Information consists of raw, unprocessed facts and figures, while smart data is refined and contextually relevant, enabling better decision-making. Smart data enhances the value of information by filtering out noise and highlighting insights through analysis and interpretation. This transformation allows businesses to leverage data strategically for improved efficiency and innovation.
Table of Comparison
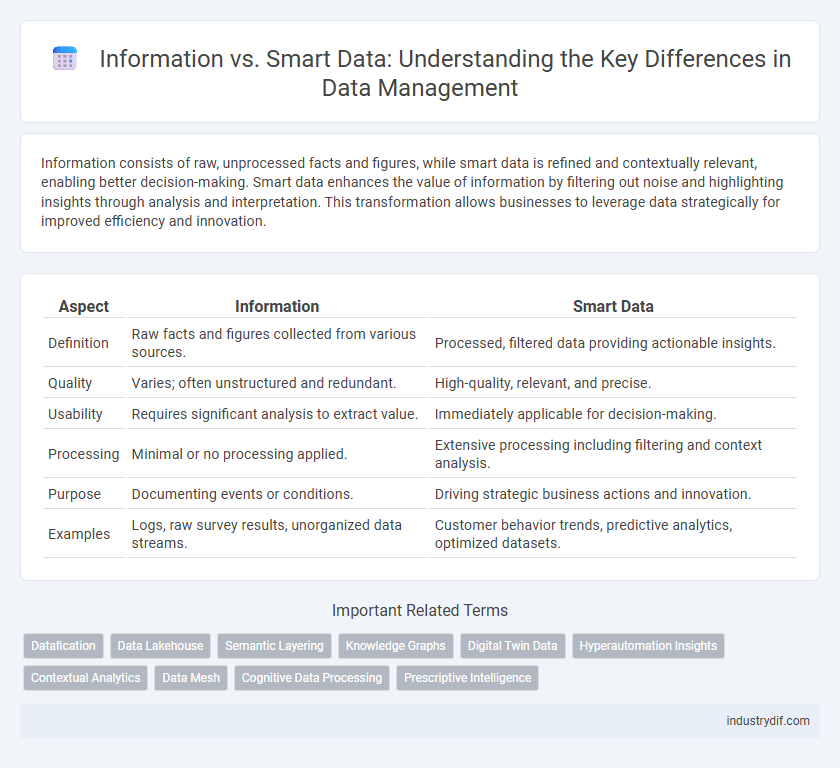
| Aspect | Information | Smart Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw facts and figures collected from various sources. | Processed, filtered data providing actionable insights. |
| Quality | Varies; often unstructured and redundant. | High-quality, relevant, and precise. |
| Usability | Requires significant analysis to extract value. | Immediately applicable for decision-making. |
| Processing | Minimal or no processing applied. | Extensive processing including filtering and context analysis. |
| Purpose | Documenting events or conditions. | Driving strategic business actions and innovation. |
| Examples | Logs, raw survey results, unorganized data streams. | Customer behavior trends, predictive analytics, optimized datasets. |
Understanding Information: Definition and Scope
Information comprises raw data, facts, and figures that represent observed phenomena without inherent interpretation or relevance. Smart data refines this information by filtering, contextualizing, and structuring it for actionable insights and decision-making. Understanding information involves recognizing its scope as the foundational input that, when processed, transforms into valuable knowledge.
What is Smart Data? Key Characteristics
Smart Data is refined information that has been processed, filtered, and analyzed to provide actionable insights and support decision-making. Key characteristics include relevance, accuracy, timeliness, and context-awareness, enabling businesses to focus on meaningful data rather than raw, unstructured information. Unlike general information, Smart Data drives efficiency by reducing noise and highlighting critical patterns or trends essential for strategic planning.
Information vs Smart Data: Core Differences
Information refers to raw data that has been collected but may lack context or relevance, whereas smart data is refined and processed to provide actionable insights tailored to specific business needs. Smart data emphasizes quality over quantity by filtering out noise and focusing on meaningful patterns that improve decision-making efficiency. This distinction highlights the core difference: information is abundant and unstructured, while smart data is curated, contextualized, and strategically valuable.
The Evolution from Information to Smart Data
The evolution from information to smart data marks a significant transformation in data utilization by shifting from mere collection to contextual analysis and actionable insights. Smart data integrates advanced analytics, machine learning algorithms, and real-time processing to enhance decision-making accuracy and efficiency. This progression enables organizations to derive value from vast datasets, turning raw information into targeted, predictive, and optimized intelligence.
How Smart Data Enhances Business Decision-Making
Smart data refines raw information by filtering, organizing, and analyzing relevant insights that directly impact business outcomes. This enhanced data quality improves decision-making accuracy, accelerates response times, and drives strategic initiatives with actionable intelligence. Leveraging smart data enables businesses to identify trends, optimize operations, and gain a competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Data Quality: Turning Information into Smart Data
Data quality is the cornerstone of transforming raw information into smart data by ensuring accuracy, completeness, and relevance. High-quality data undergoes rigorous validation and cleansing processes that eliminate errors and inconsistencies, enabling more reliable insights. This refinement enhances data usability, driving informed decision-making and operational efficiency across businesses.
Challenges in Converting Information to Smart Data
Converting raw information into smart data presents challenges such as data quality issues, including inaccuracies and inconsistencies that hinder effective analysis. Integrating heterogeneous data sources and ensuring semantic interoperability requires sophisticated algorithms and metadata management. Furthermore, maintaining privacy and security during data transformation demands robust encryption and compliance with regulatory standards.
Industry Applications: Smart Data in Practice
Smart data transforms raw information into actionable insights by filtering noise and highlighting relevant patterns, significantly enhancing decision-making in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and finance. In manufacturing, smart data enables predictive maintenance and optimizes supply chain management by analyzing sensor data in real time. Healthcare leverages smart data for personalized treatment plans and improved patient outcomes through integration of diverse clinical and genomic information.
Technological Trends Influencing Smart Data
Technological trends such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics are significantly transforming raw information into smart data by enhancing its accuracy and relevance for decision-making. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices enables continuous data collection and real-time processing, driving the shift from volume-heavy information to actionable insights. Cloud computing platforms facilitate scalable storage and advanced data processing capabilities, allowing organizations to harness smart data effectively for predictive analytics and operational efficiency.
Future Outlook: Smart Data’s Role in Digital Transformation
Smart Data drives the future of digital transformation by transforming raw information into actionable insights through advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. Organizations leveraging Smart Data experience enhanced decision-making, operational efficiency, and personalized customer experiences, fueling competitive advantage. The integration of Smart Data with emerging technologies like IoT and 5G accelerates innovation and supports scalable, adaptive business models in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Related Important Terms
Datafication
Datafication transforms raw information into smart data by organizing and contextualizing it for enhanced analysis and decision-making. Smart data enables businesses to extract actionable insights, improve operational efficiency, and drive innovation beyond the limitations of unprocessed information.
Data Lakehouse
Information evolves into smart data through advanced analytics and machine learning within a Data Lakehouse, which unifies data warehouses and data lakes for seamless storage, processing, and retrieval. This integration enables organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights by ensuring data quality, governance, and real-time accessibility.
Semantic Layering
Information consists of raw, unprocessed data that lacks context, while Smart Data arises from semantic layering techniques that add meaningful metadata and relationships, enabling enhanced accuracy and relevance in decision-making processes. Semantic layering structures data in interconnected formats, facilitating advanced analytics and efficient knowledge extraction across diverse applications.
Knowledge Graphs
Information consists of raw, unprocessed data, while smart data is curated and structured to provide meaningful insights through context and relationships. Knowledge graphs enhance smart data by linking entities and attributes semantically, enabling advanced data integration, reasoning, and improved decision-making capabilities.
Digital Twin Data
Digital Twin data transforms raw information into smart data by integrating real-time sensor inputs, simulations, and machine learning algorithms to enable predictive analytics and operational optimization. This semantic enhancement allows businesses to make informed decisions, reduce downtime, and improve asset performance by leveraging context-rich, actionable insights from their digital replicas.
Hyperautomation Insights
Information represents raw data collected from various sources, while Smart Data is refined, context-rich, and actionable, enhancing decision-making processes. Hyperautomation leverages Smart Data by integrating AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation to deliver real-time, predictive insights that drive operational efficiency and strategic growth.
Contextual Analytics
Information represents raw data collected from various sources, while smart data is refined through contextual analytics to reveal actionable insights and meaningful patterns. Contextual analytics leverages metadata, user behavior, and environmental factors to transform information into smart data, enhancing decision-making accuracy and operational efficiency.
Data Mesh
Information refers to raw, unprocessed data that lacks contextual relevance, whereas Smart Data is refined through Data Mesh principles, enabling decentralized ownership and real-time accessibility across domains. Data Mesh architecture transforms information into actionable insights by promoting data as a product, enhancing scalability and collaboration within complex data ecosystems.
Cognitive Data Processing
Information represents raw, unprocessed facts, whereas smart data undergoes cognitive data processing techniques--including natural language understanding, pattern recognition, and machine learning--to extract meaningful insights and enhance decision-making. Cognitive data processing transforms disparate information into actionable intelligence by mimicking human thought processes and enabling adaptive analysis.
Prescriptive Intelligence
Prescriptive intelligence transforms raw information into smart data by analyzing patterns and recommending actionable decisions that optimize outcomes. This advanced approach leverages predictive analytics and machine learning to deliver precise insights, enabling businesses to proactively solve problems and enhance efficiency.
Information vs Smart Data Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com