Information sharing involves distributing specific data sets among selected individuals or groups to enhance collaboration and decision-making. Data democratization expands this concept by making data accessible to all members of an organization, empowering them to analyze and utilize information independently. This shift from restricted access to open availability fosters innovation, improves transparency, and accelerates insights across all levels.
Table of Comparison
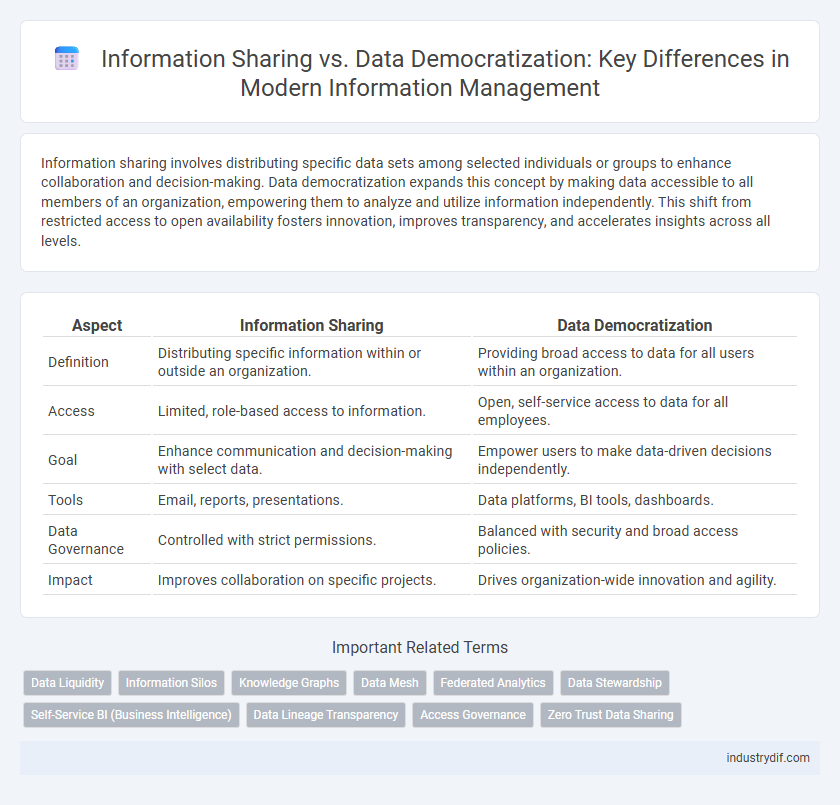
| Aspect | Information Sharing | Data Democratization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributing specific information within or outside an organization. | Providing broad access to data for all users within an organization. |
| Access | Limited, role-based access to information. | Open, self-service access to data for all employees. |
| Goal | Enhance communication and decision-making with select data. | Empower users to make data-driven decisions independently. |
| Tools | Email, reports, presentations. | Data platforms, BI tools, dashboards. |
| Data Governance | Controlled with strict permissions. | Balanced with security and broad access policies. |
| Impact | Improves collaboration on specific projects. | Drives organization-wide innovation and agility. |
Understanding Information Sharing in Modern Organizations
Information sharing in modern organizations involves the deliberate exchange of relevant data and insights across departments to enhance collaboration, decision-making, and innovation. Effective information sharing relies on secure platforms and clear communication protocols to ensure accuracy and confidentiality. Emphasizing transparency and accessibility fosters a culture where employees are empowered to access and utilize shared knowledge efficiently.
Defining Data Democratization: Scope and Significance
Data democratization refers to the process of making data accessible to all employees within an organization, regardless of their technical expertise, enabling informed decision-making across all levels. It expands the scope of information sharing by breaking down traditional data silos and providing tools and platforms that facilitate seamless data access, analysis, and collaboration. This approach significantly enhances organizational agility and innovation by empowering a data-driven culture where users can leverage insights independently and responsibly.
Key Differences Between Information Sharing and Data Democratization
Information sharing involves controlled distribution of data among specific users or groups, emphasizing security and compliance, whereas data democratization enables broader, organization-wide access to data without gatekeepers, promoting self-service analytics and decision-making. Information sharing often relies on predefined channels and permissions, while data democratization leverages user-friendly tools and platforms to empower non-technical users with direct data access. The key difference lies in the scope and accessibility: information sharing is limited and curated, whereas data democratization fosters open, widespread data availability.
Benefits of Information Sharing for Business Efficiency
Information sharing enhances business efficiency by enabling seamless communication and collaboration across departments, leading to faster decision-making. It reduces redundancies and errors by ensuring all stakeholders have access to accurate, up-to-date information. This transparency fosters innovation and agility, helping businesses adapt quickly to market changes.
How Data Democratization Empowers Decision-Makers
Data democratization empowers decision-makers by providing widespread access to accurate, real-time data across all organizational levels, fostering informed decisions without bottlenecks. Unlike traditional information sharing, which often restricts data flow to select individuals, democratization enables autonomous analysis and insight generation, enhancing agility and innovation. Enhanced data literacy programs complement this approach, ensuring decision-makers can effectively interpret complex data and drive strategic initiatives.
Challenges in Implementing Information Sharing Systems
Implementing information sharing systems faces challenges such as data security risks, compliance with privacy regulations, and ensuring data accuracy across distributed sources. Organizational silos and resistance to change hinder seamless collaboration, while integrating disparate technologies complicates data interoperability. Effective governance and ongoing training remain critical to overcoming these obstacles and fostering a culture of open information exchange.
Barriers to Achieving True Data Democratization
Barriers to achieving true data democratization include data silos, lack of standardized governance, and inadequate data literacy across organizations. Restricted access to quality data and concerns over security, compliance, and privacy further hinder widespread data sharing. Overcoming cultural resistance and investing in scalable infrastructure are essential to unlocking the full potential of democratized data environments.
Best Practices for Balancing Security and Accessibility
Implementing role-based access controls ensures sensitive information remains secure while enabling appropriate data sharing across teams. Encrypting data both at rest and in transit protects against unauthorized access, supporting data democratization initiatives. Regular audits and user training foster a culture of accountability, balancing security needs with accessibility for effective information sharing.
Tools and Technologies Driving Information Sharing and Data Democratization
Advanced analytics platforms and cloud-based collaboration tools are pivotal in driving information sharing by enabling real-time access and seamless communication across organizational boundaries. Data democratization is propelled by self-service business intelligence solutions and AI-powered data cataloging technologies that empower non-technical users to discover, analyze, and utilize data independently. Together, these technologies enhance data visibility, reduce bottlenecks, and foster a data-driven culture across enterprises.
The Future of Organizational Knowledge: Integration or Divergence?
Information sharing promotes controlled access to specific data sets within an organization, ensuring accuracy and security, while data democratization empowers all employees with unrestricted data access for innovation and decision-making. The future of organizational knowledge hinges on integrating both approaches, balancing governance with open access to foster collaboration and agility. Leveraging advanced analytics and robust data governance frameworks will be critical to harmonizing information sharing and data democratization for sustainable competitive advantage.
Related Important Terms
Data Liquidity
Data liquidity enhances the flow and accessibility of data across organizational boundaries, enabling seamless information sharing and accelerating decision-making processes. Unlike traditional information sharing, data democratization emphasizes empowering all users with easy, real-time access to accurate and relevant datasets, increasing operational agility and innovation potential.
Information Silos
Information silos hinder effective information sharing by isolating data within departments, limiting organizational transparency and collaboration. Data democratization breaks down these silos by providing broader access to data, enabling decision-makers across all levels to leverage insights and drive innovation.
Knowledge Graphs
Information sharing involves controlled dissemination of data among stakeholders, whereas data democratization empowers broader organizational access to data, promoting autonomy and innovation. Knowledge graphs enhance both by structuring complex relationships and enabling intuitive querying, thereby improving data integration, context understanding, and decision-making accuracy.
Data Mesh
Information sharing involves controlled access to specific datasets, whereas data democratization empowers all organizational users with self-serve access to data, enabling decentralized decision-making. Data Mesh architecture enhances data democratization by decentralizing data ownership to domain teams, promoting scalability and agility in large enterprises.
Federated Analytics
Information sharing enables controlled access to specific datasets across organizations, while data democratization promotes widespread availability of data to empower all users. Federated analytics supports these goals by allowing secure, decentralized data analysis without moving sensitive data, thus preserving privacy and compliance.
Data Stewardship
Data stewardship plays a critical role in both information sharing and data democratization by ensuring data quality, security, and compliance across the organization. Effective data stewardship fosters trust and accountability, enabling broader access to data while maintaining governance and ethical standards.
Self-Service BI (Business Intelligence)
Information sharing enables controlled access to data among specific users or teams, whereas data democratization in Self-Service BI empowers broader organizational access to analytics tools, fostering data-driven decision-making at all levels. Implementing data democratization with Self-Service BI platforms enhances agility by allowing users to independently explore data, generate reports, and derive insights without reliance on IT or data specialists.
Data Lineage Transparency
Data lineage transparency enhances data democratization by providing clear visibility into the origin, movement, and transformation of data, fostering trust and accountability across organizations. Unlike traditional information sharing, which often limits access to raw data, data democratization empowers users with a comprehensive understanding of data provenance, enabling informed decision-making and compliance adherence.
Access Governance
Access governance in information sharing emphasizes controlled, role-based permissions ensuring sensitive data is only accessible to authorized users, reducing security risks and compliance issues. Data democratization promotes broader data access through user-friendly platforms, but requires strong governance frameworks to maintain data integrity and prevent unauthorized usage.
Zero Trust Data Sharing
Zero Trust Data Sharing enforces strict access controls and continuous verification, ensuring that information sharing occurs securely without exposing all data to every user. Unlike general data democratization, which promotes broad data accessibility, Zero Trust frameworks limit data exposure based on strict identity and context verification, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Information Sharing vs Data Democratization Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com