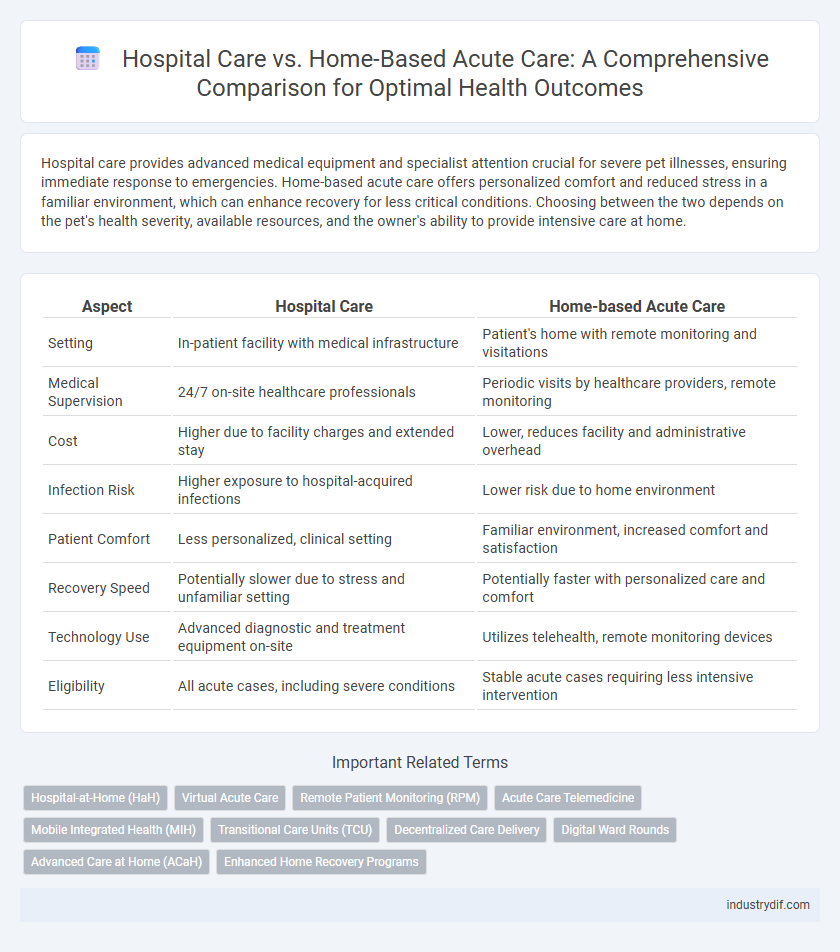
Hospital care provides advanced medical equipment and specialist attention crucial for severe pet illnesses, ensuring immediate response to emergencies. Home-based acute care offers personalized comfort and reduced stress in a familiar environment, which can enhance recovery for less critical conditions. Choosing between the two depends on the pet's health severity, available resources, and the owner's ability to provide intensive care at home.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hospital Care | Home-based Acute Care |
|---|---|---|
| Setting | In-patient facility with medical infrastructure | Patient's home with remote monitoring and visitations |
| Medical Supervision | 24/7 on-site healthcare professionals | Periodic visits by healthcare providers, remote monitoring |
| Cost | Higher due to facility charges and extended stay | Lower, reduces facility and administrative overhead |
| Infection Risk | Higher exposure to hospital-acquired infections | Lower risk due to home environment |
| Patient Comfort | Less personalized, clinical setting | Familiar environment, increased comfort and satisfaction |
| Recovery Speed | Potentially slower due to stress and unfamiliar setting | Potentially faster with personalized care and comfort |
| Technology Use | Advanced diagnostic and treatment equipment on-site | Utilizes telehealth, remote monitoring devices |
| Eligibility | All acute cases, including severe conditions | Stable acute cases requiring less intensive intervention |
Overview of Hospital Care and Home-based Acute Care
Hospital care typically involves intensive monitoring, advanced medical equipment, and multidisciplinary teams within a controlled clinical environment designed for critical conditions. Home-based acute care offers personalized treatment in a familiar setting, reducing risks of hospital-acquired infections and improving patient comfort while utilizing mobile healthcare technologies and remote monitoring systems. Both models emphasize patient safety and timely interventions but differ in resource allocation, cost efficiency, and accessibility.
Key Differences Between Hospital and Home-based Acute Care
Hospital care provides continuous monitoring by specialized medical staff using advanced technology and immediate access to emergency interventions, ensuring comprehensive management of acute conditions. Home-based acute care offers personalized treatment in a comfortable environment, promoting patient convenience and reducing hospital-related infections, but with limited onsite resources and delayed response for critical emergencies. Key differences involve the balance between intensive surveillance and technological support in hospitals versus the flexibility and comfort of home care with constrained medical resource availability.
Patient Eligibility Criteria for Each Care Setting
Patient eligibility criteria for hospital care typically include acute medical conditions requiring intensive monitoring, complex diagnostic procedures, or specialized surgical interventions. Home-based acute care is best suited for patients with stable clinical status, access to a reliable caregiver, and conditions manageable through remote monitoring and periodic professional visits. Selection protocols emphasize patient safety, support systems, and the ability to maintain treatment adherence outside the hospital environment.
Clinical Outcomes: Hospital vs Home-based Acute Care
Hospital care typically ensures rigorous clinical monitoring and immediate intervention, resulting in lower complication rates for acute conditions. Home-based acute care, supported by advanced telehealth technologies and skilled visiting professionals, has demonstrated comparable patient recovery times and reduced readmission rates. Studies indicate that personalized care in home settings can enhance patient satisfaction while maintaining clinical outcomes on par with traditional hospital care.
Cost Comparison: Hospitalization vs Home-based Acute Care
Hospitalization costs for acute care typically range from $2,000 to $4,000 per day, driven by facility fees, staffing, and intensive monitoring, whereas home-based acute care can reduce expenses by 30%-50% due to lower overhead and personalized services. Studies indicate home-based acute care may save an average of $1,500 per patient per episode without compromising quality or outcomes. Cost-efficiency in home-based acute care improves resource allocation and reduces readmission rates, benefiting healthcare systems and patients alike.
Patient Safety and Risk Management
Hospital care offers structured patient safety protocols with continuous monitoring by specialized medical staff, reducing the risk of complications during acute treatment. Home-based acute care provides personalized environments that can decrease exposure to hospital-acquired infections but requires robust risk management strategies to address emergencies and ensure adherence to treatment plans. Effective communication between healthcare providers and caregivers is critical to maintaining patient safety and managing potential risks across both settings.
Technology Integration in Home-based Acute Care
Technology integration in home-based acute care leverages advanced remote monitoring devices, telemedicine platforms, and AI-driven diagnostic tools to provide real-time patient data and enhance clinical decision-making outside traditional hospital settings. This approach reduces hospital readmissions and improves patient outcomes by facilitating continuous care and timely interventions through mobile health applications and connected medical devices. The use of wearable sensors and cloud-based health records ensures seamless communication between patients and healthcare providers, optimizing personalized treatment plans and accelerating recovery.
Impact on Patient Experience and Satisfaction
Hospital care provides patients with immediate access to specialized medical interventions and continuous monitoring, which can enhance feelings of safety and trust in treatment. Home-based acute care offers personalized comfort, familiarity, and a supportive environment that often improves patient satisfaction by reducing stress and promoting faster emotional recovery. Studies show that integrating technology in home-based care enhances communication with healthcare providers, positively affecting patient experience and perceived quality of care.
Workforce and Care Team Requirements
Hospital care demands a larger, more specialized workforce including physicians, nurses, and allied health professionals to manage complex cases and provide continuous monitoring. Home-based acute care requires a coordinated, multidisciplinary team with expertise in telemedicine, nursing, and rehabilitation to deliver personalized care while ensuring patient safety in a non-clinical setting. Workforce training for home-based care emphasizes flexibility, technology proficiency, and effective communication across remote care teams.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Considerations
Hospital care is subject to stringent regulatory standards including accreditation by bodies such as The Joint Commission, while home-based acute care must comply with varied state-specific licensing and Medicare Conditions of Participation. Reimbursement models differ significantly; hospital services typically receive bundled payments or Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) reimbursements from Medicare and private insurers, whereas home-based acute care often qualifies for alternate payment models like Medicare's Hospital at Home program, which promotes cost efficiency and patient-centered outcomes. Navigating these regulatory and reimbursement frameworks is critical for providers to ensure compliance, optimize operational sustainability, and expand access to quality acute care outside traditional hospital settings.
Related Important Terms
Hospital-at-Home (HaH)
Hospital-at-Home (HaH) programs deliver acute care services in patients' residences, reducing hospital admissions and improving patient outcomes by combining remote monitoring, virtual consultations, and in-home nursing. Studies show HaH can lower healthcare costs by up to 30%, reduce infection risks, and enhance patient satisfaction compared to traditional hospital care.
Virtual Acute Care
Virtual acute care integrates advanced telemedicine technologies to deliver hospital-level treatments directly to patients at home, reducing the risk of hospital-acquired infections and enhancing patient comfort. This approach leverages remote monitoring devices, real-time clinical assessments, and multidisciplinary care teams to ensure timely interventions and improved recovery outcomes while minimizing healthcare costs.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) enhances home-based acute care by enabling continuous tracking of vital signs and real-time data transmission to healthcare providers, reducing hospital readmissions and improving patient outcomes. RPM technology integrates wearable devices and secure platforms, supporting proactive interventions and personalized care outside traditional hospital settings.
Acute Care Telemedicine
Acute care telemedicine enables remote monitoring and treatment of critically ill patients, reducing hospital admissions and lowering healthcare costs. Telehealth technologies facilitate timely interventions, enhance patient outcomes, and improve access to specialized care in home-based acute care settings.
Mobile Integrated Health (MIH)
Mobile Integrated Health (MIH) enhances patient outcomes by delivering acute care services directly in the home, reducing hospital readmissions and healthcare costs. Leveraging advanced telehealth technology and paramedicine, MIH bridges gaps between hospital care and home-based treatment, ensuring timely interventions and personalized care plans.
Transitional Care Units (TCU)
Transitional Care Units (TCUs) bridge hospital care and home-based acute care by providing specialized, short-term medical support for patients requiring intensive monitoring and rehabilitation after hospital discharge. TCUs reduce hospital readmissions and enhance recovery outcomes by offering multidisciplinary care in a cost-effective, patient-centered environment.
Decentralized Care Delivery
Decentralized care delivery shifts acute care from hospitals to home-based settings, enhancing patient comfort and reducing hospital readmissions. Home-based acute care leverages telemedicine, remote monitoring, and mobile health teams to provide timely, personalized treatment with lower costs and improved clinical outcomes.
Digital Ward Rounds
Digital ward rounds in hospital care enable real-time patient data integration and multidisciplinary collaboration, improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment efficiency. Home-based acute care leverages digital ward rounds to remotely monitor vitals and administer personalized interventions, reducing hospital readmissions and enhancing patient comfort.
Advanced Care at Home (ACaH)
Advanced Care at Home (ACaH) delivers hospital-level acute care within a patient's residence, combining telemedicine, remote monitoring, and in-person clinical visits to reduce costs and avoid hospital-acquired infections. Studies indicate ACaH models improve patient outcomes by offering personalized care, enhancing recovery rates, and increasing patient satisfaction compared to traditional inpatient hospital stays.
Enhanced Home Recovery Programs
Enhanced home recovery programs leverage personalized monitoring technology and skilled home health professionals to reduce hospital stays while maintaining acute care quality. These programs improve patient outcomes by minimizing infection risks and promoting comfort, leading to faster recovery and lowered healthcare costs.
Hospital Care vs Home-based Acute Care Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com