Public pet initiatives prioritize community well-being by promoting responsible pet ownership and enhancing urban environments, creating tangible social benefits. These programs often incorporate social innovation by introducing novel approaches to animal welfare and community engagement that address systemic challenges. The synergy between public benefit and social innovation fosters inclusive, sustainable solutions that improve quality of life for both pets and people.
Table of Comparison
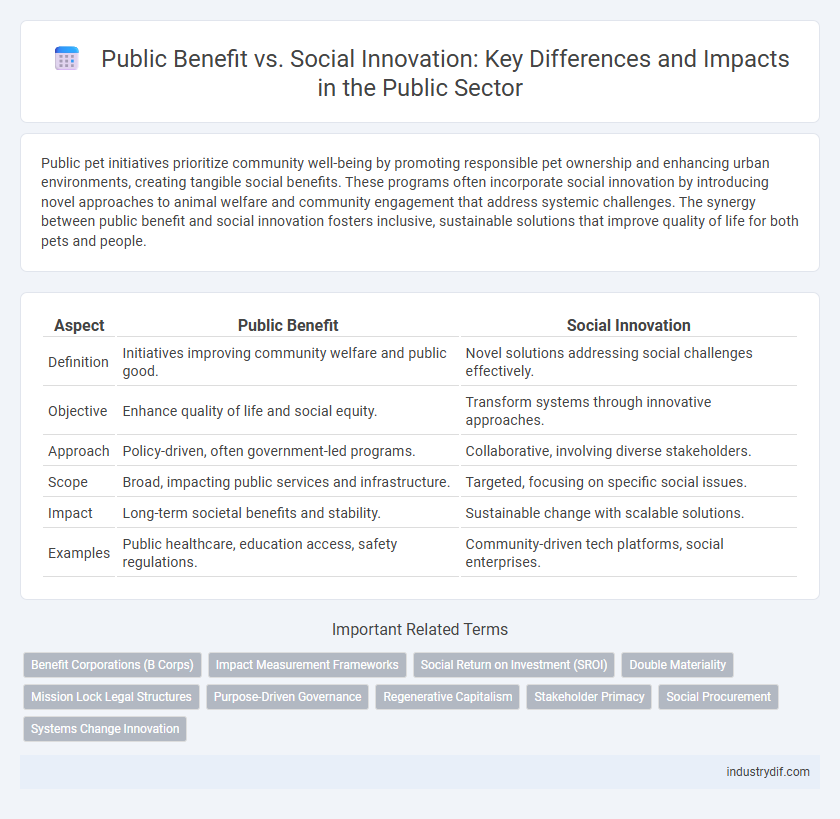
| Aspect | Public Benefit | Social Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Initiatives improving community welfare and public good. | Novel solutions addressing social challenges effectively. |
| Objective | Enhance quality of life and social equity. | Transform systems through innovative approaches. |
| Approach | Policy-driven, often government-led programs. | Collaborative, involving diverse stakeholders. |
| Scope | Broad, impacting public services and infrastructure. | Targeted, focusing on specific social issues. |
| Impact | Long-term societal benefits and stability. | Sustainable change with scalable solutions. |
| Examples | Public healthcare, education access, safety regulations. | Community-driven tech platforms, social enterprises. |
Defining Public Benefit in Modern Society
Public benefit in modern society refers to actions, policies, or projects designed to improve the well-being of the community by addressing critical needs such as health, education, and environmental sustainability. Unlike social innovation, which emphasizes novel solutions and creative processes to societal challenges, public benefit prioritizes measurable positive outcomes that serve the common good and ensure equitable resource distribution. Clear definitions of public benefit guide government decisions, nonprofit initiatives, and corporate social responsibility efforts to maximize social impact and foster inclusive growth.
Understanding Social Innovation in Practice
Social innovation involves creating and implementing novel solutions that address social challenges more effectively than existing approaches, emphasizing systemic change and sustainability. Public benefit refers to the widespread positive impact these innovations have on communities and societal well-being. Understanding social innovation in practice requires analyzing case studies where collaborative efforts between public, private, and nonprofit sectors generate measurable improvements in quality of life and social equity.
Key Differences Between Public Benefit and Social Innovation
Public benefit refers to services or actions explicitly designed to improve societal welfare, typically delivered by government or nonprofit organizations, with goals centered on broad accessibility and equity. Social innovation focuses on developing novel solutions to social problems, emphasizing creativity and sustainability to achieve systemic change. Key differences include the origin and framework--public benefit operates within established institutional structures, while social innovation often emerges from grassroots or hybrid initiatives aiming to transform existing social systems.
Historical Evolution of Public Benefit Initiatives
Public benefit initiatives have evolved from early charitable organizations in the 19th century focusing on poverty alleviation to contemporary models emphasizing systemic change and community empowerment. Social innovation emerged in the late 20th century as a dynamic approach, introducing novel solutions that address complex social challenges through collaboration and technology. This historical progression highlights a shift from traditional philanthropy to strategic, scalable interventions designed to create sustainable social impact.
The Role of Social Innovation in Addressing Public Needs
Social innovation plays a pivotal role in addressing public needs by creating novel solutions that enhance social well-being and drive systemic change. Unlike traditional public benefits, which often rely on established welfare programs, social innovation emphasizes collaborative approaches and scalable impact across diverse communities. This dynamic process fosters resilience, inclusivity, and sustainable growth by integrating technology, policies, and community engagement to solve complex societal challenges.
Measuring Impact: Public Benefit Versus Social Innovation
Measuring impact in public benefit initiatives emphasizes quantifiable outcomes such as improved community health, economic uplift, and access to essential services, often tracked through standardized metrics and government reports. Social innovation impact measurement prioritizes adaptive, scalable solutions that address systemic issues, using qualitative assessments like stakeholder feedback, behavior change analysis, and long-term sustainability indicators. Combining both approaches enhances accountability and effectiveness by balancing immediate public benefits with transformative social change.
Stakeholders Involved: From Governments to Grassroots
Public benefit initiatives engage a diverse spectrum of stakeholders, ranging from governments and policymakers to grassroots organizations and community members, each playing a critical role in addressing societal challenges. Social innovation thrives through the collaboration of businesses, nonprofits, academia, and citizens, leveraging collective expertise and resources to create sustainable solutions. Effective stakeholder involvement ensures accountability, inclusivity, and adaptability, driving impactful outcomes in public welfare and community development.
Challenges in Scaling Public Benefit Programs
Scaling public benefit programs faces challenges such as limited funding, bureaucratic hurdles, and difficulties in measuring long-term impact. Social innovation often demands flexibility and rapid iteration, which can conflict with public sector requirements for accountability and regulatory compliance. Addressing these obstacles requires integrating innovative approaches with scalable frameworks that ensure sustainability and effective resource allocation.
Case Studies: Public Benefit vs Social Innovation Success Stories
Case studies reveal that public benefit projects, such as affordable housing initiatives in New York City, directly address community needs by improving living conditions and access to resources. Social innovation success stories, like the rise of microfinance models in Bangladesh, demonstrate how novel approaches empower underserved populations through sustainable financial inclusion. Both paradigms drive societal impact, with public benefit focusing on immediate improvements and social innovation emphasizing long-term systemic change.
Future Trends in Public Benefit and Social Innovation
Future trends in public benefit emphasize technology-driven solutions that enhance community well-being and resource distribution. Social innovation increasingly incorporates data analytics and AI to design scalable programs addressing inequality and environmental challenges. Collaboration between public institutions and private sectors is predicted to accelerate impact through integrated digital platforms and participatory governance models.
Related Important Terms
Benefit Corporations (B Corps)
Benefit Corporations (B Corps) blend public benefit and social innovation by legally committing to generate positive social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. These certified entities leverage innovative business models to address societal challenges while maintaining transparency and accountability to stakeholders.
Impact Measurement Frameworks
Impact Measurement Frameworks in public benefit organizations prioritize quantifiable outcomes to assess effectiveness, while social innovation frameworks emphasize iterative learning and systemic change. Both approaches integrate qualitative and quantitative data but differ in scope, with public benefit models often focusing on compliance and accountability, whereas social innovation frameworks drive adaptive strategies for long-term societal transformation.
Social Return on Investment (SROI)
Social Return on Investment (SROI) quantifies the broader impact of social innovation by measuring social, environmental, and economic value generated beyond financial returns. While public benefit emphasizes general societal welfare, SROI provides a detailed framework to assess how innovations create measurable positive changes for communities and stakeholders.
Double Materiality
Public benefit initiatives prioritize positive societal impact, while social innovation focuses on novel solutions addressing social challenges; double materiality integrates these approaches by evaluating both the financial and non-financial effects of actions on society and the environment. This framework ensures organizations measure and report how their activities create value for stakeholders and contribute to sustainable development beyond traditional financial metrics.
Mission Lock Legal Structures
Mission lock legal structures provide robust frameworks that ensure public benefit organizations maintain their core social objectives over time, preventing mission drift and safeguarding community impact. These structures, including benefit corporations and nonprofit charters with embedded mission protections, align legal accountability with social innovation, fostering sustainable solutions that prioritize societal value over profit maximization.
Purpose-Driven Governance
Purpose-driven governance aligns public benefit with social innovation by embedding transparent accountability and stakeholder engagement into decision-making processes. This approach fosters sustainable community development through mission-centric policies that balance economic viability and social impact.
Regenerative Capitalism
Regenerative Capitalism integrates public benefit with social innovation by fostering systems that restore and sustain economic, social, and ecological well-being, moving beyond mere profit to create long-term value for communities and the environment. This approach emphasizes circular economies, inclusive governance, and stakeholder-centric models that drive resilience and equitable growth.
Stakeholder Primacy
Stakeholder primacy emphasizes balancing the interests of all stakeholders, including customers, employees, and communities, to maximize public benefit by driving socially innovative solutions that address collective needs. This approach shifts focus from shareholder profit to inclusive value creation, fostering sustainable social impact through collaborative innovation.
Social Procurement
Social procurement leverages purchasing power to generate positive social outcomes by prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate social innovation and community impact. This approach transforms traditional public benefits into sustainable solutions that address systemic social challenges through innovative products, services, and business practices.
Systems Change Innovation
Systems Change Innovation drives transformative public benefit by addressing root causes of social issues through coordinated multi-sector collaboration, fostering sustainable impact beyond traditional social innovation. This approach reshapes institutional structures and policies, enabling long-term systemic improvements in public welfare and equity.
public benefit vs social innovation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com