Peak demand represents the highest level of electricity consumption during a specific period, often straining the power grid and increasing operational costs. Demand response programs help manage peak demand by incentivizing consumers to reduce or shift their electricity usage during critical periods, enhancing grid reliability and reducing the need for costly infrastructure investments. Effective demand response strategies optimize energy consumption patterns, lower electricity bills, and promote sustainable energy use.
Table of Comparison
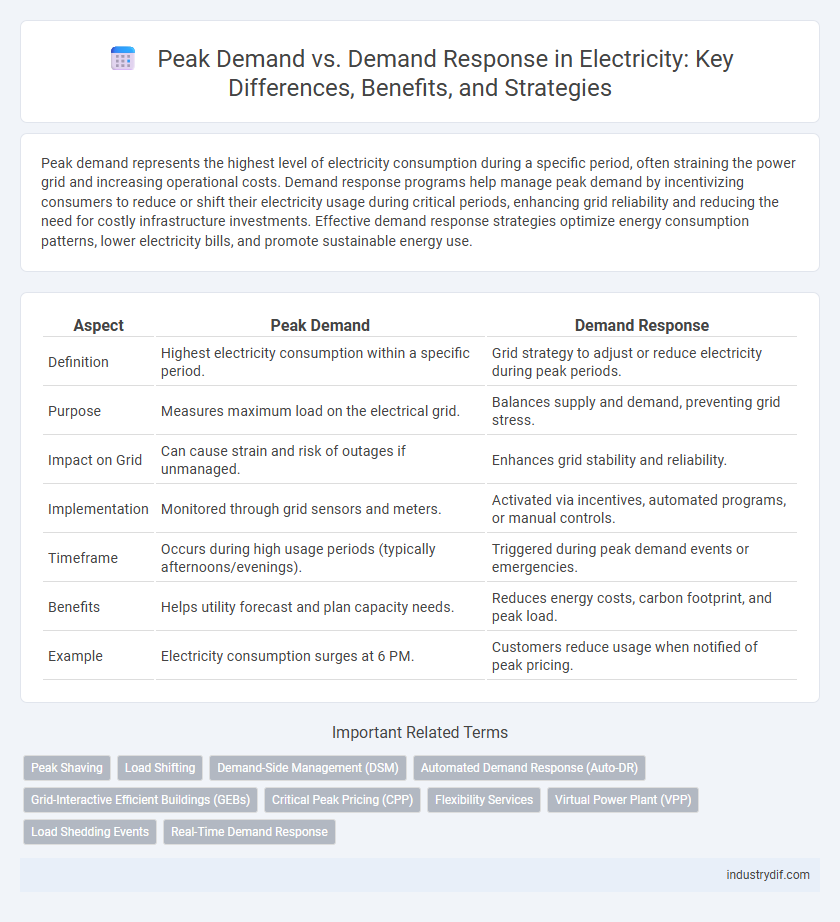
| Aspect | Peak Demand | Demand Response |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Highest electricity consumption within a specific period. | Grid strategy to adjust or reduce electricity during peak periods. |
| Purpose | Measures maximum load on the electrical grid. | Balances supply and demand, preventing grid stress. |
| Impact on Grid | Can cause strain and risk of outages if unmanaged. | Enhances grid stability and reliability. |
| Implementation | Monitored through grid sensors and meters. | Activated via incentives, automated programs, or manual controls. |
| Timeframe | Occurs during high usage periods (typically afternoons/evenings). | Triggered during peak demand events or emergencies. |
| Benefits | Helps utility forecast and plan capacity needs. | Reduces energy costs, carbon footprint, and peak load. |
| Example | Electricity consumption surges at 6 PM. | Customers reduce usage when notified of peak pricing. |
Introduction to Peak Demand and Demand Response
Peak demand refers to the highest level of electricity consumption occurring within a specific period, often stressing the power grid during peak hours. Demand response involves strategic adjustments in electricity usage by consumers to reduce or shift this peak load, enhancing grid stability and efficiency. Implementing effective demand response programs helps utilities manage peak demand, lower operational costs, and decrease the need for additional infrastructure.
Understanding Peak Demand in the Electricity Industry
Peak demand in the electricity industry refers to the highest level of electrical power consumption observed within a specific period, typically during extreme weather conditions or peak operational hours. Managing peak demand is crucial for grid stability and cost efficiency, as it often requires activating additional power plants or purchasing expensive energy from reserve sources. Demand response programs help mitigate peak demand by incentivizing consumers to reduce or shift their electricity usage during these critical times, improving overall grid reliability and reducing operational costs.
What is Demand Response?
Demand Response is a strategic approach to managing electricity consumption by adjusting or reducing usage during peak demand periods, helping to balance supply and demand on the grid. It involves incentivizing consumers, such as residential, commercial, and industrial users, to shift their energy usage to off-peak times or reduce consumption temporarily. This not only improves grid reliability and reduces the need for costly peaking power plants but also supports integration of renewable energy sources.
Key Differences Between Peak Demand and Demand Response
Peak demand refers to the highest level of electricity consumption occurring during specific time periods, often causing strain on the electrical grid and requiring additional generation capacity. Demand response involves consumers reducing or shifting their electricity usage during these peak periods in response to price signals or incentives, helping to maintain grid stability and avoid costly infrastructure investments. The key difference lies in peak demand being a measure of consumption intensity, while demand response is an active strategy to manage and mitigate that consumption.
The Role of Peak Demand in Grid Stability
Peak demand represents the highest level of electricity consumption within a specific period, often straining the electrical grid's capacity and risking instability. Effective management of peak demand through demand response programs helps balance load, preventing blackouts and ensuring consistent voltage levels. Grid operators rely on real-time data and automated controls to reduce peak demand spikes, enhancing overall grid reliability and operational efficiency.
How Demand Response Mitigates Peak Load
Demand response programs reduce peak demand by incentivizing consumers to shift or lower their electricity usage during high-demand periods, preventing grid overloads and the need for costly peaker plants. By adjusting consumption patterns through real-time pricing or automated controls, demand response enhances grid stability and efficiency. This mitigation of peak load decreases operational costs and supports the integration of renewable energy sources.
Economic Impacts of Peak Demand vs Demand Response
Peak demand significantly increases electricity costs due to the need for utilities to activate expensive peaking power plants and invest in additional infrastructure, driving up energy prices for consumers. Demand response programs reduce these economic burdens by incentivizing consumers to lower or shift their electricity usage during peak periods, thus mitigating the need for costly capacity expansions. By decreasing peak demand, demand response enhances grid efficiency and stability, resulting in substantial savings for utilities and end-users while delaying infrastructure investments.
Technological Solutions for Managing Demand
Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and smart grid technologies enable real-time monitoring and control of electricity usage, allowing utilities to implement effective demand response programs during peak demand periods. Automated demand response (ADR) systems integrate with smart appliances and industrial equipment to reduce consumption instantaneously, balancing load without compromising user comfort. Energy storage solutions, such as batteries, complement these technologies by absorbing excess energy during low demand and releasing it during peak times, optimizing grid stability and efficiency.
Regulatory Policies on Peak Demand and Demand Response
Regulatory policies on peak demand emphasize the imposition of demand charges and time-of-use pricing to incentivize consumers and utilities to reduce electricity consumption during high-demand periods. Demand response programs are supported by regulations that facilitate financial incentives, enforce participation standards, and enable automated load control technologies to balance grid stability. These policies aim to optimize energy efficiency, reduce peak load stress on infrastructure, and promote the integration of distributed energy resources.
Future Trends in Demand Management Strategies
Future trends in demand management strategies emphasize integrating advanced demand response technologies with real-time data analytics to better handle peak demand challenges. Smart grid systems and AI-driven automation enable dynamic load shifting, optimizing energy consumption while reducing strain during peak periods. These innovations support grid reliability and promote renewable energy integration, essential for sustainable electricity management.
Related Important Terms
Peak Shaving
Peak shaving reduces electricity peak demand by strategically lowering consumption during high load periods, easing grid stress and avoiding costly infrastructure upgrades. Demand response programs incentivize consumers to shift or curtail energy use, effectively supporting peak shaving efforts and enhancing overall grid reliability.
Load Shifting
Peak demand represents the highest electricity consumption period when the grid experiences maximum strain, typically in the late afternoon or early evening. Demand response strategies leverage load shifting by encouraging consumers to move energy-intensive tasks to off-peak hours, thereby reducing peak load and improving grid stability.
Demand-Side Management (DSM)
Peak demand represents the highest electricity consumption level during a specific period, often straining grid capacity and increasing operational costs. Demand response, a key component of Demand-Side Management (DSM), enables consumers to adjust or reduce their electricity usage during peak periods, enhancing grid reliability and promoting energy efficiency.
Automated Demand Response (Auto-DR)
Automated Demand Response (Auto-DR) systems optimize peak demand management by automatically adjusting electricity usage in real-time, reducing strain on the grid during high consumption periods. These systems leverage smart grid technologies and advanced algorithms to enable rapid, seamless load reductions without compromising operational efficiency.
Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings (GEBs)
Peak demand represents the highest electrical load on the grid during specific periods, straining infrastructure and increasing costs, while demand response in Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings (GEBs) enables dynamic load adjustment by optimizing energy use through real-time communication and control technologies. GEBs enhance grid stability and reduce peak demand impacts by integrating advanced sensors, smart appliances, and distributed energy resources to actively participate in grid services and energy management.
Critical Peak Pricing (CPP)
Critical Peak Pricing (CPP) directly addresses peak demand by charging higher rates during periods of extreme electricity use, incentivizing consumers to reduce consumption and alleviate stress on the grid. This demand response strategy optimizes energy distribution, minimizes the need for costly infrastructure upgrades, and enhances grid reliability during critical peak hours.
Flexibility Services
Peak demand represents the highest electrical power consumption within a specific period, often straining grid capacity and increasing costs. Demand response enhances grid flexibility by incentivizing consumers to reduce or shift their electricity usage during peak times, balancing supply and optimizing energy distribution.
Virtual Power Plant (VPP)
Peak demand represents the highest electricity consumption within a specific period, putting stress on grid infrastructure, while demand response programs, especially through Virtual Power Plants (VPPs), aggregate decentralized energy resources to dynamically reduce or shift consumption, enhancing grid reliability and efficiency. VPPs integrate distributed energy resources like solar panels, batteries, and flexible loads, enabling real-time coordination to alleviate peak demand and optimize energy distribution without the need for new power plants.
Load Shedding Events
Peak demand represents the highest electricity consumption period stressing the grid, often triggering load shedding events to prevent system overload. Demand response programs actively reduce consumption during these peaks by incentivizing consumers to lower usage and mitigate the need for widespread load shedding.
Real-Time Demand Response
Real-time demand response dynamically adjusts electricity usage during peak demand periods by automatically reducing load to stabilize the grid and prevent blackouts. This approach enhances grid reliability and operational efficiency by leveraging smart technologies and consumer participation to balance supply and demand instantaneously.
Peak Demand vs Demand Response Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com