E-learning offers flexible access to educational content, allowing learners to study at their own pace using digital platforms. Immersive learning enhances engagement by utilizing virtual reality, simulations, and interactive environments that mimic real-world scenarios. This combination of accessibility and experiential learning results in improved knowledge retention and skill development.
Table of Comparison
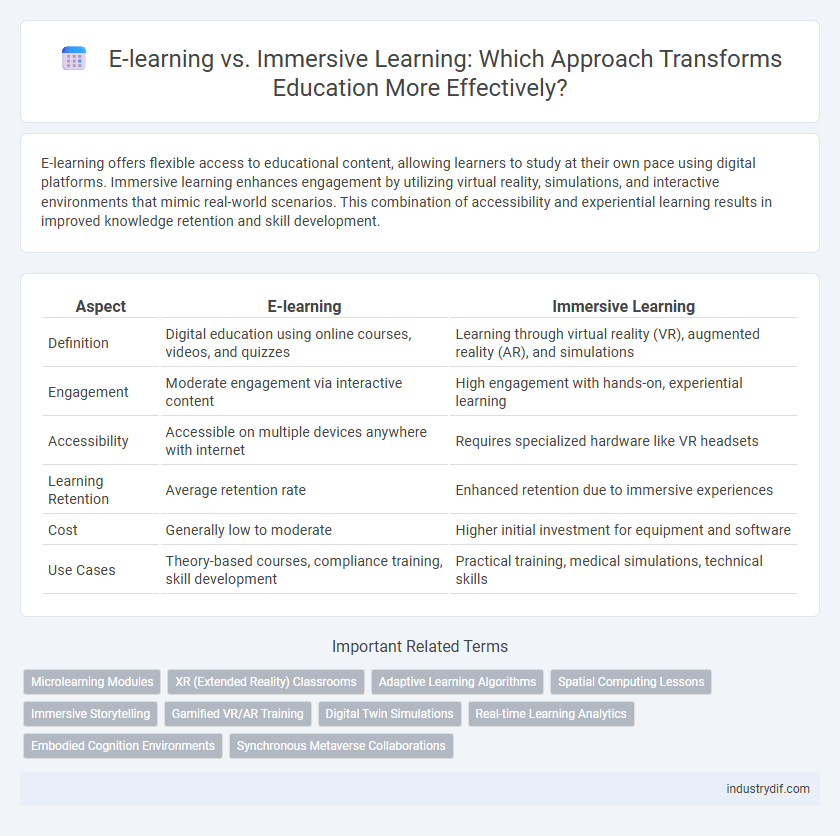
| Aspect | E-learning | Immersive Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital education using online courses, videos, and quizzes | Learning through virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and simulations |
| Engagement | Moderate engagement via interactive content | High engagement with hands-on, experiential learning |
| Accessibility | Accessible on multiple devices anywhere with internet | Requires specialized hardware like VR headsets |
| Learning Retention | Average retention rate | Enhanced retention due to immersive experiences |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate | Higher initial investment for equipment and software |
| Use Cases | Theory-based courses, compliance training, skill development | Practical training, medical simulations, technical skills |
Defining E-learning and Immersive Learning
E-learning refers to the use of electronic technologies and digital platforms to deliver educational content remotely, enabling flexible access to courses and resources. Immersive learning involves interactive simulations and virtual or augmented reality environments that engage learners through experiential and hands-on activities. Both methods enhance education by leveraging technology, but immersive learning emphasizes deeper engagement and realistic practice scenarios.
Key Technologies Powering Each Approach
E-learning relies heavily on Learning Management Systems (LMS), video conferencing tools, and interactive multimedia content to deliver flexible, accessible education remotely. Immersive learning leverages advanced technologies such as Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and 3D simulations to create engaging, hands-on experiences that enhance skill acquisition and retention. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analytics play a pivotal role in both approaches by personalizing learning pathways and tracking learner progress for optimized outcomes.
Content Delivery Methods Compared
E-learning primarily utilizes digital platforms such as videos, quizzes, and interactive modules to deliver content, allowing for self-paced learning and wider accessibility. Immersive learning employs virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and simulations to create experiential environments that enhance engagement and retention through active participation. The combination of multimedia content in e-learning contrasts with the sensorimotor and spatial interactions unique to immersive learning, influencing how learners process and apply information.
Student Engagement and Interaction Levels
E-learning platforms provide flexible access to educational content but often face challenges in maintaining high student engagement and interaction levels. Immersive learning environments, such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), significantly enhance student participation by creating interactive, experiential experiences that foster active learning. Research indicates that immersive learning can increase retention rates by up to 75% compared to traditional e-learning methods due to its multisensory, hands-on approach.
Accessibility and Scalability in Education
E-learning platforms enhance accessibility by enabling students worldwide to access diverse educational content anytime with internet connectivity, breaking down geographical barriers. Immersive learning, using VR and AR technologies, offers scalable, engaging experiences but often faces challenges in widespread adoption due to hardware costs and technical requirements. Both methods expand educational reach; however, e-learning currently provides more scalable solutions, while immersive learning excels in delivering interactive, experiential education where infrastructure permits.
Measuring Learning Outcomes
Measuring learning outcomes in e-learning relies heavily on data analytics, quizzes, and standardized assessments to track knowledge retention and skill acquisition. Immersive learning leverages virtual reality and simulations to provide real-time feedback, enabling deeper engagement and practical application that can be quantitatively measured through performance metrics. Both methods offer valuable insights, but immersive learning often yields higher retention rates and improved critical thinking skills due to its experiential nature.
Cost Implications for Institutions and Learners
E-learning reduces costs for institutions by eliminating physical infrastructure expenses and enabling scalable course delivery, while learners save money on commuting and accommodation. Immersive learning, using VR and AR technologies, requires significant investment in hardware and software maintenance, leading to higher initial costs but potentially greater engagement and retention. Institutions must balance budget constraints against the long-term benefits of immersive experiences, whereas learners may face higher access costs despite richer learning environments.
Integration with Traditional Classrooms
E-learning platforms offer flexible access to digital content and assessments, enabling seamless integration with traditional classrooms through blended teaching models. Immersive learning technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) enhance experiential learning by simulating real-world scenarios, which can be embedded into curricula to increase student engagement and retention. Combining e-learning's scalability with immersive learning's interactivity creates a comprehensive educational environment that supports diverse learning styles and improves academic outcomes.
Future Trends in Digital Education
E-learning platforms are increasingly integrating artificial intelligence and adaptive learning technologies to personalize educational content, enhancing learner engagement and retention. Immersive learning, utilizing virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), offers experiential environments that improve skill acquisition and critical thinking through hands-on simulations. Future trends in digital education point towards hybrid models combining AI-driven e-learning and immersive technologies to create comprehensive, interactive, and scalable learning experiences.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
E-learning offers flexible access to diverse course materials through online platforms, making it ideal for self-paced learners seeking convenience and broad subject variety. Immersive learning leverages virtual reality and simulations to provide experiential, hands-on training that enhances retention and engagement, particularly for skill-based or complex topics. Selecting the right solution depends on your learning goals, available technology, and preference for interaction depth versus accessibility.
Related Important Terms
Microlearning Modules
Microlearning modules in e-learning provide concise, focused content ideal for quick skill acquisition, while immersive learning enhances engagement through interactive simulations and virtual environments. Combining microlearning's efficiency with immersive technology maximizes retention and practical application in educational settings.
XR (Extended Reality) Classrooms
XR (Extended Reality) classrooms leverage augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) to create immersive learning experiences that enhance student engagement and knowledge retention compared to traditional e-learning platforms. These XR environments provide interactive simulations and 3D visualizations, enabling personalized and experiential education that bridges theoretical concepts with real-world application.
Adaptive Learning Algorithms
Adaptive learning algorithms enhance e-learning platforms by personalizing content delivery based on individual learner performance and preferences, optimizing engagement and knowledge retention. In immersive learning environments, these algorithms dynamically adjust virtual scenarios in real-time, creating tailored experiences that significantly improve skill acquisition and cognitive development.
Spatial Computing Lessons
Spatial computing lessons in immersive learning environments leverage 3D simulations and augmented reality to enhance student engagement and retention, surpassing traditional e-learning modules that primarily rely on 2D content delivery. These technologies enable interactive, hands-on experiences that improve spatial awareness and practical application of complex concepts in fields such as engineering, medicine, and architecture.
Immersive Storytelling
Immersive storytelling in education leverages virtual reality, augmented reality, and interactive simulations to create engaging, memorable learning experiences that enhance comprehension and retention more effectively than traditional e-learning methods. This approach facilitates active participation, emotional connection, and contextual understanding, fostering deeper cognitive processing and skill acquisition in diverse subjects.
Gamified VR/AR Training
Gamified VR/AR training in immersive learning significantly enhances student engagement and knowledge retention by providing interactive, realistic simulations that adapt to individual learning paces. Compared to traditional e-learning, these technologies deliver multisensory experiences that improve spatial understanding and practical skills application across various educational fields.
Digital Twin Simulations
Digital Twin Simulations enhance e-learning by creating interactive, real-time virtual replicas of physical environments that allow students to practice complex skills with immediate feedback, increasing engagement and retention. Immersive learning through these simulations bridges theory and practice by enabling deeper understanding of subject matter, especially in fields like engineering, healthcare, and aviation.
Real-time Learning Analytics
Real-time learning analytics in e-learning platforms enable instant tracking of student performance, providing educators with data-driven insights to personalize instruction and improve outcomes. Immersive learning environments leverage these analytics to adapt scenarios dynamically, enhancing engagement and retention through interactive feedback loops.
Embodied Cognition Environments
Embodied cognition environments in immersive learning leverage sensorimotor experiences to enhance knowledge retention and cognitive processing more effectively than traditional e-learning platforms. These environments integrate physical interaction with digital content, fostering deep understanding through active participation and multi-sensory engagement.
Synchronous Metaverse Collaborations
Synchronous metaverse collaborations in immersive learning environments enhance real-time interaction and engagement, offering richer sensory experiences compared to traditional e-learning platforms. These virtual spaces enable students and educators to co-create, problem-solve, and participate in simulations, significantly improving knowledge retention and practical skills development.
E-learning vs Immersive Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com