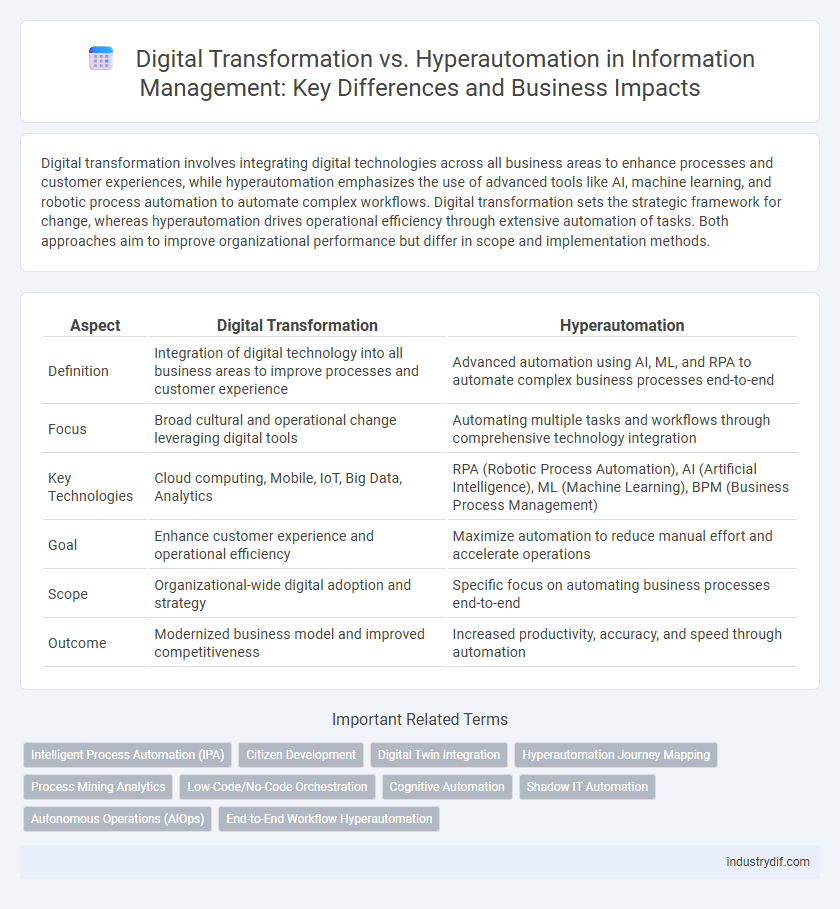
Digital transformation involves integrating digital technologies across all business areas to enhance processes and customer experiences, while hyperautomation emphasizes the use of advanced tools like AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation to automate complex workflows. Digital transformation sets the strategic framework for change, whereas hyperautomation drives operational efficiency through extensive automation of tasks. Both approaches aim to improve organizational performance but differ in scope and implementation methods.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Digital Transformation | Hyperautomation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of digital technology into all business areas to improve processes and customer experience | Advanced automation using AI, ML, and RPA to automate complex business processes end-to-end |
| Focus | Broad cultural and operational change leveraging digital tools | Automating multiple tasks and workflows through comprehensive technology integration |
| Key Technologies | Cloud computing, Mobile, IoT, Big Data, Analytics | RPA (Robotic Process Automation), AI (Artificial Intelligence), ML (Machine Learning), BPM (Business Process Management) |
| Goal | Enhance customer experience and operational efficiency | Maximize automation to reduce manual effort and accelerate operations |
| Scope | Organizational-wide digital adoption and strategy | Specific focus on automating business processes end-to-end |
| Outcome | Modernized business model and improved competitiveness | Increased productivity, accuracy, and speed through automation |
Introduction to Digital Transformation and Hyperautomation
Digital Transformation involves integrating digital technologies into all business areas to enhance operational efficiency, customer experience, and innovation. Hyperautomation extends this concept by leveraging advanced tools like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic process automation to automate complex business processes beyond traditional automation. Both strategies focus on streamlining workflows, reducing manual intervention, and driving faster decision-making in the digital era.
Key Definitions: Digital Transformation vs Hyperautomation
Digital Transformation refers to the integration of digital technology into all areas of a business, fundamentally changing how organizations operate and deliver value to customers. Hyperautomation extends this concept by combining advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and robotic process automation (RPA) to automize complex business processes at scale. The core difference lies in Digital Transformation being a broader strategic initiative, while Hyperautomation focuses specifically on automating workflows to increase efficiency and accuracy.
Core Technologies Driving Each Approach
Digital transformation is primarily driven by core technologies such as cloud computing, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence, enabling organizations to modernize operations and enhance customer experiences. Hyperautomation relies heavily on robotic process automation (RPA), advanced machine learning algorithms, and intelligent business process management suites to automate complex workflows and increase efficiency. Both approaches leverage AI, but hyperautomation focuses more on integrating multiple automation tools to create end-to-end automated processes.
Business Objectives and Strategic Outcomes
Digital transformation drives business objectives by leveraging digital technologies to enhance operational efficiency, customer experience, and market agility, enabling organizations to innovate and stay competitive. Hyperautomation accelerates strategic outcomes by automating complex workflows through AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation, reducing costs and improving accuracy across enterprise processes. Together, these approaches align digital initiatives with measurable business goals, fostering sustainable growth and optimized resource utilization.
Industry Applications: Use Cases Compared
Digital transformation drives industry innovation by integrating digital technologies to streamline operations, enhance customer engagement, and improve decision-making across sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. Hyperautomation expands on this by combining AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation to autonomously optimize complex workflows, reduce manual tasks, and increase efficiency, particularly in supply chain management, financial services, and telecommunications. Use cases in automotive manufacturing demonstrate how digital transformation digitizes production lines while hyperautomation enables real-time defect detection and predictive maintenance for superior operational excellence.
Benefits and Challenges of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation offers benefits such as enhanced operational efficiency, improved customer experiences, and increased agility through the adoption of cloud computing, AI, and IoT technologies. Challenges include high implementation costs, resistance to organizational change, and data security concerns that require robust governance frameworks. By addressing these obstacles, businesses can harness digital transformation to drive innovation and maintain competitive advantage in rapidly evolving markets.
Advantages and Limitations of Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation accelerates business processes by integrating advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation, leading to increased operational efficiency and reduced human error. Its advantages include enhanced scalability, improved decision-making through data analytics, and the ability to automate complex workflows across multiple systems. Limitations involve high implementation costs, the need for skilled personnel to manage sophisticated tools, and potential challenges in integrating legacy systems with new automation technologies.
Integration Strategies and Best Practices
Digital Transformation leverages integration strategies such as API management, cloud platforms, and real-time data synchronization to unify disparate systems and enhance operational agility. Hyperautomation emphasizes combining robotic process automation (RPA) with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to automate complex workflows, requiring seamless integration of intelligent tools across IT environments. Best practices include adopting modular architectures, ensuring data interoperability through standardized protocols, and continuous monitoring to optimize integration performance and scalability.
Measuring ROI: Metrics and KPIs
Measuring ROI in digital transformation involves tracking metrics such as customer acquisition cost, revenue growth, and operational efficiency improvements, while hyperautomation ROI focuses on KPIs like process automation rate, error reduction, and cycle time savings. Digital transformation emphasizes broad organizational benefits measured by KPIs including employee productivity and digital adoption rates. Hyperautomation leverages real-time data analytics to quantify gains in workflow optimization and technology utilization, providing precise ROI insights.
Future Trends in Digital Transformation and Hyperautomation
Future trends in digital transformation emphasize AI-driven decision-making, cloud-native technologies, and the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) for enhanced automation and data analytics. Hyperautomation advances with intelligent process automation combining robotic process automation (RPA), machine learning, and natural language processing to accelerate operational efficiency and scalability. Organizations adopting these trends will experience increased agility, reduced operational costs, and enhanced customer experiences in the evolving digital landscape.
Related Important Terms
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)
Digital Transformation encompasses the integration of digital technologies across business processes, while Hyperautomation specifically leverages Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) to combine AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA) for end-to-end process optimization. IPA drives hyperautomation by enabling advanced data analysis, decision-making, and dynamic workflow adjustments, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and agility.
Citizen Development
Digital transformation accelerates business innovation through technology integration, while hyperautomation enhances this by combining AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation to streamline workflows; citizen development empowers non-technical employees to create applications, increasing agility and reducing IT bottlenecks. Organizations leveraging citizen developers within hyperautomation frameworks achieve faster deployment of solutions, improved process efficiency, and greater adaptability to market changes.
Digital Twin Integration
Digital twin integration enhances digital transformation by creating real-time virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling precise monitoring and optimization of processes. Hyperautomation leverages these digital twins to automate complex workflows through AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation, driving higher efficiency and predictive insights.
Hyperautomation Journey Mapping
Hyperautomation journey mapping involves identifying and analyzing business processes to prioritize automation opportunities using AI, machine learning, and RPA technologies. This approach enhances digital transformation efforts by creating a detailed roadmap that accelerates operational efficiency and drives continuous innovation.
Process Mining Analytics
Process Mining Analytics plays a critical role in both Digital Transformation and Hyperautomation by providing data-driven insights into business processes, enabling organizations to identify inefficiencies and optimize workflows. While Digital Transformation leverages these analytics for broad organizational change, Hyperautomation integrates Process Mining with AI and RPA to automate complex, end-to-end processes with higher precision and scalability.
Low-Code/No-Code Orchestration
Digital transformation leverages low-code/no-code orchestration to accelerate application development and streamline business processes, enabling organizations to adapt rapidly to market changes. Hyperautomation extends this capability by integrating AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation, creating fully automated workflows that optimize efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Cognitive Automation
Cognitive automation, a subset of hyperautomation, enhances digital transformation by integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning to replicate human decision-making processes, enabling more advanced data analysis and operational efficiency. Unlike basic digital transformation tools, cognitive automation drives intelligent process automation, transforming complex workflows through natural language processing, computer vision, and predictive analytics.
Shadow IT Automation
Shadow IT automation poses significant risks in digital transformation initiatives by enabling unmonitored process automations that bypass traditional IT controls, potentially causing security vulnerabilities and data silos. Embracing hyperautomation with centralized governance integrates AI-driven tools and robotic process automation (RPA) to eliminate shadow IT practices, optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring compliance across enterprises.
Autonomous Operations (AIOps)
Digital Transformation integrates AIOps to enhance Autonomous Operations by leveraging AI-driven analytics, automating IT incident response, and optimizing resource management. Hyperautomation extends this approach through advanced AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation to fully automate complex workflows, improving system resilience and operational efficiency.
End-to-End Workflow Hyperautomation
End-to-End Workflow Hyperautomation extends digital transformation by integrating AI, RPA, and advanced analytics to automate complex business processes across multiple systems, enabling seamless data flow and decision-making without human intervention. This holistic approach optimizes operational efficiency, reduces errors, and accelerates scalability beyond traditional digital transformation initiatives.
Digital Transformation vs Hyperautomation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com