Patient engagement involves actively involving pets and their owners in the healthcare process through education, communication, and support to improve overall health outcomes. Patient activation goes a step further by empowering pet owners with the knowledge, skills, and confidence necessary to take independent actions that promote their pet's well-being. Both concepts are essential for effective pet health management, enhancing adherence to treatment plans and fostering proactive care.
Table of Comparison
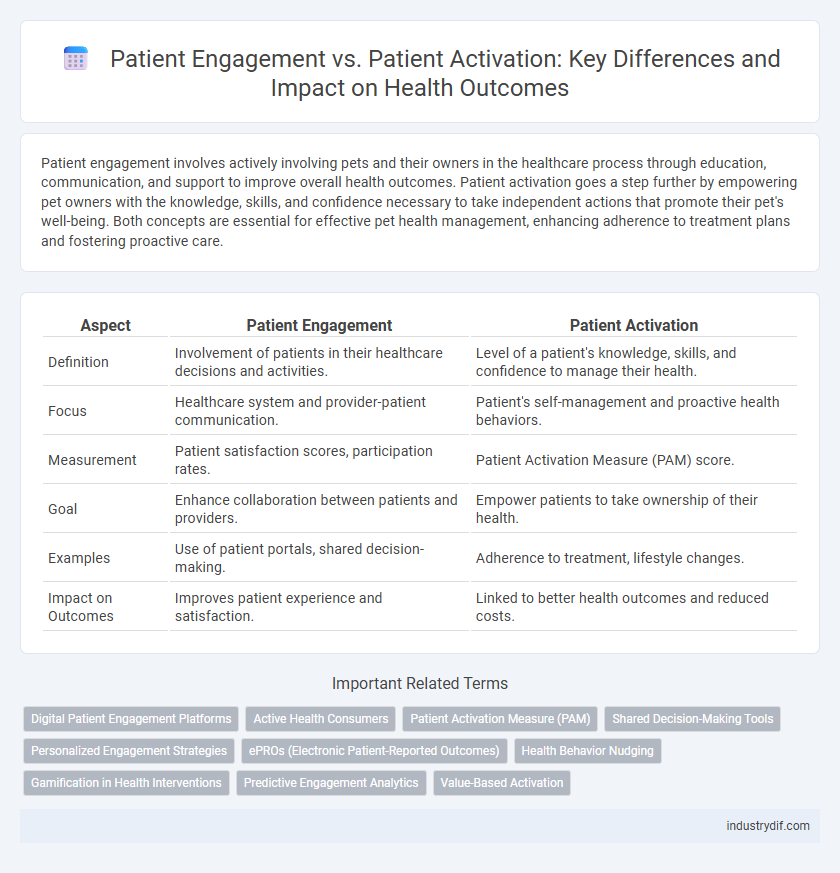
| Aspect | Patient Engagement | Patient Activation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Involvement of patients in their healthcare decisions and activities. | Level of a patient's knowledge, skills, and confidence to manage their health. |
| Focus | Healthcare system and provider-patient communication. | Patient's self-management and proactive health behaviors. |
| Measurement | Patient satisfaction scores, participation rates. | Patient Activation Measure (PAM) score. |
| Goal | Enhance collaboration between patients and providers. | Empower patients to take ownership of their health. |
| Examples | Use of patient portals, shared decision-making. | Adherence to treatment, lifestyle changes. |
| Impact on Outcomes | Improves patient experience and satisfaction. | Linked to better health outcomes and reduced costs. |
Understanding Patient Engagement: Definition and Importance
Patient engagement refers to the collaboration between patients and healthcare providers to actively involve patients in their own care, encompassing communication, education, and shared decision-making processes. It plays a critical role in improving health outcomes by fostering patient satisfaction, adherence to treatment plans, and chronic disease management. Effective patient engagement strategies leverage digital tools, personalized care, and continuous support to empower patients and enhance overall healthcare quality.
Patient Activation Explained: Key Concepts
Patient activation refers to a patient's knowledge, skills, confidence, and willingness to manage their own health and healthcare. Higher levels of patient activation correlate with improved health outcomes, better chronic disease management, and more effective use of healthcare resources. Assessing patient activation using tools like the Patient Activation Measure (PAM) enables personalized interventions that empower patients to take an active role in their treatment plans.
Differences Between Patient Engagement and Patient Activation
Patient engagement refers to the broader process of involving patients in their healthcare decisions and communication with providers, emphasizing active participation in managing health. Patient activation specifically measures a patient's knowledge, skills, and confidence needed to manage their health effectively. The key difference lies in patient engagement encompassing a wider range of interactions, while patient activation focuses on the individual's readiness and ability to take health-related actions.
Measuring Patient Engagement in Healthcare
Measuring patient engagement in healthcare involves assessing the extent to which patients participate actively in their own care, including communication with providers, adherence to treatment plans, and involvement in decision-making. Tools such as the Patient Activation Measure (PAM) quantify patient activation levels by evaluating knowledge, skills, and confidence in managing health. Effective measurement of engagement enables personalized interventions that improve health outcomes and increase patient satisfaction.
Assessing Levels of Patient Activation
Assessing levels of patient activation involves measuring a patient's knowledge, skills, and confidence in managing their own health and healthcare. Tools like the Patient Activation Measure (PAM) quantify activation across different stages, helping healthcare providers tailor interventions to improve self-management and health outcomes. Higher patient activation correlates with better adherence to treatment plans, reduced hospitalizations, and overall enhanced patient engagement.
Impact of Engagement and Activation on Health Outcomes
Patient engagement involves the actions patients take to become involved in their healthcare, while patient activation reflects their knowledge, skills, and confidence to manage their health. Higher levels of patient activation correlate with improved chronic disease management, medication adherence, and preventive care utilization. Enhanced patient engagement fosters better communication with healthcare providers, resulting in reduced hospital readmissions and improved overall health outcomes.
Strategies to Improve Patient Engagement
Effective strategies to improve patient engagement include personalized communication, leveraging digital health tools like mobile apps and patient portals, and fostering strong patient-provider relationships to enhance trust and information exchange. Incorporating educational resources tailored to individual health literacy levels empowers patients to participate actively in their care. Structured follow-up protocols and shared decision-making models also promote sustained engagement, differentiating from patient activation, which emphasizes the patient's readiness and confidence to take health-related actions.
Techniques to Increase Patient Activation
Techniques to increase patient activation include personalized education, goal-setting strategies, and motivational interviewing, which empower patients to take an active role in their health management. Utilizing digital tools such as mobile health apps and remote monitoring devices helps track progress and reinforce positive behaviors. Regular feedback and support from healthcare providers enhance confidence and sustain long-term engagement in self-care activities.
The Role of Technology in Patient Engagement and Activation
Technology enhances patient engagement by providing platforms for continuous communication, personalized health education, and real-time monitoring, which foster active participation in care decisions. Digital tools like mobile health apps and wearable devices facilitate patient activation by encouraging self-management behaviors and adherence to treatment plans through reminders and progress tracking. Integration of electronic health records (EHR) with patient portals empowers patients with access to their medical data, promoting informed decision-making and sustained health behavior change.
Best Practices for Integrating Engagement and Activation in Care Models
Effective integration of patient engagement and activation in care models requires personalized communication strategies that leverage digital health tools and real-time data analytics to address individual patient needs. Incorporating multidisciplinary care teams and shared decision-making fosters collaboration, enhancing patients' confidence and motivation to manage their health proactively. Continuous feedback loops and outcome tracking enable refinement of interventions, ensuring sustained participation and improved clinical outcomes.
Related Important Terms
Digital Patient Engagement Platforms
Digital patient engagement platforms enhance patient interaction by providing personalized health information and real-time communication tools, which improve patient engagement through continuous access and support. These platforms also drive patient activation by empowering individuals with actionable insights and self-management resources, fostering proactive health behaviors and adherence to treatment plans.
Active Health Consumers
Active health consumers demonstrate high patient activation by taking initiative in managing their health, using digital tools and personalized data to make informed decisions. Patient engagement encompasses this activation but also includes emotional and behavioral involvement in healthcare, fostering sustained interaction with providers and adherence to treatment plans.
Patient Activation Measure (PAM)
Patient Activation Measure (PAM) quantifies a patient's knowledge, skills, and confidence essential for managing their health effectively, distinguishing it from the broader concept of patient engagement which encompasses overall involvement in healthcare processes. Higher PAM scores correlate with improved adherence to treatment plans and better health outcomes, making PAM a critical tool for tailoring interventions in chronic disease management.
Shared Decision-Making Tools
Shared decision-making tools enhance patient engagement by facilitating meaningful conversations between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring that care decisions align with patients' values and preferences. These tools also boost patient activation by empowering individuals with the knowledge and confidence needed to participate actively in managing their health conditions.
Personalized Engagement Strategies
Personalized engagement strategies tailor communication and interventions based on individual patient preferences, behaviors, and health data, enhancing patient engagement by fostering meaningful interactions. Patient activation focuses on empowering patients with the knowledge, skills, and confidence to manage their health, making personalized strategies essential for improving activation levels and overall health outcomes.
ePROs (Electronic Patient-Reported Outcomes)
Patient engagement involves continuous communication and involvement of patients in their healthcare journey, enhanced by ePROs that facilitate real-time symptom tracking and feedback. Patient activation refers to the patient's knowledge, skills, and confidence to manage their health, improved through ePROs by delivering personalized data that empowers informed decision-making.
Health Behavior Nudging
Patient engagement involves the ongoing relationship and participation of individuals in their healthcare, while patient activation specifically measures their knowledge, skills, and confidence to manage health. Health behavior nudging leverages subtle cues and incentives to enhance both engagement and activation, promoting sustained adherence to treatment plans and healthier lifestyle choices.
Gamification in Health Interventions
Patient engagement involves building a sustained relationship between patients and healthcare providers, emphasizing ongoing interaction and support, while patient activation specifically measures a patient's knowledge, skills, and confidence to manage their health. Gamification in health interventions enhances both engagement and activation by using game design elements such as rewards, challenges, and feedback to motivate patients, improve adherence, and foster proactive health behaviors.
Predictive Engagement Analytics
Predictive engagement analytics leverages data patterns to identify patients' likelihood of active participation in their healthcare, enhancing tailored interventions for higher patient activation levels. Utilizing real-time health metrics and behavioral insights, healthcare providers can proactively boost patient engagement by predicting and addressing barriers before they arise.
Value-Based Activation
Patient engagement involves patients' emotional and cognitive involvement in their healthcare, while patient activation measures their actual knowledge, skills, and confidence to manage health. Value-based activation enhances outcomes by aligning patient behaviors with personalized, evidence-based care plans that optimize cost-effectiveness and quality.
Patient Engagement vs Patient Activation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com