Multi-family properties offer spacious living with shared amenities, catering to families and long-term residents seeking comfort and community. Micro-units maximize urban space by providing compact, affordable housing ideal for singles and professionals prioritizing location and cost-efficiency over size. Developers and investors weigh multi-family units' higher capital and maintenance costs against micro-units' scalable potential and quick rental turnover.
Table of Comparison
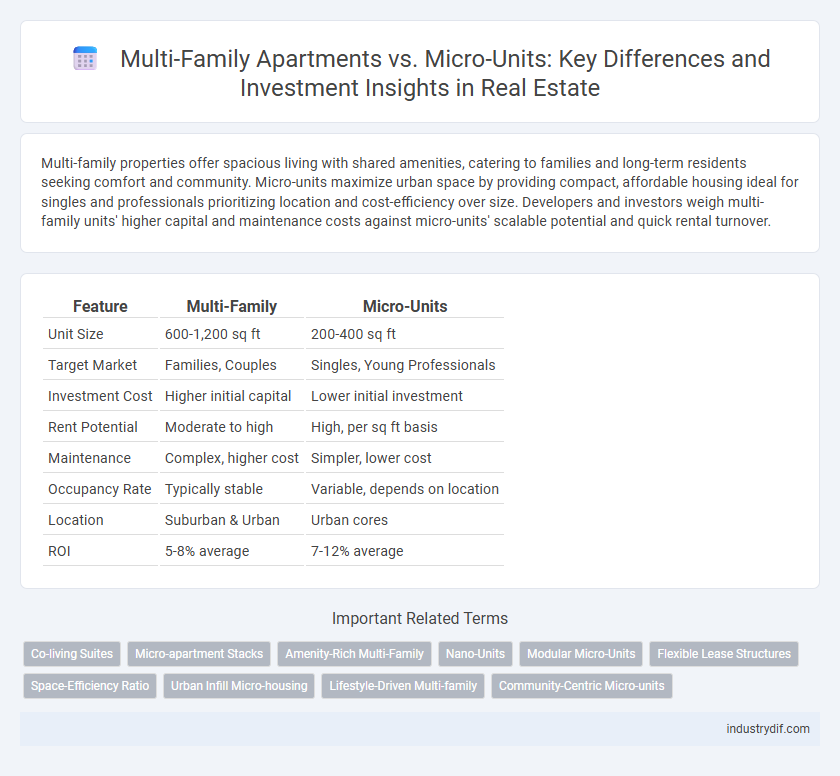
| Feature | Multi-Family | Micro-Units |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Size | 600-1,200 sq ft | 200-400 sq ft |
| Target Market | Families, Couples | Singles, Young Professionals |
| Investment Cost | Higher initial capital | Lower initial investment |
| Rent Potential | Moderate to high | High, per sq ft basis |
| Maintenance | Complex, higher cost | Simpler, lower cost |
| Occupancy Rate | Typically stable | Variable, depends on location |
| Location | Suburban & Urban | Urban cores |
| ROI | 5-8% average | 7-12% average |
Defining Multi-Family Properties and Micro-Units
Multi-family properties consist of residential buildings designed to house multiple separate families, such as duplexes, triplexes, and apartment complexes, providing diverse living spaces under one roof. Micro-units refer to compact, efficiently designed apartments typically ranging from 200 to 400 square feet, aimed at maximizing affordability and urban living convenience for single occupants. Both property types cater to different market demands, with multi-family focusing on scalable rental income and micro-units targeting cost-effective urban housing solutions.
Key Differences in Space and Layout
Multi-family units typically offer larger living spaces with multiple bedrooms and full kitchens, designed to accommodate families or groups, while micro-units prioritize minimalism with compact layouts often featuring combined living, sleeping, and kitchenette areas. The spatial efficiency in micro-units maximizes urban affordability by reducing square footage, whereas multi-family units focus on comfort and privacy through segregated rooms and expansive common areas. These fundamental differences influence tenant demographics, with multi-family spaces appealing to families and micro-units attracting single professionals or students seeking economical housing solutions.
Target Demographics for Each Housing Type
Multi-family housing predominantly attracts families, young professionals, and retirees seeking spacious living with community amenities. Micro-units cater primarily to urban singles, students, and transient workers prioritizing affordability and proximity to city centers. Each housing type aligns with distinct lifestyle needs and financial capabilities, shaping their target demographics.
Cost Efficiency and Investment Returns
Multi-family properties offer cost efficiency through shared infrastructure and scalable maintenance, resulting in lower per-unit expenses compared to micro-units. Micro-units maximize rental income per square foot by catering to urban professionals seeking affordability and flexibility, leading to higher investment returns in dense markets. Investors prioritize multi-family for stable cash flow and micro-units for rapid appreciation and demand-driven occupancy rates.
Amenities: Multi-Family Buildings vs. Micro-Units
Multi-family buildings typically offer extensive amenities such as fitness centers, swimming pools, communal lounges, and on-site management services, enhancing the living experience for residents. In contrast, micro-units emphasize efficient use of space with essential in-unit features like compact kitchens and smart storage solutions but often lack shared amenities due to limited building size. The choice between multi-family and micro-units depends on the demand for lifestyle amenities versus affordability and space efficiency in urban real estate markets.
Location Trends and Urban Development
Multi-family housing thrives in suburban areas with access to quality schools and public transportation, catering to families seeking space and community amenities. Micro-units are increasingly popular in dense urban centers where proximity to employment hubs, entertainment, and walkability are prioritized by young professionals and singles. Urban development trends show a shift toward mixed-use neighborhoods that blend multi-family complexes with micro-unit buildings to accommodate diverse demographic needs and maximize land use efficiency.
Rental Yields and Occupancy Rates
Multi-family properties typically offer stable rental yields averaging 6-8% with occupancy rates around 90-95%, driven by strong tenant demand and diversified income streams. Micro-units, while smaller in size, can achieve higher rental yields of 8-12% due to premium per-square-foot pricing but may experience more variable occupancy rates between 85-90% due to niche market appeal. Investors must weigh steady income from multi-family assets against potentially higher returns and occupancy fluctuations in micro-unit portfolios.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Multi-family housing typically offers greater energy efficiency through shared walls, centralized heating, and cooling systems, reducing overall utility consumption compared to micro-units. Micro-units contribute to sustainability by minimizing living space per occupant, lowering material use and energy demand per unit, which supports urban density goals and decreases carbon footprints. Both housing types incorporate advanced insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and renewable energy technologies to enhance sustainability outcomes in real estate development.
Market Demand and Future Growth
Multi-family properties continue to dominate market demand due to their appeal to families and long-term renters seeking more space and amenities. Micro-units, however, are gaining traction in urban centers where affordability and proximity to work drive future growth potential. Projections indicate that micro-unit developments will expand rapidly as younger demographics prioritize location and cost-efficiency over square footage.
Regulatory Considerations and Zoning Laws
Multi-family developments often face stringent zoning laws that require minimum unit sizes and parking spaces, while micro-unit projects benefit from more flexible regulations targeting urban density and affordable housing. Local governments may offer incentives or expedited permitting for micro-units to address housing shortages and promote efficient land use. Compliance with fire safety codes, occupancy limits, and accessibility standards varies significantly between traditional multi-family buildings and micro-unit complexes, influencing project feasibility and timelines.
Related Important Terms
Co-living Suites
Co-living suites within multi-family developments optimize space by combining private micro-unit bedrooms with extensive shared amenities, fostering community while reducing individual costs. These designs attract urban professionals seeking affordability and social interaction, making co-living an efficient solution in high-demand real estate markets.
Micro-apartment Stacks
Micro-apartment stacks maximize urban space efficiency by offering compact, affordable living units ideal for high-density areas and young professionals. These vertical arrangements enhance rental yields and reduce construction costs compared to traditional multi-family developments, attracting investors seeking higher returns in limited land markets.
Amenity-Rich Multi-Family
Amenity-rich multi-family properties typically feature extensive shared facilities such as fitness centers, communal lounges, rooftop terraces, and co-working spaces, which significantly enhance resident experience and justify higher rental premiums compared to micro-units. These multi-family developments attract long-term tenants seeking lifestyle convenience, social interaction, and comprehensive service offerings that micro-units, often limited in space and amenities, cannot provide.
Nano-Units
Nano-units offer a compact, efficient living solution within multi-family developments, maximizing space utilization while catering to urban residents seeking affordability and minimalism. These ultra-small apartments, typically under 250 square feet, enhance occupancy rates and provide flexible housing options in high-demand city centers.
Modular Micro-Units
Modular micro-units offer a cost-effective and space-efficient alternative to traditional multi-family housing by utilizing prefabricated construction techniques that reduce build time and materials waste. These compact living spaces maximize urban density while providing essential amenities, appealing to young professionals and investors seeking high rental yields in growing metropolitan markets.
Flexible Lease Structures
Multi-family properties offer traditional lease terms with options for annual or semi-annual agreements, providing tenants stability and predictable costs, whereas micro-units often feature flexible lease structures such as month-to-month or short-term leases to accommodate transient renters and maximize occupancy. This flexibility in micro-units appeals to urban professionals and students seeking affordability and convenience in high-demand areas, while multi-family developments cater to long-term residents preferring consistency.
Space-Efficiency Ratio
Multi-family properties offer larger space-efficiency ratios by providing diverse unit sizes that cater to families, maximizing usable living area compared to micro-units, which prioritize minimalistic designs in smaller footprints. Space-efficiency in multi-family developments improves resident comfort and utility per square foot, while micro-units focus on compact layouts with a higher density of units within limited space.
Urban Infill Micro-housing
Urban infill micro-units maximize land efficiency in high-demand metropolitan areas by offering compact, affordable living spaces that attract young professionals and reduce urban sprawl. Unlike traditional multi-family buildings, these micro-units foster sustainable density and support walkable communities with accessible transit and local amenities.
Lifestyle-Driven Multi-family
Lifestyle-driven multi-family developments emphasize community amenities, shared spaces, and social interaction to attract young professionals and urban dwellers seeking convenience and connectivity. Unlike micro-units, which prioritize minimalistic living and cost efficiency, multi-family properties enhance quality of life through on-site gyms, coworking areas, and curated social events that foster a vibrant community atmosphere.
Community-Centric Micro-units
Community-centric micro-units foster social interaction and shared amenities, creating a vibrant living environment within limited space, unlike traditional multi-family units which often prioritize individual privacy over communal engagement. These micro-units optimize urban density by combining compact private spaces with thoughtfully designed common areas, promoting affordability and connectivity in high-demand real estate markets.
Multi-family vs Micro-units Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com