Hierarchy in management emphasizes clear authority lines and structured decision-making, fostering order and accountability. Holacracy promotes a decentralized approach where roles are fluid and teams self-organize, enhancing flexibility and innovation. Choosing between these models depends on organizational goals, culture, and the need for adaptability versus control.
Table of Comparison
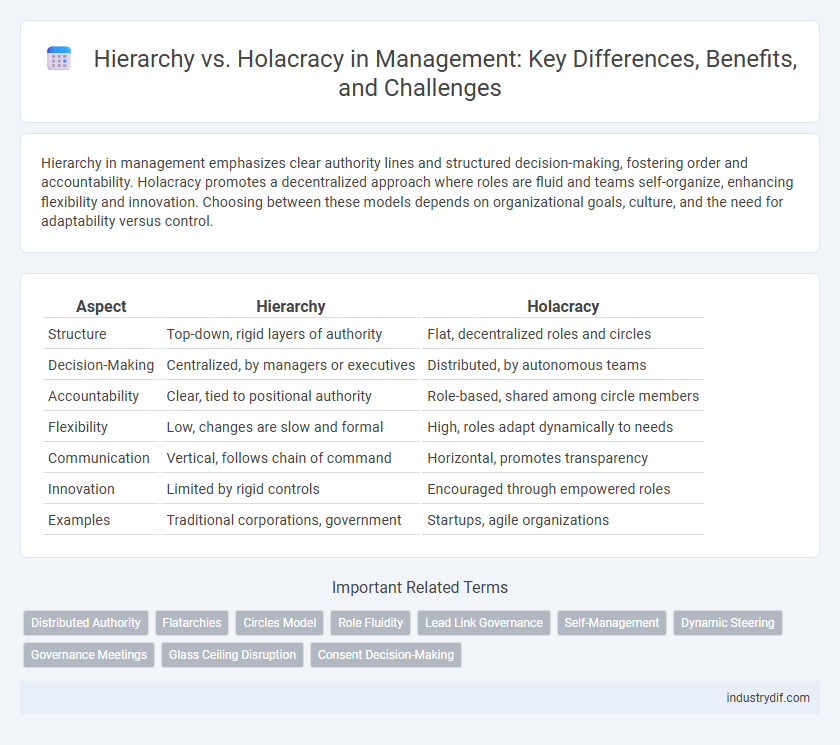
| Aspect | Hierarchy | Holacracy |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Top-down, rigid layers of authority | Flat, decentralized roles and circles |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, by managers or executives | Distributed, by autonomous teams |
| Accountability | Clear, tied to positional authority | Role-based, shared among circle members |
| Flexibility | Low, changes are slow and formal | High, roles adapt dynamically to needs |
| Communication | Vertical, follows chain of command | Horizontal, promotes transparency |
| Innovation | Limited by rigid controls | Encouraged through empowered roles |
| Examples | Traditional corporations, government | Startups, agile organizations |
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizational structures define the framework for decision-making and workflow within a company, where hierarchy establishes clear, top-down leadership and accountability. Holacracy restructures this approach by distributing authority across self-organizing teams, promoting agility and employee empowerment. Understanding the balance between centralized control in hierarchical models and the decentralized nature of holacracy is essential for effective management and innovation.
Defining Hierarchy in Management
Hierarchy in management establishes a structured chain of command where authority and responsibilities flow from top-level executives to lower-level employees. This model emphasizes clear roles, decision-making power concentrated at the upper levels, and defined reporting relationships that streamline organizational control. Hierarchical structures facilitate accountability by delineating specific managerial levels responsible for various operational functions.
Understanding Holacracy as a Management Model
Holacracy is a decentralized management model that replaces traditional hierarchical structures with self-organizing teams or circles, empowering employees to take on multiple roles and make decisions autonomously. This approach enhances agility by distributing authority and increasing transparency across organizational processes, fostering innovation and accountability. Companies adopting holacracy often report improved responsiveness and collaborative problem-solving compared to rigid top-down hierarchies.
Key Differences: Hierarchy vs Holacracy
Hierarchy relies on a top-down structure with clear lines of authority and decision-making concentrated at higher levels, ensuring control and accountability. Holacracy distributes power across self-organizing teams, promoting flexibility, transparency, and rapid adaptation through defined roles rather than rigid titles. Key differences include centralized command in hierarchy versus decentralized empowerment in holacracy, impacting organizational agility and employee autonomy.
Decision-Making Processes in Both Models
Hierarchy centralizes decision-making authority at the top management levels, enabling clear accountability and streamlined directive execution. Holacracy distributes decision-making across self-organizing teams, promoting agility, transparency, and employee empowerment. Organizations adopting holacracy often experience faster innovation cycles due to collaborative governance structures, while hierarchical models emphasize control and consistency.
Impact on Employee Engagement and Autonomy
Hierarchy often limits employee autonomy by enforcing rigid roles and top-down decision-making, which can reduce engagement and stifle creativity. Holacracy promotes a decentralized structure where employees have more control and ownership over their work, leading to higher engagement and intrinsic motivation. This shift empowers individuals to contribute meaningfully, fostering a culture of accountability and continuous innovation.
Scalability and Flexibility in Organizations
Hierarchical structures offer clear scalability through defined roles and top-down decision-making, which streamlines coordination in large organizations but may hinder rapid adaptation to change. Holacracy promotes flexibility by distributing authority across self-organizing teams, enabling faster innovation and responsiveness in dynamic markets. Organizations balancing scalability and flexibility often adopt hybrid models combining hierarchical oversight with holacratic elements to optimize growth and agility.
Challenges and Risks of Each Approach
Hierarchy often faces challenges such as rigid decision-making processes, limited employee autonomy, and potential communication bottlenecks that can hinder innovation and responsiveness. Holacracy risks include ambiguity in roles and responsibilities, potential conflicts due to decentralized authority, and difficulties scaling the model in larger organizations. Both approaches require careful management to balance control and flexibility while mitigating risks related to organizational efficiency and employee engagement.
Case Studies: Companies Using Hierarchy and Holacracy
Companies like General Electric and Walmart exemplify traditional hierarchy by employing top-down management structures that emphasize clear authority lines and centralized decision-making. In contrast, organizations such as Zappos and Medium have adopted holacracy, implementing decentralized governance with self-managed teams to foster agility and employee autonomy. Case studies highlight that while hierarchy supports scale and predictability, holacracy enhances innovation and adaptability in dynamic markets.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Organization
Choosing the right organizational structure depends on your company's size, culture, and goals, with hierarchy offering clear authority lines and efficient decision-making in large or regulated environments. Holacracy promotes decentralized decision-making and employee empowerment, fostering innovation and agility, ideal for startups and dynamic industries. Evaluating operational complexity and the need for flexibility helps determine whether a traditional hierarchy or a holacratic system better supports sustainable growth and employee engagement.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Authority
Distributed authority in holacracy replaces traditional hierarchical management by decentralizing decision-making power across self-organizing teams, enhancing agility and accountability. This structure fosters innovation and responsiveness by empowering individuals at all levels to take initiative without rigid supervisory control.
Flatarchies
Flatarchies blend traditional hierarchy with holacracy's decentralized decision-making to foster agility and innovation within organizations. This hybrid model balances clear leadership structures and employee autonomy, enhancing responsiveness and collaboration in dynamic business environments.
Circles Model
The Circles Model in Holacracy replaces traditional hierarchy by distributing authority across self-organizing teams, enhancing agility and accountability within organizations. This model fosters transparent governance through defined roles and integrative decision-making processes, promoting dynamic collaboration without centralized control.
Role Fluidity
In traditional hierarchy, role fluidity is limited by fixed job descriptions and rigid authority lines, whereas holacracy promotes dynamic role allocation that adapts to organizational needs, enhancing flexibility and employee empowerment. This fluidity in holacracy supports rapid decision-making and innovation by enabling individuals to assume multiple roles based on expertise rather than formal position.
Lead Link Governance
Lead Link governance in Holacracy replaces traditional hierarchical management by distributing authority across roles instead of individuals, enabling dynamic role allocation and accountability. This system enhances organizational agility and clarity by defining clear purpose, domains, and accountabilities within circles, contrasting with rigid top-down hierarchy structures.
Self-Management
Self-management in holacracy replaces traditional hierarchical control by distributing decision-making authority across autonomous teams, enhancing agility and employee empowerment. This decentralized structure fosters accountability and innovation by enabling individuals to manage roles dynamically without relying on rigid supervisory chains.
Dynamic Steering
Dynamic steering in management contrasts traditional hierarchy's rigid command structure with holacracy's flexible, decentralized decision-making, enabling faster adaptation to change. Holacracy distributes authority across self-organizing teams, enhancing responsiveness and innovation, while hierarchy centralizes control, often slowing dynamic responses.
Governance Meetings
Hierarchy governance meetings typically follow a top-down structure where leaders set agendas and make decisions, ensuring clear authority and accountability lines. Holacracy governance meetings distribute decision-making across roles, emphasizing transparency and collaborative rule-setting to adapt dynamically to organizational needs.
Glass Ceiling Disruption
Holacracy disrupts the traditional glass ceiling by eliminating rigid hierarchical layers, empowering employees with distributed authority and decision-making roles. This decentralized management approach fosters transparency and meritocracy, enabling talent to rise based on contribution rather than positional power.
Consent Decision-Making
Consent decision-making in hierarchy relies on top-down authority where leaders approve or veto proposals, often slowing responsiveness and limiting employee empowerment. Holacracy emphasizes decentralized consent, enabling teams to rapidly approve changes unless objections relate to roles or responsibilities, fostering agility and collective ownership.
Hierarchy vs Holacracy Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com