Information systems are structured frameworks designed to collect, process, store, and distribute data to support decision-making and organizational operations. Data fabric, on the other hand, is an advanced architectural approach that integrates disparate data sources across hybrid and multi-cloud environments, enabling seamless data access and management. While information systems focus on specific applications and workflows, data fabric emphasizes unified data connectivity and governance across the entire enterprise.
Table of Comparison
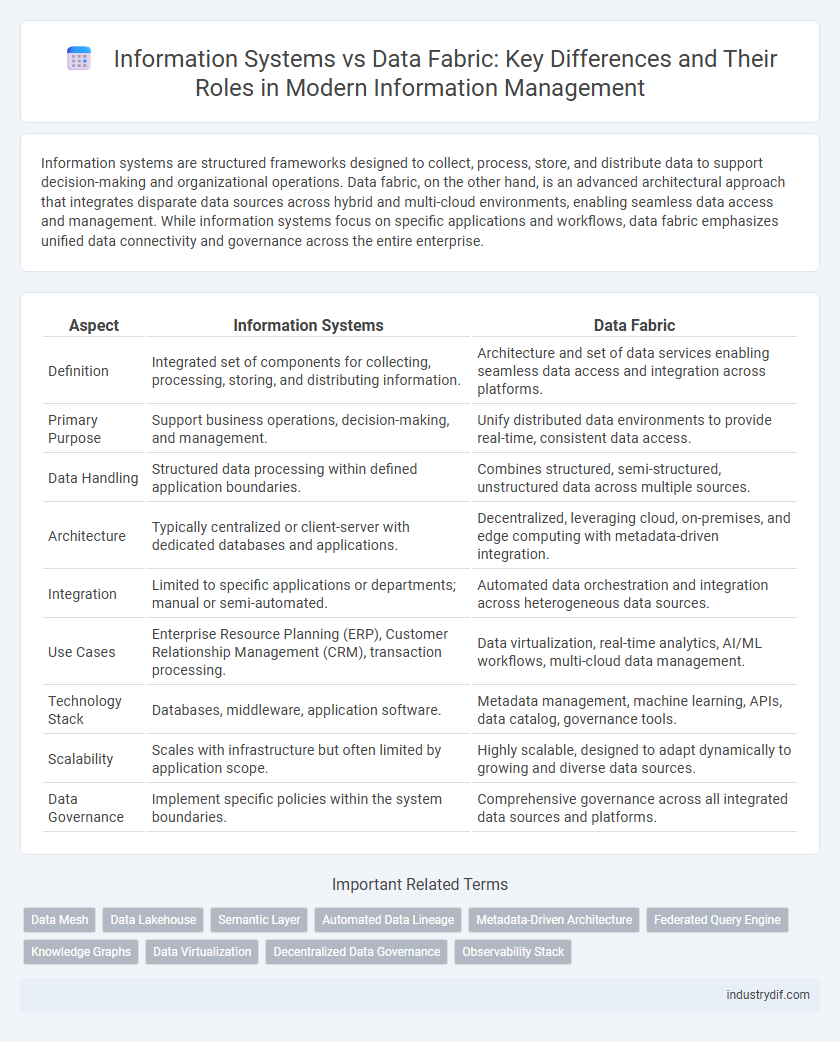
| Aspect | Information Systems | Data Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated set of components for collecting, processing, storing, and distributing information. | Architecture and set of data services enabling seamless data access and integration across platforms. |
| Primary Purpose | Support business operations, decision-making, and management. | Unify distributed data environments to provide real-time, consistent data access. |
| Data Handling | Structured data processing within defined application boundaries. | Combines structured, semi-structured, unstructured data across multiple sources. |
| Architecture | Typically centralized or client-server with dedicated databases and applications. | Decentralized, leveraging cloud, on-premises, and edge computing with metadata-driven integration. |
| Integration | Limited to specific applications or departments; manual or semi-automated. | Automated data orchestration and integration across heterogeneous data sources. |
| Use Cases | Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), transaction processing. | Data virtualization, real-time analytics, AI/ML workflows, multi-cloud data management. |
| Technology Stack | Databases, middleware, application software. | Metadata management, machine learning, APIs, data catalog, governance tools. |
| Scalability | Scales with infrastructure but often limited by application scope. | Highly scalable, designed to adapt dynamically to growing and diverse data sources. |
| Data Governance | Implement specific policies within the system boundaries. | Comprehensive governance across all integrated data sources and platforms. |
Introduction to Information Systems and Data Fabric
Information Systems are integrated frameworks designed to collect, process, store, and distribute data to support decision-making, coordination, and control in organizations. Data Fabric is an advanced data management architecture that provides seamless integration, real-time access, and orchestration of data across diverse sources and environments. While Information Systems focus on processing and managing organizational information, Data Fabric enhances data accessibility and agility by unifying data infrastructure under a single, intelligent layer.
Key Concepts: Understanding Information Systems
Information systems integrate hardware, software, data, procedures, and people to collect, process, store, and distribute information essential for decision-making. These systems offer structured frameworks for managing data flows within organizations, supporting operations, management, and strategic goals. Understanding core components such as databases, networks, and user interfaces highlights the contrast with data fabric, which emphasizes seamless data integration across distributed environments.
Defining Data Fabric in Modern Enterprises
Data Fabric in modern enterprises refers to an integrated architecture that enables seamless data access, management, and sharing across diverse platforms and environments. Unlike traditional Information Systems that store and process data within siloed applications, Data Fabric uses intelligent automation and metadata-driven processes to unify data landscapes, enhancing real-time analytics and decision-making. This approach supports scalability, agility, and consistent data governance, crucial for enterprises managing vast, distributed data ecosystems.
Core Differences Between Information Systems and Data Fabric
Information systems integrate hardware, software, and processes to collect, process, and manage data for organizational decision-making. Data fabric is an architectural approach that unifies data management across diverse sources, enabling seamless access and analytics through automation and metadata-driven orchestration. Core differences lie in scope and functionality: information systems focus on structured workflows and transaction handling, while data fabric emphasizes real-time data integration, scalability, and pervasive data accessibility.
Information Management: Centralized vs. Distributed Approaches
Information systems rely on centralized information management to consolidate data in a unified repository, enhancing control and consistency across organizational processes. In contrast, data fabric employs a distributed approach that integrates data from multiple sources in real-time, enabling seamless access and agility without physical data movement. This distributed architecture in data fabric supports dynamic data governance and scalability, addressing the limitations of traditional centralized systems.
Integration Capabilities: Traditional vs. Data Fabric Solutions
Traditional information systems rely on predefined integration methods such as ETL processes, APIs, and middleware, often resulting in complex, siloed data environments. Data Fabric solutions use AI-driven automation and metadata management to create a unified, dynamic integration layer that supports real-time data access across disparate sources. This approach enhances scalability, reduces latency, and improves data consistency compared to conventional integration frameworks.
Data Governance and Security Implications
Data Fabric integrates data governance frameworks that enhance security by providing unified policy enforcement and real-time monitoring across distributed environments. Information Systems rely on traditional security measures that may not offer seamless visibility or automated compliance management, increasing risks of data breaches. Implementing Data Fabric improves data integrity and access controls, crucial for regulatory compliance and minimizing security vulnerabilities in complex data ecosystems.
Scalability and Flexibility in Information Delivery
Information Systems provide structured data management with scalability primarily through modular expansions and hardware enhancements, supporting consistent data processing across enterprise applications. Data Fabric offers greater flexibility by seamlessly integrating diverse data sources in real-time, enabling dynamic information delivery and adaptive analytics across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. The scalability of Data Fabric is enhanced by its distributed architecture, which optimizes data workflows and ensures responsive access regardless of data volume or complexity.
Use Cases: Industry Applications of Both Technologies
Information systems enable efficient management of organizational processes across industries such as finance, healthcare, and retail by integrating data collection, processing, and reporting. Data fabric technology enhances data accessibility and real-time analytics by unifying disparate data sources in sectors like manufacturing, telecommunications, and government, supporting advanced AI and machine learning applications. Use cases for information systems emphasize operational efficiency and decision support, while data fabric focuses on seamless data integration and dynamic data management for innovation-driven industries.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Information Systems and Data Fabric requires evaluating organizational data complexity, integration needs, and scalability goals. Information Systems provide structured frameworks for managing specific business processes, while Data Fabric offers a unified architecture that enables seamless data access across diverse platforms. Prioritizing factors like real-time data availability, automation capabilities, and ease of implementation ensures alignment with long-term digital transformation strategies.
Related Important Terms
Data Mesh
Data Mesh decentralizes data ownership by assigning domain-specific teams control over data pipelines, contrasting with centralized Information Systems and integrated Data Fabric architectures. This approach enhances scalability and agility by promoting domain-oriented data products and self-serve data infrastructure within the enterprise.
Data Lakehouse
Data Lakehouse combines the structured data management of Information Systems with the scalability and flexibility of Data Fabric, enabling unified analytics and real-time data processing. This architecture supports diverse workloads by integrating data lakes' large-scale storage with data warehouses' optimized query performance, streamlining enterprise data management and decision-making.
Semantic Layer
Information systems integrate diverse data sources and applications to support business processes, relying heavily on a semantic layer to standardize and interpret data meaning across platforms. Data fabric enhances this by creating a unified semantic layer that dynamically connects and harmonizes data from distributed environments, enabling real-time, context-aware analytics and decision-making.
Automated Data Lineage
Automated data lineage in information systems provides detailed tracking of data flow and transformations, enhancing transparency and compliance. Data fabric integrates automated data lineage across diverse sources, enabling real-time visibility and unified governance for complex data environments.
Metadata-Driven Architecture
Metadata-driven architecture in Information Systems organizes and manages data assets by leveraging detailed metadata to enable dynamic integration, governance, and interoperability across diverse data sources. In contrast, Data Fabric employs metadata as the foundation for creating a unified and intelligent data layer, facilitating seamless data access, real-time analytics, and automated data management across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Federated Query Engine
A Federated Query Engine in Information Systems enables seamless access and integration across diverse data sources without data consolidation, enhancing real-time analytics and operational efficiency. Unlike Data Fabric, which provides an overarching architecture for unified data management, the Federated Query Engine specializes in querying distributed databases, making it crucial for hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Knowledge Graphs
Knowledge graphs serve as a critical component in both information systems and data fabric by enabling semantic integration and real-time data relationships mapping across disparate sources. While information systems primarily focus on structured data management, data fabric leverages knowledge graphs to provide a unified, adaptive architecture for delivering seamless data access and contextual insights.
Data Virtualization
Information systems rely on structured frameworks to collect, process, and store data, while data fabric utilizes data virtualization technology to seamlessly integrate and access diverse data sources in real-time without physical movement. Data virtualization facilitates unified views across disparate databases and cloud environments, enabling faster decision-making and reducing data silos compared to traditional information systems.
Decentralized Data Governance
Information systems typically rely on centralized data governance models, which can create bottlenecks and reduce data agility across departments. Data fabric architecture enables decentralized data governance by integrating distributed data sources via automated metadata management and AI-driven analytics, enhancing data accessibility and control while maintaining compliance.
Observability Stack
Information systems integrate data processing and management tools, while data fabric provides a unified architecture for seamless data access across distributed environments; an observability stack enhances both by delivering real-time monitoring, tracing, and logging for improved system performance and data flow transparency. This integrated observability approach enables proactive issue detection, efficient troubleshooting, and optimized data governance in complex IT ecosystems.
Information Systems vs Data Fabric Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com