Conventional electricity meters provide basic consumption data, requiring manual readings for billing purposes, which can lead to delays and inaccuracies. Smart meters offer real-time energy usage monitoring, enabling automated data collection and more precise billing while empowering consumers to manage their electricity consumption effectively. The integration of smart meters supports advanced grid management and promotes energy efficiency across residential and commercial sectors.
Table of Comparison
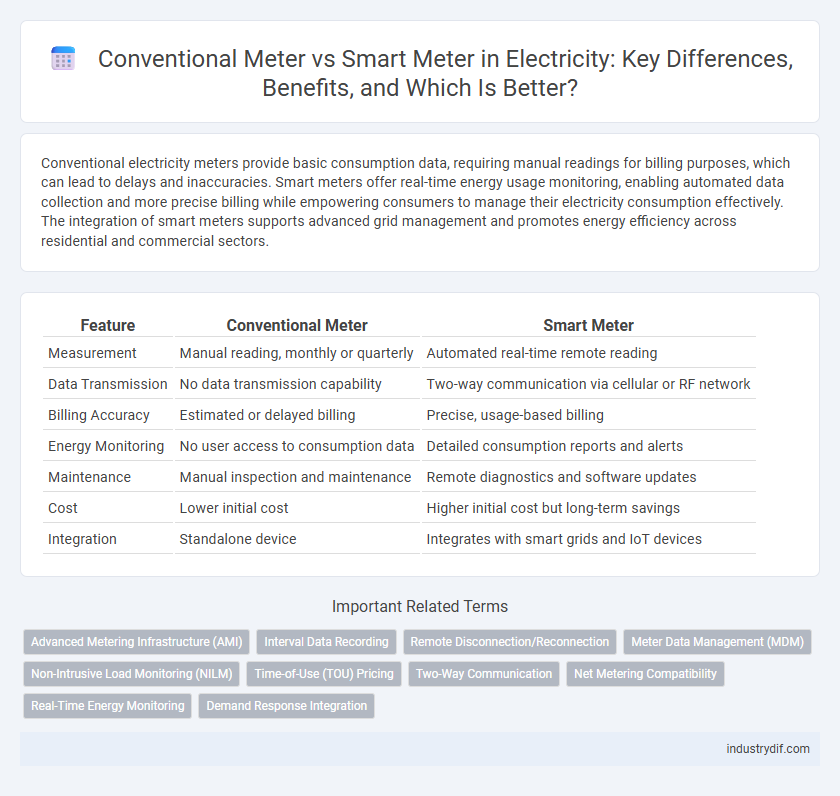
| Feature | Conventional Meter | Smart Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement | Manual reading, monthly or quarterly | Automated real-time remote reading |
| Data Transmission | No data transmission capability | Two-way communication via cellular or RF network |
| Billing Accuracy | Estimated or delayed billing | Precise, usage-based billing |
| Energy Monitoring | No user access to consumption data | Detailed consumption reports and alerts |
| Maintenance | Manual inspection and maintenance | Remote diagnostics and software updates |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but long-term savings |
| Integration | Standalone device | Integrates with smart grids and IoT devices |
Introduction to Electricity Meters
Electricity meters measure energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh) to enable accurate billing and usage tracking. Conventional meters use mechanical or electromechanical components to record energy usage, requiring manual reading, while smart meters utilize digital technology to provide real-time data transmission and remote monitoring. Smart meters support advanced features like time-of-use pricing, demand response, and integration with smart grids, enhancing energy management and efficiency.
What is a Conventional Meter?
A conventional meter, also known as an analog or electromechanical meter, measures electricity consumption using a rotating disk and dials to display kilowatt-hours (kWh). It requires manual reading by utility personnel, leading to less frequent data collection and potential for human error. Conventional meters lack remote communication capabilities, limiting real-time monitoring and automated billing.
What is a Smart Meter?
A smart meter is an advanced digital device that records electricity consumption in real-time, enabling two-way communication between the meter and the utility provider. It provides detailed usage data, helps detect outages quickly, and supports dynamic pricing models to encourage energy efficiency. Unlike conventional meters, smart meters eliminate manual readings and offer improved accuracy and convenience for both consumers and energy suppliers.
Key Differences Between Conventional and Smart Meters
Conventional meters record electricity consumption manually through mechanical or electromechanical means, requiring physical readings by utility personnel, whereas smart meters use digital technology to automatically transmit real-time data to utility companies. Smart meters enable accurate billing, remote monitoring, and detailed usage insights, supporting demand response and energy management systems. Conventional meters lack these communication capabilities, resulting in delayed consumption data and less efficient energy management.
Installation Process: Conventional vs Smart Meters
Conventional electricity meters require manual installation by a technician who physically connects the device to the electrical panel, typically involving more time and potential disruptions. Smart meters feature a streamlined installation process with wireless connectivity and automated configuration, allowing for quicker setup and remote activation. The smart meter's plug-and-play capabilities reduce labor costs and enhance efficiency compared to conventional meter installations.
Accuracy and Reliability of Meter Readings
Smart meters offer superior accuracy and reliability in electricity consumption readings compared to conventional meters due to their advanced digital sensors and real-time data transmission capabilities. Conventional meters often rely on manual readings, which can lead to human error and delayed data reporting, whereas smart meters minimize these risks through automated, continuous monitoring. The enhanced precision of smart meters supports more accurate billing and energy management, reducing disputes and improving overall grid efficiency.
Data Communication and Real-Time Monitoring
Conventional meters rely on manual readings and lack data communication capabilities, limiting real-time monitoring of electricity consumption. Smart meters utilize advanced communication technologies such as RF mesh networks or cellular connectivity to transmit consumption data continuously to utility providers. This real-time data transmission enables dynamic load management, instant outage detection, and enhanced consumer energy usage insights.
Impact on Energy Consumption and Billing
Smart meters enable real-time energy consumption tracking, promoting greater efficiency and reduced electricity usage compared to conventional meters, which only record cumulative consumption. The enhanced data accuracy from smart meters supports dynamic pricing models and timely billing, reducing errors and disputes common in conventional meter readings. As a result, consumers benefit from more transparent billing and opportunities for energy savings, while utilities improve demand management and operational costs.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Conventional electricity meters offer limited data collection, reducing risks related to data privacy but lack advanced security measures against tampering. Smart meters collect detailed consumption data in real-time, increasing risks of unauthorized data access and potential misuse, necessitating robust encryption and cybersecurity protocols. Privacy concerns also arise from the granularity of data, which can reveal user behavior patterns, requiring strict regulatory frameworks and user consent mechanisms to safeguard consumer information.
Future Trends in Electricity Metering Technology
Smart meters are revolutionizing electricity metering technology with real-time data monitoring, remote meter reading, and enhanced grid management capabilities, enabling utilities to optimize energy distribution and reduce outages. Conventional meters lack these digital features and rely on manual reading, which limits responsiveness and accuracy. Emerging trends also include integration with IoT devices, advanced analytics for predictive maintenance, and dynamic pricing models that promote energy efficiency and renewable energy adoption.
Related Important Terms
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
Conventional meters provide basic electricity consumption readings requiring manual collection, whereas smart meters utilize Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) to enable real-time data transmission, remote monitoring, and two-way communication between utilities and consumers. AMI enhances grid reliability, supports demand response programs, and facilitates accurate billing through continuous data analytics and automated meter reading.
Interval Data Recording
Conventional meters record cumulative electricity usage without detailed time intervals, limiting real-time energy consumption insights. Smart meters capture interval data recording at regular increments, enabling precise monitoring, demand response, and improved grid management.
Remote Disconnection/Reconnection
Conventional electricity meters require manual intervention for disconnection and reconnection, resulting in time-consuming and labor-intensive processes. Smart meters enable remote disconnection and reconnection through real-time communication with utility providers, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing service disruption times.
Meter Data Management (MDM)
Smart meters enhance Meter Data Management (MDM) by providing real-time, granular consumption data, enabling utilities to optimize billing accuracy and demand forecasting. Conventional meters rely on manual readings, leading to delayed data collection, which limits the effectiveness of MDM systems in energy management and outage detection.
Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM)
Conventional electricity meters provide total energy consumption data without distinguishing between individual appliances, limiting detailed usage analysis. Smart meters equipped with Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM) technology enable real-time appliance-level monitoring by analyzing energy consumption patterns, enhancing energy efficiency and demand response capabilities.
Time-of-Use (TOU) Pricing
Conventional meters record total electricity consumption without detailing usage patterns, whereas smart meters enable Time-of-Use (TOU) pricing by providing real-time data on electricity use during peak and off-peak hours. This granular data allows utilities to charge different rates based on demand periods, encouraging consumers to shift consumption to lower-cost times and optimize energy efficiency.
Two-Way Communication
Conventional electricity meters record energy consumption with mechanical or simple digital displays, lacking the ability to communicate usage data remotely, whereas smart meters utilize advanced two-way communication technology to send real-time consumption information to utilities and receive updates or commands. This two-way communication enables dynamic energy management, faster outage detection, and more accurate billing, enhancing grid efficiency and customer engagement.
Net Metering Compatibility
Smart meters offer enhanced net metering compatibility by accurately recording electricity consumption and generation in real-time, enabling seamless integration of renewable energy sources like solar panels into the grid. Conventional meters, on the other hand, are limited to measuring total energy usage without distinguishing between energy exported and consumed, making them less efficient for net metering applications.
Real-Time Energy Monitoring
Conventional meters provide only cumulative energy usage data, requiring manual readings and lacking real-time insights, while smart meters enable real-time energy monitoring by transmitting instantaneous consumption data to both consumers and utility providers. This real-time visibility facilitates dynamic load management, demand response, and enhances energy efficiency through immediate feedback and remote access capabilities.
Demand Response Integration
Conventional electricity meters record consumption data manually or at fixed intervals, limiting real-time demand response integration and reducing grid efficiency. Smart meters enable automated, real-time monitoring and two-way communication between consumers and utilities, facilitating dynamic demand response programs that optimize energy usage and grid stability.
Conventional meter vs Smart meter Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com