowledge in a relevant subject, enabling quicker enrollment. This difference aligns with degree programs' emphasis on comprehensive education versus nanodegrees' targeted, skill-specific training.
Learning Experience and Methodology
Degree programs offer a comprehensive curriculum with a structured timeline, emphasizing theoretical foundations and broad academic knowledge, typically delivered through lectures, seminars, and exams. Nanodegree programs prioritize practical, project-based learning with real-world applications, often leveraging online platforms and mentorship for accelerated skill acquisition. The methodology of nanodegrees supports flexible, self-paced learning focused on industry-relevant competencies, contrasting with the formal assessment and institutional framework of traditional degrees.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Goals
Degree programs provide comprehensive education with recognized accreditation, ideal for careers requiring formal qualifications and in-depth study. Nanodegree programs offer targeted, flexible learning focused on specific skills and emerging technologies, perfect for rapid upskilling and project-based experience. Evaluating career objectives, time commitment, and industry demands ensures selecting the right educational path for maximizing professional growth.
Related Important Terms
Microcredentialing
Degree programs offer comprehensive, multi-year education culminating in accredited diplomas, while nanodegree programs provide targeted microcredentialing through shorter, skill-specific courses designed for rapid workforce entry. Microcredentials earned from nanodegree programs validate specialized competencies that enhance career mobility and are increasingly recognized by employers in sectors like technology and business.
Stackable Degrees
Stackable degrees offer a flexible and efficient pathway for learners by allowing the accumulation of credits from various nanodegree programs, ultimately leading to a full degree credential. These programs bridge the gap between traditional degree courses and specialized nanodegrees, enhancing skill acquisition and career advancement in a modular format.
Modular Learning Paths
Degree programs offer comprehensive, multi-year curricula designed to build foundational knowledge and advanced expertise across disciplines, often including general education and electives for broad academic development. Nanodegree programs emphasize modular learning paths tailored for specific skills or industries, enabling flexible, accelerated mastery of targeted competencies with practical, project-based assignments.
Alternative Credentialing
Degree programs offer comprehensive academic training with formal accreditation, while nanodegree programs provide focused, skill-specific education through alternative credentialing that enhances employability in rapidly evolving industries. Alternative credentialing bridges the gap between traditional education and workforce demands by delivering flexible, affordable, and industry-aligned learning pathways.
Competency-Based Education (CBE)
Degree programs typically offer comprehensive, semester-based curricula emphasizing theoretical knowledge, while nanodegree programs focus on competency-based education (CBE) through targeted, skills-driven modules designed for rapid mastery and real-world application. CBE structures in nanodegrees prioritize measurable outcomes and personalized pacing, enabling learners to acquire specific competencies aligned with industry demands more efficiently than traditional degree timelines.
Digital Badges
Degree programs often provide comprehensive education with formal accreditation and recognized degrees, while nanodegree programs focus on specific skills and digital badges that demonstrate targeted expertise in fields like technology and digital marketing. Digital badges serve as verifiable credentials that enhance a learner's portfolio by showcasing mastery of particular competencies in a concise, industry-recognized format.
Just-in-Time Learning
Degree programs offer comprehensive education with in-depth theoretical knowledge, while nanodegree programs prioritize just-in-time learning by providing targeted, skill-specific content that aligns with current industry demands. Nanodegree programs enable learners to quickly acquire practical skills and apply them immediately, enhancing career readiness and adaptability.
Skill Gap Mapping
Degree programs offer comprehensive theoretical knowledge and broad academic foundations, while nanodegree programs target specific skill gaps through focused, industry-relevant curricula designed for rapid upskilling. Skill gap mapping in education highlights that nanodegree programs address immediate workforce needs more effectively by aligning learning outcomes with current job market demands.
Bootcamp Certification
Bootcamp certification programs offer intensive, project-based learning experiences designed to quickly equip students with practical skills in fields like coding, data science, and UX design, making them ideal for career changers or skill upgraders. Unlike traditional degree programs that provide comprehensive theoretical knowledge over several years, bootcamp certifications emphasize hands-on application and immediate job readiness in high-demand tech industries.
Personalized Learning Tracks
Degree programs offer structured curricula with fixed timelines, providing comprehensive subject mastery and recognized academic credentials, while nanodegree programs emphasize personalized learning tracks tailored to individual skill levels and career goals, leveraging flexible, project-based coursework designed for rapid skill acquisition in specific fields. Personalized learning tracks within nanodegree programs optimize learner engagement through adaptive content, allowing for customized pacing and targeted knowledge, which supports continuous professional development in dynamic industries.
Degree Programs vs Nanodegree Programs Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com