Public sector organizations primarily focus on delivering pet-related services funded by government resources, aiming to provide universal access and regulatory oversight. Social enterprises operate with a dual purpose, combining mission-driven goals to improve animal welfare with sustainable business models that generate revenue through community engagement and pet care services. This blend allows social enterprises to innovate and respond flexibly to public needs while reinvesting profits to enhance their social impact in the pet care landscape.
Table of Comparison
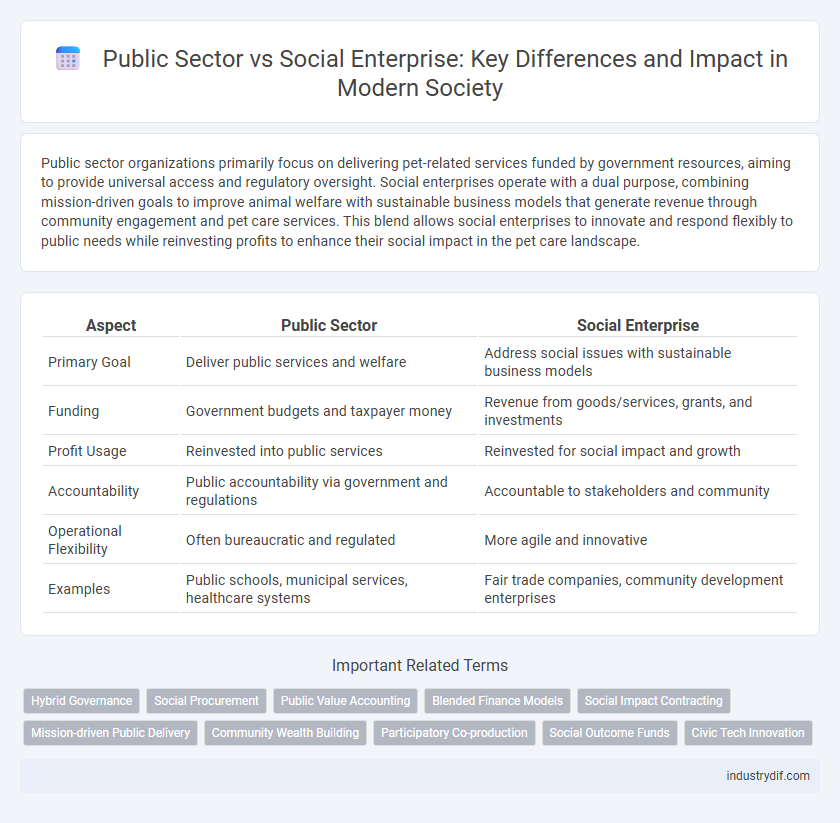
| Aspect | Public Sector | Social Enterprise |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Deliver public services and welfare | Address social issues with sustainable business models |
| Funding | Government budgets and taxpayer money | Revenue from goods/services, grants, and investments |
| Profit Usage | Reinvested into public services | Reinvested for social impact and growth |
| Accountability | Public accountability via government and regulations | Accountable to stakeholders and community |
| Operational Flexibility | Often bureaucratic and regulated | More agile and innovative |
| Examples | Public schools, municipal services, healthcare systems | Fair trade companies, community development enterprises |
Defining the Public Sector
The public sector encompasses government-owned organizations and agencies responsible for delivering essential services such as healthcare, education, and public safety, funded primarily through taxation. Unlike social enterprises, which operate with a business model aiming to achieve social impact alongside financial sustainability, the public sector prioritizes public welfare and equitable access. Key entities in the public sector include federal, state, and local government bodies that implement policies and manage resources to serve the community.
What Is a Social Enterprise?
A social enterprise operates with the primary goal of addressing social or environmental issues while generating revenue, blending commercial strategies with mission-driven objectives. Unlike traditional public sector organizations funded primarily by government budgets to provide public services, social enterprises reinvest profits into their social goals to achieve sustainable impact. This hybrid model enables social enterprises to tackle community challenges innovatively while maintaining financial viability.
Core Objectives: Public Good vs. Profit with Purpose
Public sector organizations prioritize delivering essential services and promoting societal welfare without profit motives, focusing on public good through equitable access and regulatory compliance. Social enterprises blend business strategies with social missions, aiming to generate sustainable profits while addressing specific community needs or environmental challenges. Both models emphasize impact, but public sector entities operate primarily through taxpayer funding, whereas social enterprises rely on market-driven revenue to achieve purpose-driven goals.
Funding Models Compared
Public sector organizations primarily rely on government funding, grants, and taxpayer revenues to sustain operations, ensuring stable but often restricted budgets tied to political priorities. Social enterprises utilize a hybrid funding model combining earned income through business activities, philanthropic donations, and impact investments, enabling greater financial flexibility and mission-driven innovation. The distinct funding approaches affect accountability, risk tolerance, and scalability, with public entities prioritizing public accountability and social enterprises emphasizing sustainability and market-based solutions.
Governance and Accountability Structures
Public sector organizations operate under government regulations with hierarchical governance and statutory accountability to elected officials, ensuring transparency and public interest protection. Social enterprises implement hybrid governance models combining social mission oversight with business management principles, often involving stakeholder representation and impact measurement. Both sectors emphasize accountability, but social enterprises prioritize adaptive frameworks that balance financial sustainability with social responsibility.
Service Delivery Approaches
Public sector organizations typically rely on bureaucratic structures and standardized procedures to ensure consistent service delivery, emphasizing accountability to taxpayers and regulatory compliance. Social enterprises adopt innovative, market-driven approaches that combine social objectives with entrepreneurial methods to address specific community needs more flexibly. Both models prioritize impact, but social enterprises leverage revenue generation and community engagement to enhance service adaptability and sustainability.
Stakeholder Engagement and Community Impact
Public sector organizations prioritize inclusive stakeholder engagement by involving government bodies, citizens, and regulatory agencies to ensure transparency and accountability. Social enterprises actively engage diverse community members and beneficiaries, leveraging their input to co-create sustainable solutions that address specific social needs. Both models measure community impact through collaborative feedback mechanisms, yet social enterprises often achieve more direct and immediate social outcomes due to their mission-driven approach.
Measuring Success: Metrics and Outcomes
Measuring success in the public sector often relies on standardized performance indicators such as service delivery efficiency, compliance rates, and budget adherence, reflecting accountability to taxpayers and regulatory frameworks. Social enterprises prioritize a blend of financial sustainability metrics alongside social impact measures, including beneficiary outcomes, community engagement levels, and environmental improvements. Both sectors increasingly incorporate data analytics and outcome-based evaluation tools to balance quantitative results with qualitative social value generation.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaboration between public sector organizations and social enterprises enhances resource sharing, innovation, and community impact by leveraging each entity's unique strengths. Public sector agencies provide regulatory support and funding, while social enterprises contribute agile approaches and deep local knowledge. Strategic partnerships foster sustainable solutions addressing social challenges more effectively than isolated efforts.
Key Challenges and Future Trends
Public sector organizations face key challenges such as bureaucratic inefficiencies and limited funding flexibility, while social enterprises struggle with balancing social impact goals and financial sustainability. Emerging trends include increased adoption of digital technologies for service delivery and a shift toward hybrid models combining public funding with social entrepreneurship. Future developments emphasize data-driven decision-making and greater collaboration between public institutions and social enterprises to enhance community outcomes.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Governance
Hybrid governance in the public sector integrates traditional bureaucratic oversight with social enterprise innovation to enhance service delivery and social impact. This approach leverages public accountability mechanisms alongside market-driven strategies to address complex societal challenges efficiently and sustainably.
Social Procurement
Social procurement in the public sector leverages government spending to prioritize social value by contracting social enterprises that deliver measurable community benefits and promote inclusive economic growth. Unlike traditional public sector procurement focused on cost-efficiency, social procurement integrates social, environmental, and economic outcomes, fostering innovation and equitable opportunities within marginalized communities.
Public Value Accounting
Public Value Accounting in the public sector emphasizes transparent measurement of social, economic, and environmental outcomes to enhance accountability and resource allocation. Social enterprises integrate Public Value Accounting to balance financial sustainability with social impact, driving mission-oriented performance beyond traditional profit metrics.
Blended Finance Models
Blended finance models leverage public sector funding to de-risk investments and attract private capital into social enterprises, accelerating sustainable development projects with measurable social impact. By combining grants, concessional loans, and equity investments, these models enhance financial viability while addressing market gaps that neither public institutions nor private investors can fill alone.
Social Impact Contracting
Social Impact Contracting leverages performance-based agreements to fund initiatives that address social challenges, distinguishing social enterprises by driving measurable community benefits through private and public sector collaboration. Public sector entities often contract social enterprises to enhance service delivery efficiency and outcome accountability in areas like healthcare, education, and employment support.
Mission-driven Public Delivery
Public sector organizations prioritize mission-driven public delivery by focusing on equitable access and regulatory oversight, ensuring essential services meet community needs without profit motives. Social enterprises blend social objectives with business strategies, reinvesting profits to address societal challenges while maintaining operational sustainability.
Community Wealth Building
Public sector organizations drive Community Wealth Building by reinvesting local resources and prioritizing public value over profit. Social enterprises complement this approach through entrepreneurial activities that generate sustainable community benefits while addressing social challenges.
Participatory Co-production
Participatory co-production in the public sector emphasizes citizen engagement through formal channels, driving accountability and public service improvements. Social enterprises leverage collaborative stakeholder involvement to innovate solutions and sustain social impact beyond traditional public participation frameworks.
Social Outcome Funds
Social Outcome Funds finance innovative social enterprises that deliver measurable impact by linking investment returns to specific social outcomes, contrasting with the public sector's traditional funding methods centered on budget allocations and service delivery. These funds attract private capital for scalable solutions addressing societal challenges, emphasizing accountability and performance-based contracts to optimize social value.
Civic Tech Innovation
Civic tech innovation bridges public sector objectives and social enterprise agility by leveraging digital tools to enhance government transparency, citizen engagement, and service delivery. Social enterprises drive scalable solutions through community-focused design, while public institutions provide regulatory frameworks and resources crucial for long-term impact.
public sector vs social enterprise Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com