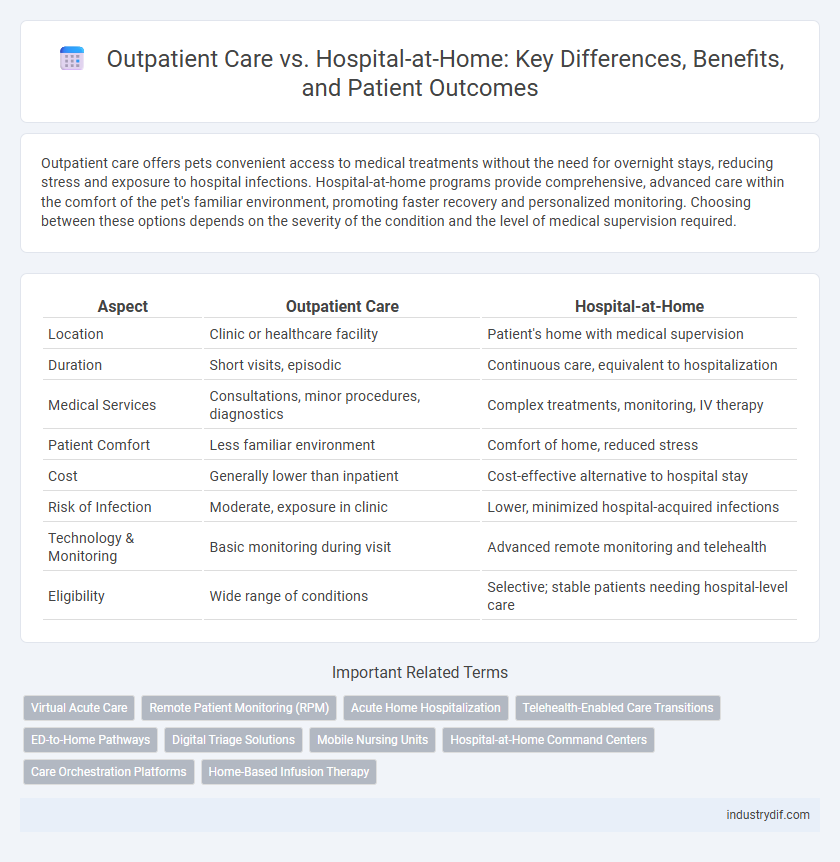
Outpatient care offers pets convenient access to medical treatments without the need for overnight stays, reducing stress and exposure to hospital infections. Hospital-at-home programs provide comprehensive, advanced care within the comfort of the pet's familiar environment, promoting faster recovery and personalized monitoring. Choosing between these options depends on the severity of the condition and the level of medical supervision required.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Outpatient Care | Hospital-at-Home |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Clinic or healthcare facility | Patient's home with medical supervision |
| Duration | Short visits, episodic | Continuous care, equivalent to hospitalization |
| Medical Services | Consultations, minor procedures, diagnostics | Complex treatments, monitoring, IV therapy |
| Patient Comfort | Less familiar environment | Comfort of home, reduced stress |
| Cost | Generally lower than inpatient | Cost-effective alternative to hospital stay |
| Risk of Infection | Moderate, exposure in clinic | Lower, minimized hospital-acquired infections |
| Technology & Monitoring | Basic monitoring during visit | Advanced remote monitoring and telehealth |
| Eligibility | Wide range of conditions | Selective; stable patients needing hospital-level care |
Understanding Outpatient Care: Key Features and Benefits
Outpatient care offers medical services without an overnight hospital stay, providing convenience and cost savings for patients with minor illnesses or routine treatments. Key features include scheduled appointments, diagnostic tests, and treatments in clinics or ambulatory centers, facilitating timely care and reducing hospital congestion. Benefits encompass faster recovery, lower infection risk, and enhanced patient comfort by allowing individuals to receive necessary care while remaining in their home environment.
What Is Hospital-at-Home? An Emerging Care Model
Hospital-at-Home is an innovative healthcare model that delivers acute hospital-level care to patients in their own homes, reducing the need for traditional inpatient stays. This approach leverages telemedicine, remote monitoring, and in-home visits by healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive treatment for conditions such as infections, chronic disease exacerbations, and post-surgical recovery. Studies show Hospital-at-Home can improve patient outcomes, increase satisfaction, and lower healthcare costs compared to conventional outpatient or inpatient care.
Outpatient Care vs Hospital-at-Home: Core Differences
Outpatient care involves patients receiving medical treatment at a healthcare facility without overnight stay, emphasizing convenience and quick access to services such as diagnostic tests and minor surgeries. Hospital-at-home programs provide acute-level care in a patient's residence, leveraging medical technology and professional home visits to manage conditions typically requiring hospitalization. The core differences lie in setting and intensity of care, with outpatient care focusing on episodic visits and hospital-at-home delivering continuous, hospital-standard treatment within the home environment.
Patient Eligibility Criteria for Each Care Setting
Patient eligibility for outpatient care typically includes individuals with stable chronic conditions, mild acute illnesses, or those requiring routine follow-up without intensive medical supervision. Hospital-at-home programs target patients who need hospital-level treatment but can safely receive care in their residence, such as those with controlled infections, congestive heart failure, or post-surgical recovery without complications. Assessments for both settings emphasize medical stability, social support, and the ability of patients to manage therapy protocols effectively.
Clinical Outcomes: Comparing Effectiveness and Safety
Outpatient care and hospital-at-home models both aim to deliver efficient healthcare but differ in clinical outcomes related to effectiveness and safety. Studies show hospital-at-home programs reduce readmission rates and infection risks by providing acute care in a controlled home environment with continuous monitoring. Outpatient care is effective for routine follow-ups and minor procedures but may lack the intensive support needed for complex acute conditions, impacting recovery and complication rates.
Cost Implications for Patients and Payers
Outpatient care typically reduces costs for patients and payers by minimizing hospital stays and associated fees, often resulting in lower co-pays and fewer facility charges. Hospital-at-home programs, while potentially more expensive per day due to the intensity of in-home services and specialized monitoring, can decrease overall expenditures by preventing readmissions and shortening recovery times. Both models aim to optimize resource utilization, but hospital-at-home may offer higher value through personalized care that reduces long-term costs despite higher initial investments.
Patient Experience and Satisfaction Levels
Outpatient care emphasizes convenience and reduced wait times, contributing to higher patient satisfaction through personalized, flexible treatment schedules. Hospital-at-home programs replicate inpatient care quality in a familiar environment, enhancing comfort, reducing stress, and improving recovery outcomes. Studies indicate patients report greater overall satisfaction and emotional well-being with hospital-at-home services compared to traditional outpatient visits.
Technology’s Role in Outpatient and Hospital-at-Home Care
Advanced remote monitoring devices and telehealth platforms significantly enhance outpatient and hospital-at-home care by enabling continuous patient data collection and real-time communication with healthcare providers. Integration of AI-powered analytics supports personalized treatment plans and early detection of complications, improving patient outcomes outside traditional hospital settings. Mobile health applications facilitate medication adherence and symptom tracking, bridging gaps in care and reducing hospital readmissions.
Staffing and Resource Requirements: A Comparative View
Outpatient care typically requires a dedicated team of healthcare professionals available on-site, including physicians, nurses, and support staff to manage patient visits and treatments efficiently. Hospital-at-home programs demand specialized staffing with skills in remote monitoring, home-based interventions, and rapid response capabilities, often involving interdisciplinary teams equipped with telehealth technologies and portable medical devices. Resource allocation in outpatient settings favors fixed infrastructure and in-person equipment, while hospital-at-home depends heavily on mobile medical tools, digital health platforms, and coordinated logistics for delivering comprehensive care in patients' residences.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Care Delivery
Outpatient care is shifting toward integrating advanced telehealth technologies and remote monitoring devices to enhance patient convenience and reduce hospital visits. Hospital-at-home models leverage sophisticated clinical protocols and real-time data analytics to provide acute care traditionally delivered in inpatient settings, promoting cost efficiency and improved patient outcomes. Future trends emphasize personalized care pathways, interoperability of health systems, and the expansion of home-based care programs driven by healthcare policy reforms and technological innovations.
Related Important Terms
Virtual Acute Care
Virtual acute care in outpatient settings leverages telemedicine and remote monitoring to deliver timely medical interventions traditionally provided in hospitals, reducing hospital admissions and exposure to nosocomial infections. This model enhances patient outcomes by combining advanced digital health technologies with personalized care plans, ensuring continuous clinical oversight while maintaining comfort and convenience at home.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) enhances outpatient care by enabling continuous tracking of vital signs and health metrics, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and improving chronic disease management. In hospital-at-home models, RPM supports real-time clinical decision-making and timely interventions, ensuring high-quality care while patients recover in their familiar home environments.
Acute Home Hospitalization
Acute Home Hospitalization offers acute-level medical care in a home setting, providing continuous monitoring, nursing, and physician support comparable to outpatient care but with the added benefit of patient comfort and reduced hospital stay. Studies show this model improves patient outcomes, decreases readmissions, and lowers healthcare costs, making it a viable alternative to traditional outpatient care for eligible patients.
Telehealth-Enabled Care Transitions
Telehealth-enabled care transitions significantly enhance outpatient care by providing remote monitoring, virtual consultations, and timely interventions, reducing hospital readmissions and improving patient outcomes. Hospital-at-home models leverage advanced telehealth technologies to deliver acute care in a home setting, offering the benefits of personalized treatment and continuous clinical oversight without the costs and risks associated with traditional inpatient hospitalization.
ED-to-Home Pathways
ED-to-Home pathways enhance patient outcomes by transitioning care from emergency departments directly to outpatient or hospital-at-home services, reducing hospital admissions and lowering healthcare costs. This approach leverages remote monitoring and coordinated care plans to manage acute conditions effectively while maintaining patient comfort and safety outside traditional hospital settings.
Digital Triage Solutions
Digital triage solutions enhance outpatient care by enabling remote symptom assessment, personalized care pathways, and timely interventions that reduce unnecessary hospital visits. Hospital-at-home programs integrate these digital tools to monitor patients continuously, improving safety and outcomes while minimizing inpatient admissions and healthcare costs.
Mobile Nursing Units
Mobile nursing units provide essential outpatient care by delivering personalized, high-quality medical services directly to patients' homes, reducing hospital admissions and enhancing comfort. This model bridges the gap between traditional outpatient clinics and hospital-at-home programs, offering continuous monitoring, wound care, and medication management with advanced telehealth integration.
Hospital-at-Home Command Centers
Hospital-at-Home Command Centers utilize advanced technology and remote monitoring to deliver acute care within patients' residences, significantly reducing hospital admissions and associated costs while maintaining high-quality clinical outcomes. These centralized hubs coordinate multidisciplinary teams, manage patient data in real-time, and enable rapid response to emergencies, enhancing patient safety and satisfaction compared to traditional outpatient care models.
Care Orchestration Platforms
Care orchestration platforms streamline communication and coordination among healthcare providers, enhancing the efficiency and quality of both outpatient care and hospital-at-home services. These platforms integrate patient data, schedule management, and treatment protocols to ensure timely interventions and personalized care delivery in diverse settings.
Home-Based Infusion Therapy
Home-based infusion therapy in outpatient care offers patients the convenience of receiving intravenous medications in their own homes while reducing hospital stays and associated costs. Hospital-at-home programs enhance this approach by providing comprehensive medical supervision and real-time monitoring, improving treatment safety and patient outcomes.
Outpatient Care vs Hospital-at-Home Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com