Artisanal pet food emphasizes natural ingredients and traditional preparation methods to ensure high-quality nutrition and flavor tailored for pets. Lab-grown pet food employs cellular agriculture technology to produce sustainable and consistent meals with reduced environmental impact. Choosing between artisanal and lab-grown options depends on pet owners' preferences for natural sourcing versus innovation-driven sustainability.
Table of Comparison
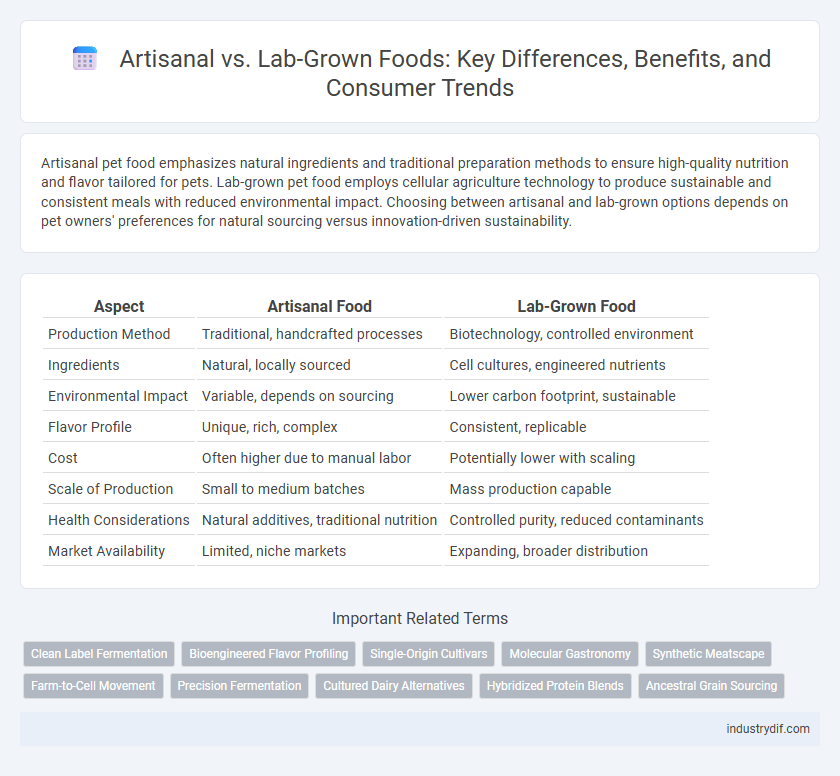
| Aspect | Artisanal Food | Lab-Grown Food |
|---|---|---|
| Production Method | Traditional, handcrafted processes | Biotechnology, controlled environment |
| Ingredients | Natural, locally sourced | Cell cultures, engineered nutrients |
| Environmental Impact | Variable, depends on sourcing | Lower carbon footprint, sustainable |
| Flavor Profile | Unique, rich, complex | Consistent, replicable |
| Cost | Often higher due to manual labor | Potentially lower with scaling |
| Scale of Production | Small to medium batches | Mass production capable |
| Health Considerations | Natural additives, traditional nutrition | Controlled purity, reduced contaminants |
| Market Availability | Limited, niche markets | Expanding, broader distribution |
Defining Artisanal and Lab-Grown Foods
Artisanal foods are handcrafted products made using traditional methods and high-quality, often locally sourced ingredients, emphasizing unique flavors and craftsmanship. Lab-grown foods, also known as cultured or cell-based foods, are produced through cellular agriculture by cultivating animal cells in controlled environments without animal slaughter. These two categories differ significantly in production techniques, environmental impact, and consumer appeal, with artisanal foods prioritizing authenticity and lab-grown foods focusing on sustainability and innovation.
Historical Evolution of Food Production
Artisanal food production, rooted in centuries-old craftsmanship, emphasizes traditional methods and local ingredients, preserving cultural heritage and biodiversity. Lab-grown food, emerging from biotechnological advancements in the 21st century, aims to address sustainability and food security by replicating natural processes in controlled environments. The historical evolution of food production reflects a shift from manual, small-scale artisanal practices to innovation-driven, scalable lab-grown techniques.
Sourcing Ingredients: Traditional vs. Synthetic
Artisanal food products rely on traditionally sourced, natural ingredients harvested from local farms, emphasizing quality, terroir, and seasonal availability. Lab-grown foods utilize synthetic or bioengineered components produced in controlled environments, ensuring consistency and scalability while reducing dependence on agricultural variability. The contrast between natural sourcing and synthetic production reflects broader trends in sustainability, food security, and consumer preferences for authenticity versus technological innovation.
Flavor Profiles: Authenticity vs. Innovation
Artisanal foods emphasize authentic, complex flavor profiles developed through traditional techniques and natural fermentation, offering rich, nuanced tastes that reflect regional heritage. Lab-grown foods, on the other hand, prioritize innovation by engineering precise flavor compounds and textures, aiming to replicate or enhance natural flavors with scientific accuracy. This contrast highlights a culinary divide between preserving genuine sensory experiences and embracing technological advancements to redefine taste.
Health and Nutritional Comparisons
Artisanal foods often contain natural nutrients and fewer additives, supporting traditional dietary benefits and promoting gut health through organic ingredients. Lab-grown products, engineered for consistency and safety, can be enriched with specific nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins, potentially enhancing overall nutritional profiles. Both offer distinct health advantages, with artisanal foods emphasizing natural complexity and lab-grown foods providing targeted nutritional optimization.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Artisanal food production relies on traditional methods often involving local sourcing and smaller-scale operations, which can support biodiversity and reduce transportation emissions. Lab-grown food, particularly cultured meat, offers significant potential to reduce land and water use, lower greenhouse gas emissions by up to 90%, and minimize animal agriculture's environmental footprint. Sustainable food systems increasingly consider lab-grown alternatives as viable solutions to address resource scarcity and climate change challenges while maintaining nutritional quality.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Artisanal food products adhere to stringent local regulatory standards and often carry certifications such as Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) that validate their traditional methods and regional authenticity. Lab-grown foods face evolving regulatory frameworks, with agencies like the FDA and EFSA developing specific guidelines to ensure safety, labeling accuracy, and environmental impact assessments. Certifications for lab-grown products are emerging, focusing on bioengineered food safety and traceability, distinguishing them from conventional artisanal certifications.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumer perception of artisanal foods emphasizes authenticity, tradition, and craftsmanship, driving preference for hand-crafted flavors and organic ingredients. Lab-grown foods gain traction through promises of sustainability, ethical production, and innovation, appealing to environmentally conscious and tech-savvy markets. Market trends reveal increasing investment in lab-grown proteins and niche artisanal products, reflecting shifting demands toward both eco-friendly alternatives and premium culinary experiences.
Cost Analysis: Craftsmanship vs. Technology
Artisanal food production often involves higher labor costs due to skilled craftsmanship and small-batch processes, driving up prices compared to lab-grown alternatives. Lab-grown foods benefit from scalable technology and automation, reducing variable costs and enabling more consistent pricing. While artisanal products emphasize quality and tradition, lab-grown costs are expected to decline with advancements in bioreactor efficiency and production optimization.
The Future of Food: Coexistence or Competition?
Artisanal food preserves traditional flavors and craftsmanship, appealing to consumers seeking authenticity and sustainability, while lab-grown alternatives offer scalable, environmentally friendly solutions to meet global protein demands. The future of food tech hinges on balancing cultural heritage with technological innovation, where both artisanal and lab-grown products can coexist through diversified market niches. Consumer trends indicate growing interest in hybrid models that integrate natural ingredients with cellular agriculture to enhance nutrition and reduce ecological footprints.
Related Important Terms
Clean Label Fermentation
Clean label fermentation enhances artisanal food products by utilizing natural microbial processes that improve flavor complexity and nutritional value without synthetic additives. Lab-grown fermentation leverages controlled environments and precision biotechnologies to produce consistent, scalable, and allergen-free ingredients while meeting consumer demand for transparency and sustainability in food production.
Bioengineered Flavor Profiling
Artisanal foods develop complex bioengineered flavor profiles through traditional fermentation and aging processes that enhance natural enzymatic reactions, resulting in rich, nuanced tastes. Lab-grown products utilize precise genetic and microbial engineering to tailor volatile compounds, creating consistent and customizable flavor experiences unattainable by conventional artisanal methods.
Single-Origin Cultivars
Single-origin cultivars in artisanal food emphasize unique terroir flavors and traditional harvesting methods, offering distinct taste profiles and traceability. Lab-grown alternatives replicate these cultivar characteristics through controlled environments, ensuring consistency and sustainability without geographic limitations.
Molecular Gastronomy
Molecular gastronomy blends the scientific principles of food chemistry with culinary arts, creating innovative textures and flavors that distinguish artisanal craftsmanship from lab-grown food production. Artisanal methods emphasize traditional techniques and ingredient origin, while lab-grown approaches utilize cellular agriculture to engineer sustainable, precisely controlled food at the molecular level.
Synthetic Meatscape
Synthetic meatscape blends cutting-edge biotechnology with artisanal craftsmanship, producing lab-grown meats that mimic traditional flavors and textures while reducing environmental impact and ethical concerns tied to conventional livestock farming. Innovations in cellular agriculture enhance protein synthesis and nutrient profiles, positioning lab-grown meats as a sustainable alternative in the evolving food industry.
Farm-to-Cell Movement
The Farm-to-Cell movement bridges traditional artisanal food craftsmanship with innovative lab-grown technologies by cultivating meat and dairy products directly from animal cells, ensuring sustainability and quality. This approach reduces environmental impact and supports ethical consumption while maintaining flavor profiles akin to farm-raised goods.
Precision Fermentation
Precision fermentation enables the production of artisanal-quality proteins and enzymes by programming microorganisms to deliver consistent, high-purity ingredients that replicate traditional food textures and flavors. This biotechnology bridges the gap between artisanal craftsmanship and lab-grown innovation by enhancing scalability and sustainability without compromising authenticity.
Cultured Dairy Alternatives
Cultured dairy alternatives, including artisanal and lab-grown products, offer diverse flavor profiles and nutritional benefits by utilizing traditional fermentation methods or cellular agriculture techniques. Lab-grown cultured dairy products provide scalable, animal-free options with controlled microbial cultures, while artisanal varieties emphasize heritage strains and handcrafted fermentation processes that enhance complexity and regional character.
Hybridized Protein Blends
Hybridized protein blends combine artisanal ingredients with lab-grown proteins to create nutrient-dense, sustainable food products that enhance flavor and texture profiles. This innovative fusion leverages traditional craftsmanship with cellular agriculture, optimizing protein quality and reducing environmental impact while appealing to health-conscious consumers.
Ancestral Grain Sourcing
Artisanal ancestral grain sourcing emphasizes traditional farming techniques and heirloom varieties, ensuring biodiversity and preserving cultural heritage while enhancing flavor profiles. Lab-grown grains utilize controlled environments to replicate nutritional content and yield consistency, offering scalable solutions but often lacking the complex taste and ecological benefits of ancestral cultivation.
Artisanal vs Lab-Grown Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com