Data refers to the information that organizations actively collect, analyze, and utilize to drive decision-making and optimize operations. Dark data consists of the information companies gather but fail to use or analyze, often stored in inaccessible formats or overlooked systems. Unlocking the potential of dark data can reveal valuable insights, enhance analytics, and improve overall business intelligence.
Table of Comparison
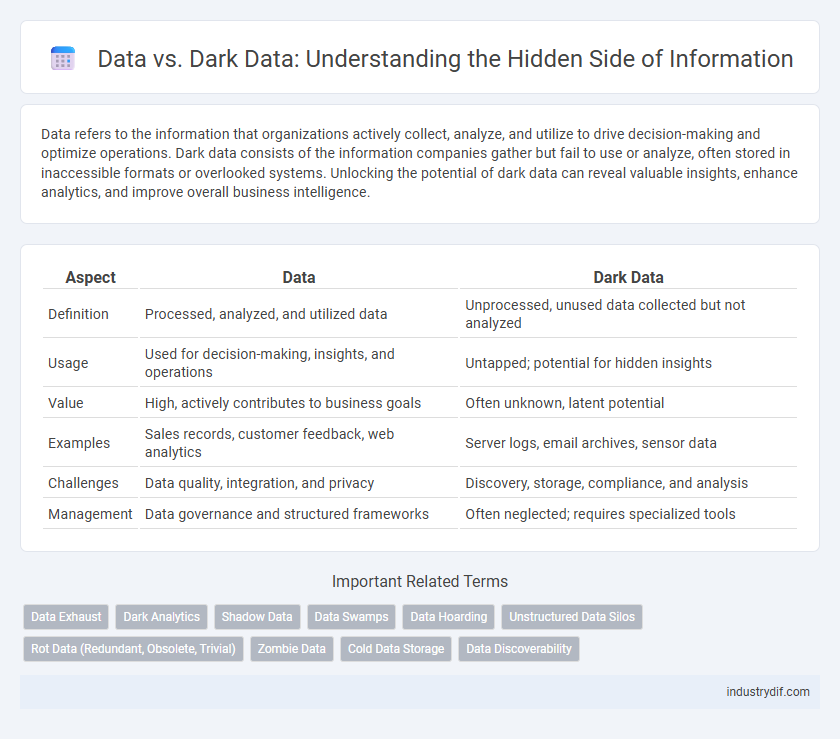
| Aspect | Data | Dark Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processed, analyzed, and utilized data | Unprocessed, unused data collected but not analyzed |
| Usage | Used for decision-making, insights, and operations | Untapped; potential for hidden insights |
| Value | High, actively contributes to business goals | Often unknown, latent potential |
| Examples | Sales records, customer feedback, web analytics | Server logs, email archives, sensor data |
| Challenges | Data quality, integration, and privacy | Discovery, storage, compliance, and analysis |
| Management | Data governance and structured frameworks | Often neglected; requires specialized tools |
Understanding Data: An Overview
Data encompasses all collected information that organizations actively use to drive decision-making, innovation, and operational efficiency, while dark data refers to the vast amount of unexplored, unstructured, or hidden information generated through everyday business activities that remains unanalyzed. Understanding the distinction between data and dark data is crucial for maximizing business intelligence and uncovering hidden insights that can improve strategic outcomes. Effective management of both data types involves leveraging advanced analytics, machine learning, and data governance practices to convert overlooked dark data into valuable information assets.
Defining Dark Data in Modern Enterprises
Dark data in modern enterprises refers to the unstructured, unused, and often overlooked information collected during regular business operations but not analyzed or leveraged for decision-making. This type of data includes emails, customer call logs, social media interactions, and log files that remain untapped due to lack of proper tools or awareness. Identifying and managing dark data is crucial for organizations to unlock hidden insights, improve operational efficiency, and enhance competitive advantage.
Sources and Types of Data Collected
Data encompasses structured information from sources like databases, sensors, and user inputs, enabling analysis and decision-making. Dark data consists of unstructured or semi-structured information from emails, server logs, and social media interactions, often overlooked and unutilized in business processes. Understanding the distinct sources and varied formats of data versus dark data is crucial for optimizing data management strategies and uncovering hidden value.
Unveiling the Hidden World of Dark Data
Dark data comprises unstructured, unused information generated through everyday business activities, often overlooked in traditional data management strategies. Unlike structured data stored in databases, dark data exists in formats such as emails, customer call recordings, and log files, harboring potential insights hidden from analytics tools. Unlocking the value of dark data requires advanced techniques like artificial intelligence and machine learning to transform it into actionable business intelligence and drive data-driven decisions.
Risks Associated with Unused Dark Data
Unused dark data poses significant security risks due to its unmonitored storage, increasing the potential for data breaches and unauthorized access. Organizations face compliance challenges as regulations like GDPR and CCPA mandate proper management of all collected data, including dark data. Inefficient use of resources and increased storage costs further escalate operational risks linked to unmanaged dark data pools.
Opportunities Presented by Leveraging Dark Data
Leveraging dark data presents significant opportunities for organizations seeking to enhance decision-making and innovation by uncovering hidden insights within unstructured or unused information. This untapped data can improve customer experiences, optimize operations, and identify new market trends, leading to competitive advantages. Harnessing advanced analytics and machine learning techniques enables companies to transform dark data into valuable assets that drive growth and efficiency.
Data Management: Best Practices and Strategies
Effective data management requires distinguishing between structured data and dark data--the vast, unstructured information often overlooked in analytics. Implementing best practices such as regular data audits, metadata tagging, and automated classification helps organizations uncover hidden insights within dark data while ensuring compliance and improving data quality. Leveraging advanced analytics tools and establishing clear governance policies maximize the value extracted from both traditional data and dark data reservoirs.
Compliance and Security Implications of Dark Data
Dark data, often unstructured and unmanaged, poses significant compliance risks due to its hidden nature and potential to contain sensitive information subject to regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Security implications include increased vulnerability to breaches, as dark data lacks proper encryption, monitoring, and access controls. Organizations must implement comprehensive data governance strategies to mitigate risks associated with dark data while ensuring regulatory compliance and protecting sensitive information.
Data vs Dark Data: Impact on Business Intelligence
Data drives business intelligence by providing actionable insights through structured and analyzed information, whereas dark data remains unutilized, representing a significant missed opportunity for competitive advantage. Dark data includes untapped information from customer interactions, system logs, and social media, which can reveal hidden patterns and forecast trends when properly leveraged. Integrating dark data into business intelligence platforms enhances decision-making accuracy, optimizes operational efficiency, and uncovers new revenue streams.
Transforming Dark Data into Business Value
Dark data, often hidden in unstructured formats like emails, logs, and multimedia files, represents a vast untapped resource with potential for business value. Advanced analytics, machine learning, and AI technologies enable organizations to extract actionable insights from this dark data, transforming it into strategic assets for decision-making and innovation. Leveraging dark data improves operational efficiency, uncovers new market opportunities, and enhances customer experience, driving measurable business growth.
Related Important Terms
Data Exhaust
Data exhaust refers to the digital trail generated unintentionally during user interactions, often classified as dark data due to its underutilization in analysis. Unlike structured data, data exhaust comprises logs, metadata, and system-generated information that hold potential insights for improving decision-making and operational efficiency when properly harnessed.
Dark Analytics
Dark analytics unlocks insights hidden within dark data, which consists of unstructured, untagged, or unused information not captured in traditional data repositories. Leveraging machine learning and AI, dark analytics extracts valuable patterns and trends from these vast, overlooked data reserves, enhancing decision-making and strategic planning.
Shadow Data
Shadow data refers to information collected and stored outside an organization's formal data management systems, often created and maintained by individual employees for specific projects. This type of data, a subset of dark data, poses significant challenges for security, compliance, and analytics due to its unmonitored and unmanaged nature.
Data Swamps
Data swamps emerge when dark data overwhelms managed data environments, resulting in disorganized, inaccessible, and low-quality data repositories. Effective governance and metadata management are critical to prevent data swamps by ensuring data integrity, discoverability, and usability across enterprise systems.
Data Hoarding
Data hoarding refers to the excessive accumulation of both structured data and dark data, often without proper organization or analysis, which hampers efficient decision-making and increases storage costs. Distinguishing valuable data from irrelevant dark data is crucial for optimizing data management strategies and enhancing organizational performance.
Unstructured Data Silos
Unstructured data silos, consisting of untagged files, emails, multimedia, and documents, contribute significantly to the volume of dark data within organizations, obscuring valuable insights and increasing storage costs. Unlike structured data warehouses, these isolated silos lack integration and metadata, hindering efficient data analysis and enterprise-wide accessibility.
Rot Data (Redundant, Obsolete, Trivial)
Rot data, also known as Redundant, Obsolete, and Trivial (ROT) data, significantly burdens organizations by occupying valuable storage space and complicating data management efforts. Identifying and eliminating ROT data enhances data quality, reduces costs, and improves overall decision-making compared to managing dark data, which remains unstructured and often hidden within systems.
Zombie Data
Zombie data refers to unattended, obsolete information that remains stored but unused, posing security risks and increasing storage costs. Unlike structured data actively utilized for analysis, zombie data lurks in databases or archives, contributing to dark data that organizations fail to leverage or even recognize.
Cold Data Storage
Cold data storage efficiently archives large volumes of infrequently accessed information, minimizing costs compared to hot data storage solutions. Dark data, often unstructured and unanalyzed within these cold storage systems, represents a hidden resource that organizations can leverage for strategic insights by applying advanced analytics and machine learning techniques.
Data Discoverability
Data discoverability enhances organizational efficiency by enabling easy access and retrieval of structured data through metadata tagging, indexing, and cataloging. Dark data, however, remains hidden and unstructured, limiting its discoverability and value extraction despite its potential insights.
Data vs Dark Data Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com