Prescription drugs remain the standard for treating chronic conditions in pets, offering targeted and effective therapy. Digital pills, embedded with ingestible sensors, provide real-time monitoring of medication adherence, enhancing treatment precision and pet health management. Combining traditional prescription drugs with digital pill technology bridges effective treatment and accurate monitoring for improved outcomes.
Table of Comparison
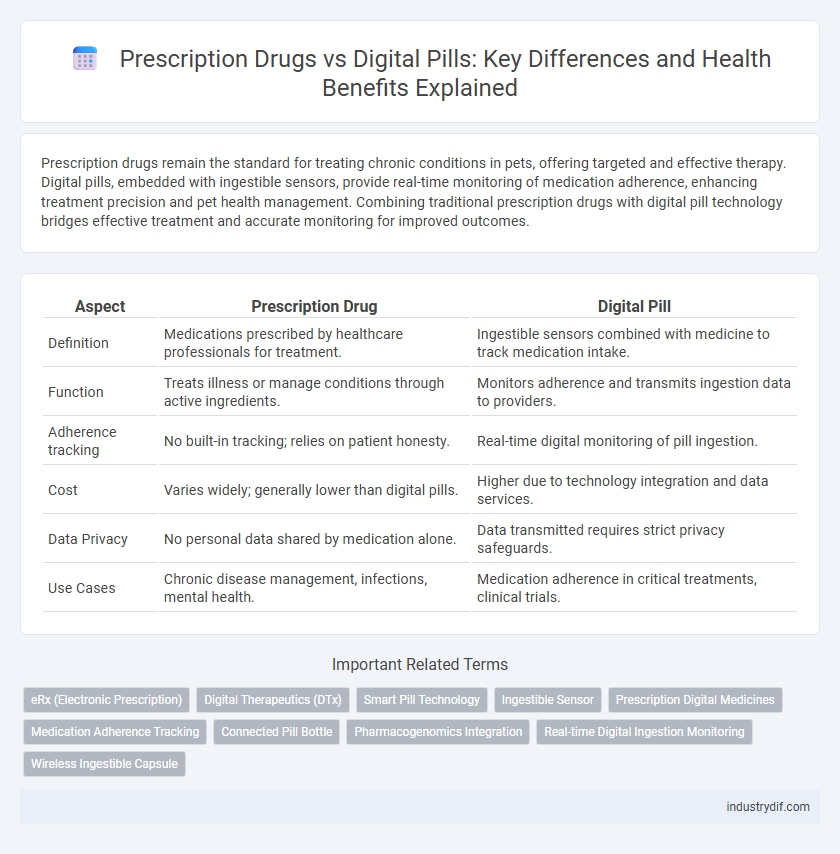
| Aspect | Prescription Drug | Digital Pill |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Medications prescribed by healthcare professionals for treatment. | Ingestible sensors combined with medicine to track medication intake. |
| Function | Treats illness or manage conditions through active ingredients. | Monitors adherence and transmits ingestion data to providers. |
| Adherence tracking | No built-in tracking; relies on patient honesty. | Real-time digital monitoring of pill ingestion. |
| Cost | Varies widely; generally lower than digital pills. | Higher due to technology integration and data services. |
| Data Privacy | No personal data shared by medication alone. | Data transmitted requires strict privacy safeguards. |
| Use Cases | Chronic disease management, infections, mental health. | Medication adherence in critical treatments, clinical trials. |
Understanding Prescription Drugs: Traditional Medication Overview
Prescription drugs are conventional medications synthesized or derived from natural sources to treat, manage, or prevent illnesses through targeted pharmacological effects. These medications undergo rigorous clinical trials and regulatory approval to ensure safety, efficacy, and dosage accuracy for conditions ranging from acute infections to chronic diseases. Traditional prescription drugs are typically administered orally, topically, or via injection, relying on patient adherence without integrated monitoring capabilities.
What Is a Digital Pill?
A digital pill is a medication embedded with a tiny ingestible sensor that transmits data to external devices, enabling real-time monitoring of patient adherence. Unlike traditional prescription drugs, digital pills provide healthcare providers with precise information on dosage intake and timing, improving treatment accuracy and patient outcomes. This advanced technology integrates pharmaceuticals and digital health, transforming compliance tracking and personalized medicine.
How Prescription Drugs Work
Prescription drugs work by interacting with specific biological targets, such as receptors or enzymes, to alter physiological processes and treat medical conditions. These medications are metabolized through the body's digestive and circulatory systems to deliver active compounds at therapeutic concentrations to affected areas. Unlike digital pills, which contain sensors to monitor ingestion, traditional prescription drugs focus solely on the biochemical effects within the body.
The Technology Behind Digital Pills
Digital pills incorporate ingestible sensors that activate upon contact with stomach fluids, transmitting real-time data to healthcare providers via Bluetooth-enabled wearable patches. This technology enables precise monitoring of medication adherence, improving treatment outcomes and patient compliance. Advanced biocompatible materials ensure safe digestion while integrating microchips, accelerometers, and wireless transmitters for seamless communication within the digital health ecosystem.
Comparing Efficacy: Prescription Drugs vs. Digital Pills
Prescription drugs deliver active pharmaceutical ingredients directly to the body, ensuring targeted therapeutic effects with well-established dosing protocols. Digital pills incorporate ingestible sensors to monitor medication adherence and physiological responses, enhancing treatment customization and patient compliance. Comparative studies indicate that digital pills can improve efficacy by providing real-time data, reducing missed doses, and enabling personalized adjustments, whereas traditional prescription drugs rely solely on patient reporting and periodic clinical assessments.
Patient Compliance and Adherence: Key Differences
Prescription drugs require patients to remember specific dosages and timing, often leading to missed or incorrect doses that reduce treatment effectiveness. Digital pills contain ingestible sensors that communicate medication ingestion data to healthcare providers, significantly enhancing patient compliance and adherence through real-time monitoring. Studies show that digital pill technology can improve adherence rates by up to 30%, reducing hospitalizations and improving overall health outcomes.
Safety and Privacy Concerns in Digital Pill Usage
Digital pills integrate ingestible sensors that track medication adherence, raising safety concerns about potential device malfunction or interference with drug efficacy. Privacy issues emerge from data collection, storage, and transmission, risking unauthorized access to sensitive health information. Robust encryption protocols and strict regulatory compliance are essential to safeguard patient confidentiality and ensure secure digital pill usage.
Regulatory Landscape: Approval Processes for Drugs and Digital Pills
Prescription drugs undergo rigorous evaluation by regulatory agencies such as the FDA, involving multiple phases of clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy before approval. Digital pills, which combine medication with ingestible sensors, face additional scrutiny for both pharmaceutical and digital components, requiring approval not only for safety and effectiveness of the drug but also for data accuracy and cybersecurity standards. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to address the complexities of digital health technologies, with agencies developing specialized guidelines to facilitate the integration of digital pills into clinical practice.
Cost Considerations: Traditional vs. Digital Medication
Prescription drugs generally incur costs related to manufacturing, distribution, and insurance coverage, often resulting in higher out-of-pocket expenses for patients. Digital pills, integrating ingestible sensors with medication, may involve increased upfront costs due to advanced technology and data management but potentially reduce long-term healthcare expenses through improved adherence and monitoring. Cost considerations between traditional and digital medication depend on factors such as healthcare policies, patient compliance, and overall treatment outcomes.
The Future of Prescription Medicine: Integrating Digital Pills
Digital pills represent the future of prescription medicine by combining traditional pharmaceuticals with ingestible sensors that provide real-time adherence data to healthcare providers. This technology enhances patient monitoring, ensures accurate dosage intake, and allows personalized treatment adjustments based on digital feedback. Integrating digital pills into prescription protocols promises improved therapeutic outcomes and reduced medication errors in clinical practice.
Related Important Terms
eRx (Electronic Prescription)
Electronic prescriptions (eRx) streamline the prescribing process by allowing healthcare providers to send prescription data directly to pharmacies, enhancing accuracy and reducing medication errors in both traditional prescription drugs and emerging digital pills. Digital pills, which incorporate ingestible sensors, complement eRx systems by providing real-time adherence data, thereby improving patient monitoring and personalized treatment plans.
Digital Therapeutics (DTx)
Digital therapeutics (DTx) deliver clinically validated medical interventions through software, offering personalized treatment plans that complement or replace traditional prescription drugs for chronic disease management. These evidence-based digital pills enhance patient adherence, enable real-time monitoring, and reduce healthcare costs by integrating behavioral therapy and medication management into daily life.
Smart Pill Technology
Smart pill technology integrates sensors within prescription drugs to monitor medication adherence and physiological responses, enhancing personalized treatment accuracy. Digital pills transmit real-time data to healthcare providers, enabling timely interventions and improving patient outcomes compared to traditional prescription drugs.
Ingestible Sensor
Prescription drugs embedded with ingestible sensors enable real-time monitoring of patient adherence by transmitting data upon consumption, enhancing personalized treatment plans. Digital pills integrate traditional medication with advanced sensor technology to improve accuracy in dosage tracking and ensure timely therapeutic interventions.
Prescription Digital Medicines
Prescription digital medicines integrate FDA-approved ingestible sensors within conventional drugs, enabling real-time monitoring of patient adherence and physiological responses through connected devices. These advanced formulations enhance treatment precision and improve health outcomes by providing actionable data to healthcare providers for personalized care management.
Medication Adherence Tracking
Prescription drugs traditionally rely on patient self-reporting and periodic check-ins to monitor medication adherence, which can result in inaccurate compliance data. Digital pills, embedded with ingestible sensors, enable real-time tracking of medication intake, improving adherence monitoring and enabling healthcare providers to deliver timely interventions.
Connected Pill Bottle
Connected pill bottles enhance medication adherence by tracking prescription drug usage in real-time and sending reminders to patients. Unlike digital pills that transmit ingestion data internally, connected pill bottles externally monitor dosage schedules to ensure consistent treatment compliance.
Pharmacogenomics Integration
Pharmacogenomics integration enhances prescription drug efficacy by tailoring medication based on genetic profiles, minimizing adverse effects. Digital pills complement this approach by providing real-time adherence data, enabling personalized treatment adjustments and improved patient outcomes.
Real-time Digital Ingestion Monitoring
Prescription drugs have traditionally relied on patient self-reporting and periodic pill counts for adherence tracking, which can be inaccurate and delay intervention. Digital pills, embedded with ingestible sensors, enable real-time digital ingestion monitoring by transmitting data directly to healthcare providers, enhancing medication adherence accuracy and facilitating timely treatment adjustments.
Wireless Ingestible Capsule
Wireless ingestible capsules represent an innovative advancement in prescription drug delivery, enabling real-time monitoring of medication adherence and physiological data through embedded sensors. These digital pills enhance treatment accuracy and patient compliance by providing clinicians with precise information on drug ingestion timing and absorption, potentially improving chronic disease management outcomes.
Prescription Drug vs Digital Pill Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com