Psychedelic-assisted therapy has emerged as a promising approach to improving mental health by addressing conditions such as PTSD, depression, and anxiety through guided use of substances like psilocybin and MDMA. This therapy facilitates profound psychological insights and emotional breakthroughs, often leading to lasting behavioral changes and symptom relief. Understanding the distinct benefits and risks of psychedelic-assisted treatment is crucial for integrating it effectively within broader mental health care strategies.
Table of Comparison
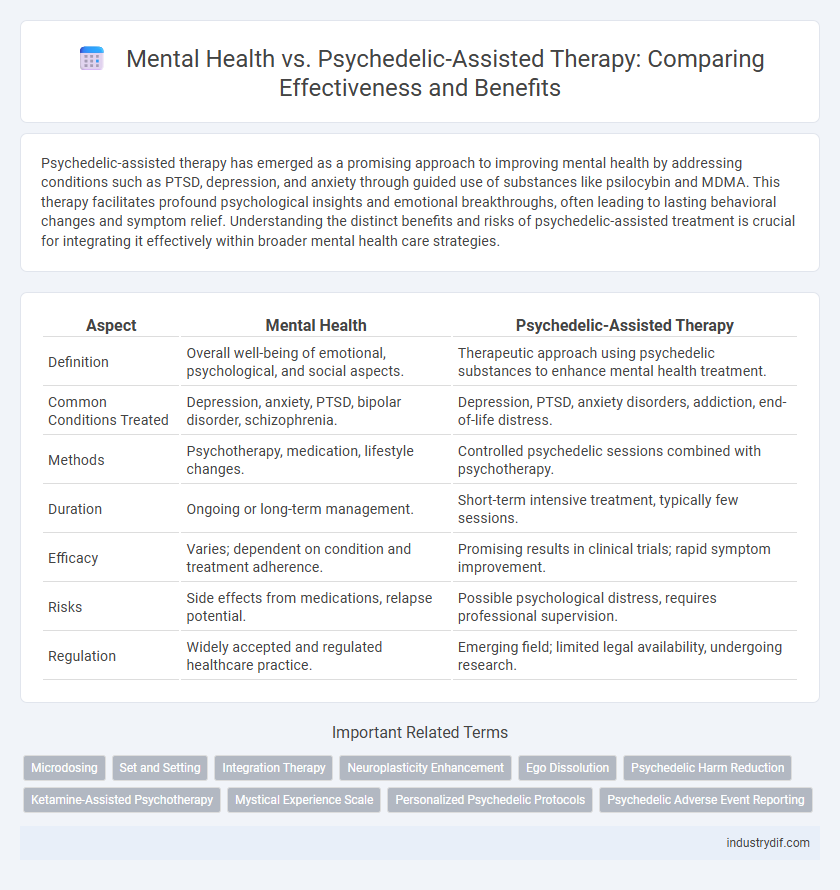
| Aspect | Mental Health | Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overall well-being of emotional, psychological, and social aspects. | Therapeutic approach using psychedelic substances to enhance mental health treatment. |
| Common Conditions Treated | Depression, anxiety, PTSD, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia. | Depression, PTSD, anxiety disorders, addiction, end-of-life distress. |
| Methods | Psychotherapy, medication, lifestyle changes. | Controlled psychedelic sessions combined with psychotherapy. |
| Duration | Ongoing or long-term management. | Short-term intensive treatment, typically few sessions. |
| Efficacy | Varies; dependent on condition and treatment adherence. | Promising results in clinical trials; rapid symptom improvement. |
| Risks | Side effects from medications, relapse potential. | Possible psychological distress, requires professional supervision. |
| Regulation | Widely accepted and regulated healthcare practice. | Emerging field; limited legal availability, undergoing research. |
Overview of Mental Health: Definitions and Scope
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing how individuals think, feel, and behave in daily life. It affects stress management, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making abilities across all ages. The scope includes common disorders such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder, highlighting the importance of early intervention and comprehensive care.
Common Approaches in Traditional Mental Health Treatment
Common approaches in traditional mental health treatment include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), psychodynamic therapy, and pharmacotherapy, which primarily focus on symptom management and behavior modification. These treatments aim to address mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and PTSD through talk therapy and medication prescribed by psychiatrists. Evidence-based therapies emphasize long-term coping strategies and gradual improvement, contrasting with the experiential and neuroplasticity-driven effects of psychedelic-assisted therapy.
Introduction to Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy
Psychedelic-assisted therapy utilizes substances like psilocybin and MDMA to enhance psychological treatment outcomes for conditions such as depression, PTSD, and anxiety. This innovative approach combines controlled psychedelic experiences with professional therapeutic support to promote emotional healing and cognitive restructuring. Clinical trials demonstrate its potential to offer rapid and sustained mental health improvements compared to traditional therapies.
Key Differences: Conventional Therapy vs Psychedelic-Assisted Approaches
Conventional mental health therapy primarily utilizes talk therapy and medication management, focusing on symptom alleviation and behavioral modification over extended periods. Psychedelic-assisted therapy involves controlled administration of substances like psilocybin or MDMA combined with therapeutic guidance, aiming to induce profound psychological insights and neuroplasticity in fewer sessions. Key differences include the mechanisms of action, duration of treatment, and potential for transformative experiences beyond traditional approaches.
Evidence and Research Supporting Psychedelic Therapies
Extensive clinical trials and meta-analyses reveal that psychedelic-assisted therapy, particularly with substances like psilocybin and MDMA, significantly reduces symptoms of treatment-resistant depression, PTSD, and anxiety. Neuroimaging studies demonstrate these therapies promote neuroplasticity and reset dysfunctional brain circuits, supporting long-lasting mental health improvements. Evidence from randomized controlled trials published in journals such as JAMA Psychiatry and The Lancet Psychiatry highlights safety profiles and efficacy surpassing traditional pharmacological interventions.
Safety, Risks, and Regulatory Considerations
Psychedelic-assisted therapy shows promise in treating mental health disorders but requires careful evaluation of safety and risks, including potential psychological distress and drug interactions. Regulatory considerations emphasize strict clinical protocols, informed consent, and controlled substance management to minimize misuse and ensure patient safety. Ongoing research and policy development aim to balance therapeutic benefits with risk mitigation and public health safeguards.
Patient Suitability and Candidacy Criteria
Patient suitability for psychedelic-assisted therapy involves careful screening to identify those with mental health conditions such as treatment-resistant depression, PTSD, or anxiety disorders who have not responded well to conventional treatments. Candidacy criteria emphasize the absence of contraindications like a history of psychosis, bipolar disorder, or cardiovascular issues to minimize adverse effects. Comprehensive evaluation by mental health professionals ensures the optimal selection of patients who can safely benefit from the therapeutic potentials of psychedelics.
Integration and Aftercare: Maximizing Therapeutic Outcomes
Integration and aftercare are critical components of psychedelic-assisted therapy, ensuring the mental health benefits extend beyond the acute experience. Structured integration sessions help patients process insights gained during treatment, reinforcing behavioral changes and emotional regulation. Comprehensive aftercare plans, including counseling and peer support, maximize long-term therapeutic outcomes and reduce the risk of relapse or psychological distress.
Societal Perceptions and Stigma: Changing Attitudes
Societal perceptions of mental health are gradually shifting as psychedelic-assisted therapy gains evidence-based recognition for its effectiveness in treating disorders like PTSD and depression. This therapy challenges traditional stigma by demonstrating neurochemical benefits and promoting holistic healing, leading to increased public acceptance and policy reform. Changing attitudes are encouraging open conversations and reducing misconceptions surrounding mental health treatments involving psychedelics.
Future Directions in Mental Health Treatment Modalities
Emerging research in psychedelic-assisted therapy reveals promising potential to revolutionize mental health treatment by targeting neural pathways linked to depression and PTSD more effectively than traditional methods. Integrating advanced neuroimaging techniques and personalized medicine could enhance therapeutic outcomes and reduce relapse rates. Future directions emphasize combining psychedelics with cognitive-behavioral interventions and digital health platforms to create comprehensive, scalable mental health solutions.
Related Important Terms
Microdosing
Microdosing psychedelic substances, such as psilocybin or LSD, has gained attention for its potential to enhance mental health by reducing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and PTSD through subtle neurochemical modulation without inducing full psychedelic experiences. Emerging research indicates that microdosing may promote neuroplasticity and improve mood, cognitive function, and emotional regulation, making it a promising adjunct to traditional mental health therapies.
Set and Setting
Set and setting critically influence the outcomes of psychedelic-assisted therapy by shaping a patient's mindset and physical environment during treatment. Optimizing these factors reduces adverse psychological reactions and enhances therapeutic benefits in mental health interventions.
Integration Therapy
Integration therapy is crucial in psychedelic-assisted treatment, facilitating the processing and meaning-making of psychedelic experiences to ensure long-term mental health benefits. Effective integration enhances emotional resilience and supports sustained improvements in conditions such as depression, PTSD, and anxiety by grounding therapeutic insights in daily life.
Neuroplasticity Enhancement
Psychedelic-assisted therapy significantly enhances neuroplasticity by promoting the growth and reorganization of neural pathways, which supports improved cognitive flexibility and emotional regulation. Unlike conventional mental health treatments, this approach directly targets brain plasticity mechanisms such as increased synaptogenesis and dendritic spine density, facilitating lasting therapeutic outcomes for conditions like depression and PTSD.
Ego Dissolution
Ego dissolution, a key experience in psychedelic-assisted therapy, facilitates profound shifts in self-perception that can alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and PTSD by disrupting rigid mental patterns. Mental health improvements from this therapeutic approach are linked to enhanced emotional flexibility and a reduced sense of self-centered distress, promoting long-term psychological healing.
Psychedelic Harm Reduction
Psychedelic-assisted therapy offers promising advancements in mental health treatment by combining controlled psychedelic substance use with professional therapeutic guidance to address conditions such as PTSD, depression, and anxiety. Emphasizing psychedelic harm reduction involves strategies like proper dosage control, set and setting optimization, integration support, and education on potential risks to ensure patient safety and maximize therapeutic outcomes.
Ketamine-Assisted Psychotherapy
Ketamine-assisted psychotherapy (KAP) has emerged as a promising treatment for mental health disorders such as depression, PTSD, and anxiety, offering rapid symptom relief compared to traditional therapies. Studies indicate that ketamine's NMDA receptor antagonism promotes neuroplasticity, enhancing therapeutic outcomes when combined with guided psychotherapy sessions.
Mystical Experience Scale
The Mystical Experience Scale (MES) quantifies subjective experiences during psychedelic-assisted therapy, correlating higher MES scores with significant improvements in mental health conditions such as depression and PTSD. Research shows that the intensity of mystical experiences measured by MES predicts long-term therapeutic outcomes, highlighting its critical role in evaluating the efficacy of psychedelic interventions compared to traditional mental health treatments.
Personalized Psychedelic Protocols
Personalized psychedelic protocols in mental health treatment leverage individual neurobiology and psychological profiles to optimize therapeutic outcomes and minimize adverse effects. Tailoring dosage, psychedelics types, and integration practices enhances efficacy in addressing conditions like depression, PTSD, and anxiety through precision mental health approaches.
Psychedelic Adverse Event Reporting
Psychedelic-assisted therapy shows promising results in treating mental health disorders, yet accurate reporting of psychedelic adverse events is critical for ensuring patient safety and advancing clinical guidelines. Systematic documentation of side effects such as anxiety, paranoia, and physiological reactions enhances understanding of risk profiles and informs safer therapeutic protocols.
Mental Health vs Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com