Multiple choice exams efficiently measure students' recall and basic understanding, allowing for quick grading and objective evaluation. Project-based assessments provide deeper insights into critical thinking, creativity, and real-world application of knowledge, fostering a more comprehensive learning experience. Combining both methods can balance standardized testing with skill development, enhancing overall educational outcomes.
Table of Comparison
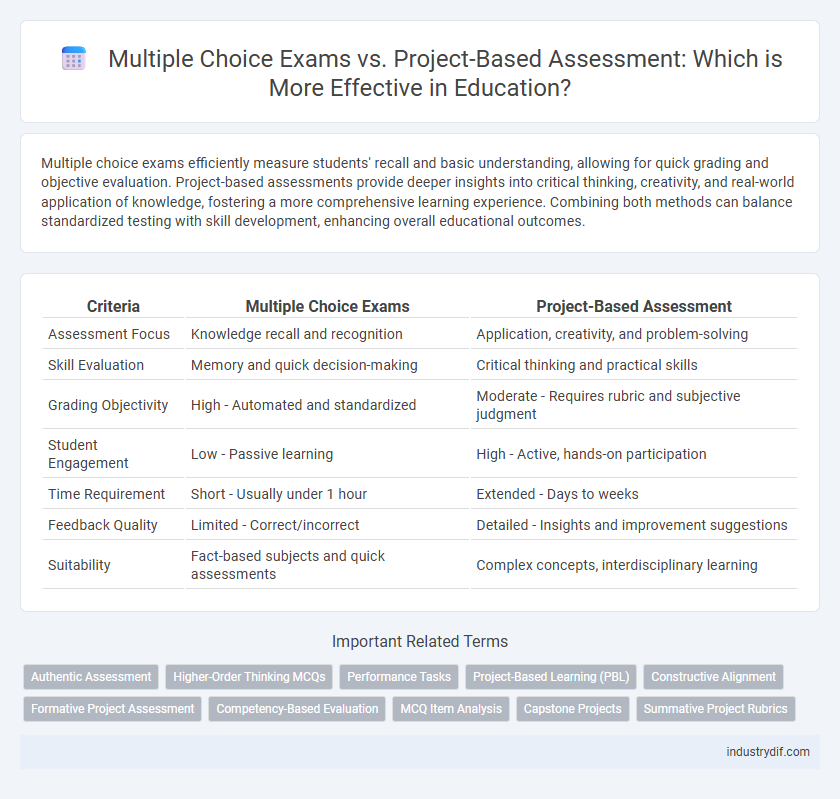
| Criteria | Multiple Choice Exams | Project-Based Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Assessment Focus | Knowledge recall and recognition | Application, creativity, and problem-solving |
| Skill Evaluation | Memory and quick decision-making | Critical thinking and practical skills |
| Grading Objectivity | High - Automated and standardized | Moderate - Requires rubric and subjective judgment |
| Student Engagement | Low - Passive learning | High - Active, hands-on participation |
| Time Requirement | Short - Usually under 1 hour | Extended - Days to weeks |
| Feedback Quality | Limited - Correct/incorrect | Detailed - Insights and improvement suggestions |
| Suitability | Fact-based subjects and quick assessments | Complex concepts, interdisciplinary learning |
Understanding Multiple Choice Exams in Education
Multiple choice exams assess students' ability to recall and recognize factual information quickly, providing a standardized method for evaluating large groups efficiently. These exams primarily measure surface-level understanding and tend to focus on breadth rather than depth of knowledge. Despite criticisms, multiple choice assessments remain valuable for gauging foundational concepts and enabling objective, quantifiable scoring in education.
Project-Based Assessment: An Overview
Project-based assessment emphasizes real-world application of knowledge by requiring students to complete complex tasks or projects that demonstrate critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills. This approach promotes deeper learning and retention as students engage actively with the material, often collaborating in teams and applying interdisciplinary concepts. Research shows project-based learning leads to improved critical thinking and higher-order cognitive skills compared to traditional multiple-choice exams.
Key Differences Between Multiple Choice and Project-Based Methods
Multiple choice exams emphasize quick recall and objective measurement of students' knowledge through predefined answers, enabling efficient grading and standardized comparison. Project-based assessments assess critical thinking, creativity, and practical application by requiring students to solve real-world problems or create tangible outputs over extended periods. The key difference lies in the evaluation scope: multiple choice tests gauge discrete information retention, while project-based methods evaluate deeper understanding and skills integration.
Measuring Student Learning Outcomes
Multiple choice exams offer a standardized method to efficiently evaluate students' factual knowledge and recall abilities across large groups, providing quantifiable data on learning outcomes. Project-based assessments assess higher-order thinking, creativity, and practical application skills by requiring students to integrate and demonstrate knowledge in real-world contexts. Comparing these methods reveals that multiple choice exams emphasize breadth and speed, while project-based assessments prioritize depth and critical thinking competencies.
Skill Development: Critical Thinking vs. Recall
Multiple choice exams primarily assess recall and recognition skills by requiring students to select correct answers from given options, limiting the depth of critical thinking. Project-based assessments foster higher-order cognitive abilities, encouraging students to engage in problem-solving, analysis, and application of knowledge in real-world contexts. This method promotes the development of transferable skills such as creativity, collaboration, and critical thinking beyond rote memorization.
Assessment Validity and Reliability
Multiple choice exams offer high reliability by providing standardized scoring and clear right or wrong answers but often lack validity in assessing higher-order thinking and real-world problem-solving skills. Project-based assessments enhance validity by evaluating students' ability to apply knowledge in practical contexts, demonstrating deeper understanding and creativity, though they can suffer from lower reliability due to subjective grading and inconsistent criteria. Balancing both methods can improve overall assessment effectiveness by combining the objective reliability of multiple choice with the authentic validity of project-based evaluation.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Multiple choice exams offer quick evaluation of knowledge but often reduce student engagement by emphasizing memorization over critical thinking. Project-based assessments increase motivation by encouraging creativity, collaboration, and real-world application of skills, leading to deeper learning experiences. Research shows students demonstrate higher retention rates and intrinsic motivation when assessed through hands-on projects compared to traditional testing formats.
Scalability and Resource Considerations
Multiple choice exams offer significant scalability advantages by enabling automated grading and standardized evaluation across large student populations, reducing the demands on instructional resources. Project-based assessments require substantial time investment from educators for individualized feedback and assessment, posing challenges in scalability for large classes. Resource considerations such as technological infrastructure and instructor availability critically impact the feasibility of implementing project-based assessments at scale compared to multiple choice exams.
Feedback and Improvement Opportunities
Multiple choice exams provide immediate, standardized feedback but often limit nuanced understanding of student learning, whereas project-based assessments offer detailed, qualitative feedback that fosters deeper reflection and skill development. Project-based assessments create continuous improvement opportunities by encouraging iterative revisions and real-world application, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Effective educational strategies integrate both methods to balance swift feedback with comprehensive growth-focused evaluation.
Selecting the Right Assessment for Learning Goals
Selecting the right assessment method depends on clearly defined learning goals, where multiple choice exams efficiently measure factual recall and comprehension, while project-based assessments evaluate higher-order thinking, creativity, and practical application. Aligning assessment types with specific learning outcomes ensures accurate measurement of student understanding and skill development. Educational strategies that incorporate both methods can provide a balanced evaluation, addressing diverse competencies and promoting comprehensive learning achievement.
Related Important Terms
Authentic Assessment
Project-based assessments provide authentic evaluation by engaging students in real-world problem solving and critical thinking, contrasting with multiple choice exams that primarily measure rote memorization and recognition skills. This approach fosters deeper understanding and application of knowledge, aligning assessment with practical competencies required in academic and professional settings.
Higher-Order Thinking MCQs
Higher-order thinking multiple-choice questions (MCQs) in higher education challenge students to analyze, evaluate, and apply knowledge rather than memorize facts, fostering critical thinking skills essential for complex problem-solving. Compared to project-based assessments, these MCQs offer efficient, scalable evaluation while still promoting cognitive processes aligned with Bloom's Taxonomy, such as synthesis and evaluation.
Performance Tasks
Performance tasks in project-based assessment foster critical thinking, problem-solving, and real-world application of knowledge, providing a deeper understanding than multiple choice exams. These tasks evaluate students' abilities to analyze, synthesize, and create, aligning closely with educational standards and 21st-century skills.
Project-Based Learning (PBL)
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills by engaging students in hands-on, interdisciplinary projects that reflect authentic challenges. Unlike multiple choice exams, PBL fosters deeper understanding and retention through active exploration and continuous feedback, aligning assessment with practical application and creativity.
Constructive Alignment
Multiple choice exams primarily assess students' recall and recognition skills, often misaligning with higher-order learning objectives outlined in constructive alignment frameworks. In contrast, project-based assessments foster deep understanding and application of knowledge by directly aligning learning activities and evaluation criteria with intended educational outcomes.
Formative Project Assessment
Formative project assessment in education provides continuous feedback, enabling students to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills through real-world applications. Unlike multiple choice exams, this assessment method fosters deeper understanding and long-term retention by emphasizing creativity and iterative learning processes.
Competency-Based Evaluation
Competency-based evaluation emphasizes assessing students' practical skills and critical thinking through project-based assessments, which provide a comprehensive understanding of their abilities beyond the factual recall measured by multiple choice exams. Project-based assessments foster deeper learning and real-world application, aligning with competency frameworks that prioritize mastery and problem-solving over rote memorization.
MCQ Item Analysis
MCQ item analysis provides a detailed evaluation of question validity, difficulty index, and discrimination index, helping educators identify poorly performing questions and enhance assessment quality. This statistical approach ensures multiple choice exams accurately measure student knowledge and support data-driven improvements in educational assessment.
Capstone Projects
Capstone projects enhance critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills by requiring students to integrate knowledge across multiple disciplines, unlike multiple choice exams that primarily test memorization and recall. Project-based assessments foster deeper engagement and practical application, making them effective evaluative tools in education compared to traditional standardized testing methods.
Summative Project Rubrics
Summative project rubrics provide clear criteria for evaluating student performance, emphasizing critical thinking, creativity, and application of knowledge over mere recall common in multiple choice exams. These rubrics enhance assessment reliability by standardizing expectations and offering detailed feedback, which better measures complex learning outcomes in educational settings.
Multiple Choice Exams vs Project-Based Assessment Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com