Teacher-led instruction provides structured guidance and clear objectives, ensuring foundational knowledge is effectively delivered. Student-centered learning promotes active engagement and critical thinking, empowering learners to take ownership of their education. Balancing both approaches enhances comprehension and fosters motivation in diverse learning environments.
Table of Comparison
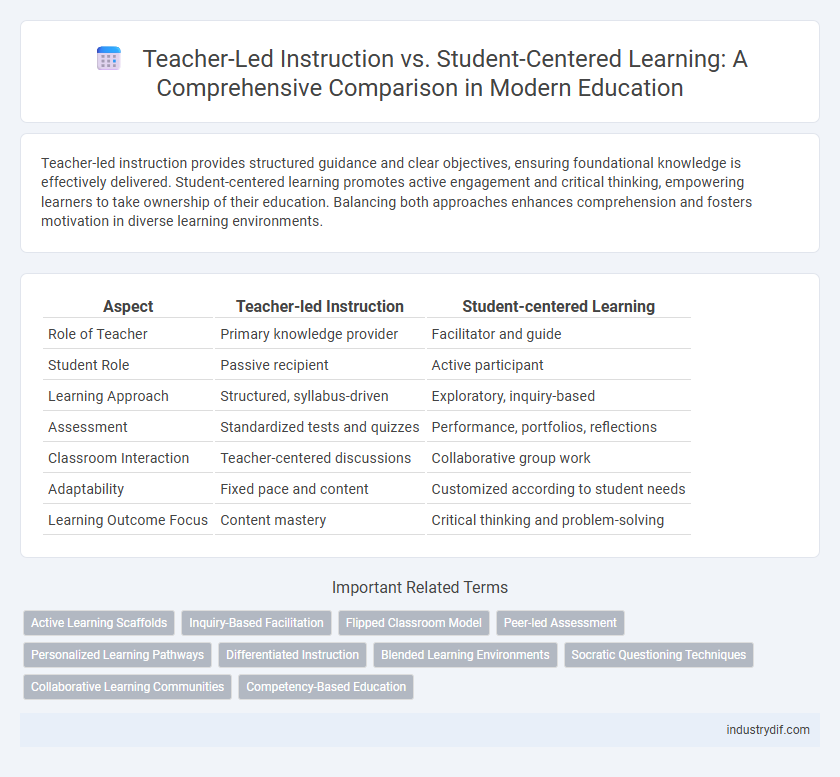
| Aspect | Teacher-led Instruction | Student-centered Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Role of Teacher | Primary knowledge provider | Facilitator and guide |
| Student Role | Passive recipient | Active participant |
| Learning Approach | Structured, syllabus-driven | Exploratory, inquiry-based |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and quizzes | Performance, portfolios, reflections |
| Classroom Interaction | Teacher-centered discussions | Collaborative group work |
| Adaptability | Fixed pace and content | Customized according to student needs |
| Learning Outcome Focus | Content mastery | Critical thinking and problem-solving |
Defining Teacher-led Instruction and Student-centered Learning
Teacher-led instruction is a structured educational approach where the teacher directs the learning process through lectures, demonstrations, and guided practice to ensure clear content delivery and mastery of specific academic standards. In contrast, student-centered learning emphasizes active student engagement, promoting autonomy, critical thinking, and collaboration by allowing learners to explore topics, ask questions, and apply knowledge in real-world contexts. Both approaches aim to enhance educational outcomes but differ fundamentally in the roles and responsibilities of teachers and students.
Historical Evolution of Educational Approaches
Teacher-led instruction originated in ancient civilizations with a focus on direct transmission of knowledge from instructor to student, emphasizing rote memorization and discipline. The 20th century witnessed a shift toward student-centered learning influenced by educational theorists like John Dewey and Jean Piaget, emphasizing active learning, critical thinking, and student engagement. Modern education blends these approaches, integrating technology and differentiated instruction to accommodate diverse learning styles and foster lifelong learning skills.
Key Principles of Teacher-led Instruction
Teacher-led instruction emphasizes structured guidance where educators deliver content through direct lectures and clear explanations, ensuring consistent curriculum coverage and mastery of fundamental concepts. This approach prioritizes teacher expertise and classroom management, fostering a controlled learning environment with measurable outcomes. Research indicates that teacher-led strategies are particularly effective in foundational subjects like mathematics and reading, where sequential knowledge acquisition is critical.
Core Elements of Student-centered Learning
Student-centered learning emphasizes active student engagement, personalized learning paths, and collaborative environments that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Core elements include student autonomy, formative assessment, and real-world relevance, promoting deeper understanding and intrinsic motivation. This approach contrasts with teacher-led instruction by shifting the focus from passive reception to active knowledge construction.
Benefits of Teacher-led Instruction in Classroom Settings
Teacher-led instruction ensures structured delivery of curriculum content, promoting consistent knowledge acquisition and clear learning objectives. It leverages the teacher's expertise to provide immediate feedback, maintain classroom discipline, and address diverse student needs effectively. This method enhances standardized test performance and supports learners who benefit from guided, direct instruction.
Advantages of Student-centered Learning Models
Student-centered learning models promote active engagement, critical thinking, and collaboration, enhancing knowledge retention and problem-solving skills. These approaches nurture autonomy, allowing students to tailor their education to individual interests and learning styles, which increases motivation and self-efficacy. Research shows that student-centered strategies significantly improve academic achievement and prepare learners for real-world challenges by fostering creativity and adaptability.
Challenges and Limitations of Teacher-led Methods
Teacher-led instruction often faces challenges such as limited student engagement and reduced opportunities for critical thinking development. This method can lead to passive learning, where students may struggle to retain information and apply concepts independently. The rigidity of teacher-led approaches also limits adaptability to diverse learning styles and hinders fostering creativity and collaboration among students.
Drawbacks and Obstacles in Student-centered Learning
Student-centered learning often faces challenges such as limited student motivation, uneven participation, and difficulty aligning with standardized curricula. Teachers may struggle to manage diverse learning paces and provide personalized feedback in large classrooms. Technology dependence and lack of adequate training further hinder the effective implementation of student-centered instructional methods.
Integrating Teacher-led and Student-centered Strategies
Integrating teacher-led instruction with student-centered learning creates a balanced educational environment that leverages the strengths of both approaches. Structured guidance from teachers ensures foundational knowledge while student-centered strategies promote critical thinking, collaboration, and active engagement. This hybrid method enhances learning outcomes by adapting to diverse student needs and fostering deeper comprehension through interactive and personalized experiences.
Future Trends in Instructional Practices
Future trends in instructional practices emphasize a blend of teacher-led instruction with student-centered learning to create adaptive and personalized educational experiences. Integrating advanced technologies like AI and data analytics enhances real-time feedback and individualized support, promoting active learning and critical thinking skills. Education systems increasingly prioritize collaborative environments that empower students while guiding them with structured expertise from educators.
Related Important Terms
Active Learning Scaffolds
Active learning scaffolds in teacher-led instruction provide structured guidance that enhances student engagement and comprehension, facilitating incremental skill development through targeted prompts and feedback. In student-centered learning, scaffolds adapt to individual learner needs by promoting autonomy and critical thinking, enabling students to construct knowledge actively while receiving timely support to overcome challenges.
Inquiry-Based Facilitation
Inquiry-based facilitation in education empowers students to actively explore and engage with content, promoting critical thinking and deeper understanding compared to traditional teacher-led instruction. This approach shifts the educator's role from information delivery to guiding inquiry, fostering autonomy and collaboration among learners.
Flipped Classroom Model
The flipped classroom model shifts traditional teacher-led instruction by delivering content outside of class and using in-person time for interactive, student-centered activities that enhance critical thinking and collaboration. This approach leverages video lectures and digital resources to empower students to learn at their own pace while maximizing teacher support during hands-on problem solving and discussions.
Peer-led Assessment
Peer-led assessment in student-centered learning fosters collaborative evaluation, enhancing critical thinking and communication skills among students, while teacher-led instruction typically relies on authoritative feedback that may limit peer interaction. Integrating peer-led assessment encourages active engagement and accountability, promoting deeper understanding and knowledge retention compared to traditional teacher-led evaluation methods.
Personalized Learning Pathways
Teacher-led instruction provides structured guidance and clear objectives, ensuring curriculum standards are met efficiently; student-centered learning fosters personalized learning pathways by encouraging autonomy, critical thinking, and adaptability in mastering content. Integrating both approaches maximizes engagement and academic achievement through tailored support that addresses diverse student needs and learning styles.
Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated instruction enhances student-centered learning by tailoring teaching methods and materials to diverse student needs, interests, and abilities rather than a one-size-fits-all teacher-led approach. This strategy improves engagement and academic outcomes by allowing students to actively participate in their learning process through personalized activities and assessments.
Blended Learning Environments
Teacher-led instruction provides structured guidance and clear objectives, ensuring foundational knowledge acquisition, while student-centered learning fosters critical thinking and autonomy. In blended learning environments, integrating these approaches enhances engagement and personalized learning through a combination of direct teaching and interactive, technology-driven activities.
Socratic Questioning Techniques
Socratic questioning techniques enhance both teacher-led instruction and student-centered learning by promoting critical thinking and deeper comprehension through guided inquiry. This method encourages educators to ask purposeful, open-ended questions that challenge students to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information, thereby fostering active engagement and reflective learning.
Collaborative Learning Communities
Teacher-led instruction provides structured guidance and clear learning objectives, fostering foundational knowledge acquisition. Student-centered learning emphasizes collaborative learning communities where peer interaction and shared problem-solving enhance critical thinking and deeper understanding.
Competency-Based Education
Competency-Based Education emphasizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge, making student-centered learning more effective by allowing learners to progress at their own pace and apply concepts in real-world contexts. Teacher-led instruction remains vital for providing foundational guidance and structured assessments to ensure competencies are accurately measured and achieved.
Teacher-led Instruction vs Student-centered Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com