Packaging in pet food plays a critical role in preserving freshness, preventing contamination, and providing convenient storage, with traditional materials like plastic and cardboard being widely used for their durability and cost-effectiveness. Edible packaging offers an innovative, sustainable alternative by reducing waste and environmental impact while potentially providing added nutritional benefits to pets. Balancing practicality, safety, and sustainability remains key in the evolving pet food packaging landscape.
Table of Comparison
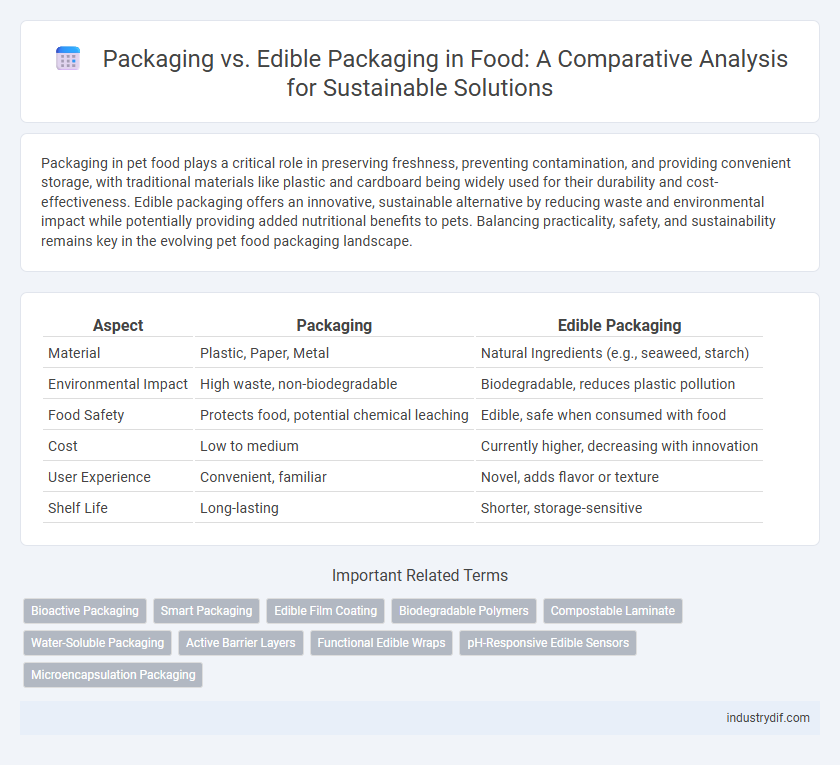
| Aspect | Packaging | Edible Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Plastic, Paper, Metal | Natural Ingredients (e.g., seaweed, starch) |
| Environmental Impact | High waste, non-biodegradable | Biodegradable, reduces plastic pollution |
| Food Safety | Protects food, potential chemical leaching | Edible, safe when consumed with food |
| Cost | Low to medium | Currently higher, decreasing with innovation |
| User Experience | Convenient, familiar | Novel, adds flavor or texture |
| Shelf Life | Long-lasting | Shorter, storage-sensitive |
Introduction to Packaging in the Food Industry
Packaging in the food industry serves as a crucial barrier protecting products from contamination, extending shelf life, and facilitating transportation and storage. Traditional packaging materials include plastics, glass, metal, and paper, each selected for specific food safety and preservation needs. Emerging edible packaging offers sustainable alternatives by reducing waste and enhancing environmental impact while maintaining product freshness.
What is Edible Packaging?
Edible packaging is a sustainable food packaging solution made from natural, biodegradable materials like starch, proteins, and seaweed that can be safely consumed along with the food product. It reduces plastic waste and environmental impact by eliminating the need for traditional plastic wraps and containers. Innovatively designed edible films and coatings enhance food preservation while providing an eco-friendly alternative in the food packaging industry.
Traditional Packaging Materials and Their Impact
Traditional packaging materials such as plastic, glass, and metal dominate the food industry due to their durability and ability to preserve product freshness. However, these materials contribute significantly to environmental pollution and waste accumulation, with plastic packaging accounting for over 30% of global marine litter. Innovations in edible packaging offer sustainable alternatives by reducing reliance on non-biodegradable materials and minimizing ecological footprints.
Advantages of Edible Packaging
Edible packaging offers significant environmental benefits by reducing plastic waste and promoting sustainability in the food industry. It enhances consumer convenience through its biodegradable nature, often providing additional nutritional value or flavor. This innovative solution supports eco-friendly practices while aligning with the growing demand for healthier and more sustainable food packaging alternatives.
Challenges of Edible Packaging Implementation
Edible packaging faces significant challenges such as limited shelf life and vulnerability to moisture, which hinder its scalability in the food industry. Regulatory hurdles and consumer acceptance also pose barriers, as safety standards for edible materials are still evolving. Developing cost-effective production methods and ensuring consistent quality remain critical issues for widespread adoption.
Regulatory Considerations for Food Packaging
Regulatory considerations for food packaging emphasize compliance with safety standards set by authorities like the FDA and EFSA to ensure materials do not leach harmful substances into food. Edible packaging must meet additional criteria, including ingredient transparency, allergen labeling, and biodegradability requirements, which differ from traditional packaging regulations. Manufacturers face rigorous testing protocols to validate the safety, durability, and environmental impact of both conventional and edible packaging solutions.
Sustainability: Edible vs Traditional Packaging
Edible packaging significantly reduces plastic waste by being biodegradable and consumable, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic packaging that often ends up in landfills and oceans. This innovative approach leverages materials like seaweed, rice, and starch that break down naturally, minimizing environmental pollution. Traditional packaging relies heavily on non-renewable resources and contributes substantially to global plastic pollution, making edible packaging a sustainable solution in the food industry.
Cost Analysis: Edible Packaging vs Conventional Packaging
Edible packaging often incurs higher initial production costs due to specialized materials and processing techniques compared to conventional packaging, which benefits from established mass production economies. However, edible packaging can reduce waste disposal expenses and align with sustainability goals, potentially lowering long-term operational costs for food companies. Cost analysis must consider raw material sourcing, consumer acceptance, and regulatory compliance to determine the overall financial viability of edible packaging solutions.
Innovations in Edible Food Packaging Technology
Innovations in edible food packaging technology focus on creating sustainable, biodegradable alternatives to traditional plastic packaging by utilizing materials such as seaweed, rice paper, and starch-based films. These edible packages not only reduce environmental pollution but also enhance food safety by incorporating antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. Advances in nanotechnology and biopolymer composites further improve the durability, flexibility, and shelf life of edible packaging, making it a promising solution for reducing plastic waste in the food industry.
Future Trends in Food Packaging Solutions
Future trends in food packaging solutions emphasize sustainability, with a significant shift towards biodegradable and edible packaging materials derived from natural sources like seaweed, rice, and milk proteins. Innovations in edible packaging not only reduce plastic waste but also enhance food safety by incorporating antimicrobial properties and nutrient enrichment. Advances in smart packaging technologies integrate edible films with sensors that monitor freshness, offering a comprehensive approach to extending shelf life while minimizing environmental impact.
Related Important Terms
Bioactive Packaging
Bioactive packaging integrates natural antimicrobial and antioxidant compounds into food packaging materials to extend shelf life and enhance food safety by actively interacting with the food product. Unlike traditional packaging, bioactive packaging reduces reliance on preservatives and minimizes environmental impact through the use of biodegradable and edible components.
Smart Packaging
Smart packaging in the food industry utilizes advanced technologies such as RFID tags, sensors, and QR codes to monitor freshness, enhance safety, and reduce waste throughout the supply chain. Edible packaging, often made from natural polymers like starch or chitosan, offers sustainable alternatives by minimizing plastic use while integrating smart indicators that signal spoilage or contamination.
Edible Film Coating
Edible film coatings are innovative food packaging solutions made from natural polymers such as proteins, lipids, and polysaccharides, designed to extend shelf life and preserve food quality without generating waste. These coatings provide a sustainable alternative to traditional plastic packaging by being biodegradable, consumable, and capable of carrying antimicrobial and antioxidant agents to enhance food safety and freshness.
Biodegradable Polymers
Biodegradable polymers in packaging reduce environmental impact by decomposing naturally, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics. Edible packaging, made from these polymers, enhances food safety and creates zero waste by being consumable, integrating seamlessly with food products.
Compostable Laminate
Compostable laminate packaging offers a sustainable alternative to traditional plastic by using biodegradable materials that break down naturally in composting environments, reducing landfill waste and environmental impact. Edible packaging, made from natural ingredients such as seaweed or starch, complements this by eliminating packaging waste altogether, promoting zero waste and enhancing food safety with natural preservatives.
Water-Soluble Packaging
Water-soluble packaging offers an innovative alternative to traditional food packaging by dissolving completely upon contact with water, significantly reducing plastic waste and environmental impact. This technology utilizes biodegradable materials like polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), enhancing sustainability while maintaining product safety and freshness in food applications.
Active Barrier Layers
Active barrier layers in food packaging enhance preservation by controlling moisture, oxygen, and microbial growth, thereby extending shelf life and maintaining product quality. Edible packaging incorporates these layers using biodegradable, food-grade materials that provide similar protective functions while reducing plastic waste and offering consumers a sustainable alternative.
Functional Edible Wraps
Functional edible wraps offer sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic packaging by combining biodegradability with food preservation properties such as moisture control and antimicrobial effects; materials like seaweed, rice paper, and starch-based films enhance shelf life without generating waste. These innovative edible packaging solutions reduce environmental impact, support food safety, and cater to consumer demand for eco-friendly, convenient options in the food industry.
pH-Responsive Edible Sensors
pH-responsive edible sensors incorporated into packaging materials offer real-time monitoring of food freshness and spoilage by detecting changes in acidity levels. These innovative sensors enhance food safety and reduce waste by providing consumers and retailers with precise indicators of product quality without generating additional packaging waste.
Microencapsulation Packaging
Microencapsulation packaging enhances traditional food packaging by embedding tiny capsules containing flavors, nutrients, or preservatives, which release contents gradually, extending shelf life and improving food safety. This innovative edible packaging technology reduces plastic waste while maintaining product freshness and offering controlled release of bioactive compounds.
Packaging vs Edible Packaging Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com