Public policy establishes formal guidelines and regulations that govern societal behavior and public services, ensuring consistency and legal compliance. Policy innovation involves creative approaches to address emerging issues or improve effectiveness beyond existing frameworks. Emphasizing flexibility and adaptability, policy innovation can complement or reform traditional public policy for better outcomes.
Table of Comparison
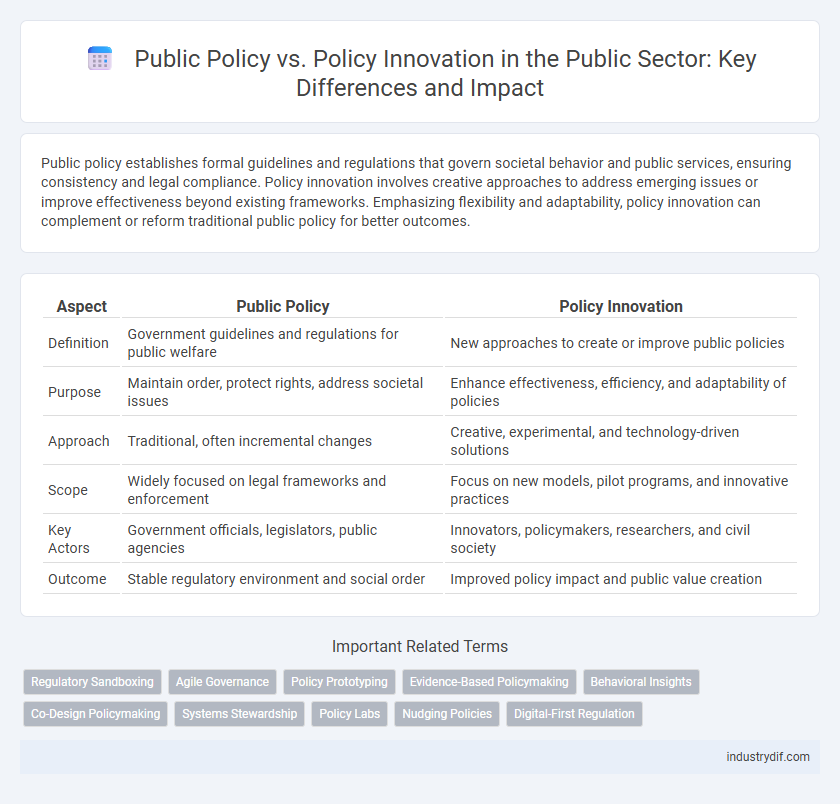
| Aspect | Public Policy | Policy Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government guidelines and regulations for public welfare | New approaches to create or improve public policies |
| Purpose | Maintain order, protect rights, address societal issues | Enhance effectiveness, efficiency, and adaptability of policies |
| Approach | Traditional, often incremental changes | Creative, experimental, and technology-driven solutions |
| Scope | Widely focused on legal frameworks and enforcement | Focus on new models, pilot programs, and innovative practices |
| Key Actors | Government officials, legislators, public agencies | Innovators, policymakers, researchers, and civil society |
| Outcome | Stable regulatory environment and social order | Improved policy impact and public value creation |
Defining Public Policy: Core Concepts
Public policy encompasses government actions and decisions designed to address societal issues through laws, regulations, and programs driven by public interest. It establishes frameworks that guide governance, resource allocation, and social behavior to achieve collective goals. Policy innovation focuses on developing novel approaches and solutions that enhance the effectiveness, efficiency, and equity of these established public policies.
Understanding Policy Innovation: An Overview
Policy innovation involves the development and implementation of new strategies, approaches, or solutions within public policy to address emerging societal challenges more effectively. It emphasizes experimentation, adaptability, and collaboration among stakeholders to improve policy outcomes and public service delivery. Understanding policy innovation requires analyzing its dynamic processes, including idea generation, diffusion, and institutionalization within the policy framework.
Key Differences Between Public Policy and Policy Innovation
Public policy refers to established government decisions and regulations designed to address societal issues, whereas policy innovation emphasizes the creation and implementation of novel, experimental approaches to solve public problems. Key differences include public policy's reliance on traditional frameworks and legal mandates, contrasting with policy innovation's focus on creativity, adaptability, and pilot testing new solutions. This distinction highlights public policy's role in maintaining order and stability, while policy innovation drives transformative change and responsiveness to emerging challenges.
Historical Evolution of Public Policy
Public policy has evolved through centuries, originating from early governance systems aimed at maintaining order and managing resources in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Rome. The Industrial Revolution marked a significant shift, introducing complex economic and social challenges that required systematic policy frameworks focused on regulation, welfare, and economic development. Policy innovation emerged in the late 20th century as governments responded to globalization, technological advances, and social changes by adopting adaptive, participatory, and evidence-based approaches to address evolving public needs.
Drivers of Policy Innovation in the Public Sector
Policy innovation in the public sector is driven by factors such as technological advancements, shifting societal needs, and political pressures for improved governance. Public organizations leverage data analytics and stakeholder engagement to design adaptive, evidence-based policies that address complex challenges. Institutional learning and collaboration across government agencies also play critical roles in fostering innovative public policy solutions.
Impact of Public Policy on Society
Public policy shapes societal structures by establishing regulatory frameworks that influence economic growth, health standards, and social equity. Effective public policies address systemic issues such as poverty, education inequality, and environmental sustainability, producing measurable outcomes like reduced unemployment rates and improved public health indicators. The impact of public policy on society is evident in enhanced social cohesion and increased access to essential services, driving long-term national development.
Case Studies: Successful Policy Innovations
Successful policy innovations often emerge from targeted case studies demonstrating measurable impacts on public welfare, such as Singapore's Smart Nation initiative enhancing digital governance and Estonia's e-Residency program transforming cross-border business facilitation. These examples highlight the shift from traditional public policy, which primarily involves regulatory frameworks, to dynamic policy innovation fostering adaptive solutions through technology and stakeholder collaboration. Emphasizing empirical results and scalability, these case studies provide valuable blueprints for replicating policy innovation in diverse governmental contexts.
Challenges in Adopting Policy Innovations
Challenges in adopting policy innovations include institutional resistance, lack of stakeholder engagement, and limited resources for implementation and evaluation. Traditional public policy frameworks often struggle to accommodate innovative approaches due to rigid regulations and bureaucratic inertia. Furthermore, uncertainty about the long-term impacts of novel policies makes policymakers hesitant to deviate from established practices.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Public Policy vs Policy Innovation
Measuring the effectiveness of public policy involves assessing predefined goals using quantitative data, such as economic impact, social outcomes, and compliance rates, to ensure policies meet established benchmarks. In contrast, policy innovation requires evaluating adaptability, scalability, and stakeholder engagement, often relying on qualitative metrics and pilot studies to gauge novel approaches' success. Both approaches demand tailored evaluation frameworks that balance traditional performance indicators with dynamic feedback loops to capture evolving societal needs.
Future Trends in Public Policy and Policy Innovation
Future trends in public policy emphasize data-driven decision-making, citizen engagement through digital platforms, and adaptive regulations addressing climate change and technological advancements. Policy innovation increasingly integrates artificial intelligence for predictive analytics and leverages collaborative governance models to tackle complex societal challenges. These developments foster resilience, transparency, and inclusivity in crafting effective public policies.
Related Important Terms
Regulatory Sandboxing
Regulatory sandboxing serves as a crucial tool in public policy for testing innovative regulations in controlled environments, enabling policymakers to adapt frameworks rapidly without compromising public safety. This approach bridges traditional public policy and policy innovation by fostering experimentation that informs evidence-based regulatory adjustments and accelerates the adoption of emerging technologies.
Agile Governance
Public policy establishes formal frameworks and regulations to address societal issues, while policy innovation emphasizes adaptive, iterative approaches like Agile Governance to enhance responsiveness and stakeholder engagement. Agile Governance integrates continuous feedback loops and cross-sector collaboration, enabling more flexible and efficient public service delivery in dynamic environments.
Policy Prototyping
Policy prototyping serves as a practical approach within policy innovation by testing small-scale models to evaluate potential public policy impacts before wide implementation. This method contrasts with traditional public policy development, which often relies on theoretical frameworks without iterative experimentation.
Evidence-Based Policymaking
Evidence-based policymaking enhances public policy by systematically integrating empirical research and data analysis to design, implement, and evaluate laws and regulations. Policy innovation drives novel approaches by leveraging evidence to address complex societal challenges, improving effectiveness and public trust in government interventions.
Behavioral Insights
Behavioral insights leverage psychological and economic research to design public policies that effectively influence citizen behavior, enhancing traditional public policy approaches by focusing on real-world decision-making processes. Policy innovation incorporates these insights to create adaptive, evidence-based strategies that improve government interventions and increase social welfare outcomes.
Co-Design Policymaking
Co-design policymaking enhances public policy by actively involving diverse stakeholders in the creation and implementation process, fostering collaboration and ensuring policies address real community needs effectively. This approach drives policy innovation by integrating multiple perspectives, improving transparency, and generating adaptive solutions tailored to complex social challenges.
Systems Stewardship
Public policy establishes structured frameworks and regulations that guide societal functions, while policy innovation introduces novel approaches to address complex challenges through adaptive and dynamic strategies. Systems stewardship emphasizes the responsible management of interconnected social, economic, and environmental systems, ensuring sustainable outcomes by integrating both traditional public policies and innovative policy solutions.
Policy Labs
Policy Labs serve as experimental hubs within public policy frameworks, driving policy innovation by applying design thinking, data analytics, and user-centered approaches to tackle complex societal challenges. These labs enable governments to test, iterate, and scale solutions rapidly, bridging the gap between traditional public policy development and adaptive, evidence-based innovations.
Nudging Policies
Nudging policies, a central tool in both public policy and policy innovation, leverage behavioral economics to subtly steer individuals towards desired choices without restricting freedom. Unlike traditional public policies that often rely on regulation and incentives, nudging emphasizes small, cost-effective adjustments to the decision-making environment to improve social and economic outcomes.
Digital-First Regulation
Digital-first regulation transforms traditional public policy by embedding technology-driven frameworks that prioritize rapid adaptation and user-centric services, enhancing transparency and efficiency in governance. This approach leverages data analytics, AI, and digital platforms to foster policy innovation, enabling more agile responses to emerging societal challenges and improving regulatory compliance.
Public Policy vs Policy Innovation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com