Single-family homes offer spacious living areas, private yards, and greater customization options, making them ideal for families and long-term residents. Micro-units provide affordable, efficient spaces in urban centers, catering to singles or young professionals seeking convenience and lower maintenance. Choosing between the two depends on lifestyle preferences, budget constraints, and location priorities.
Table of Comparison
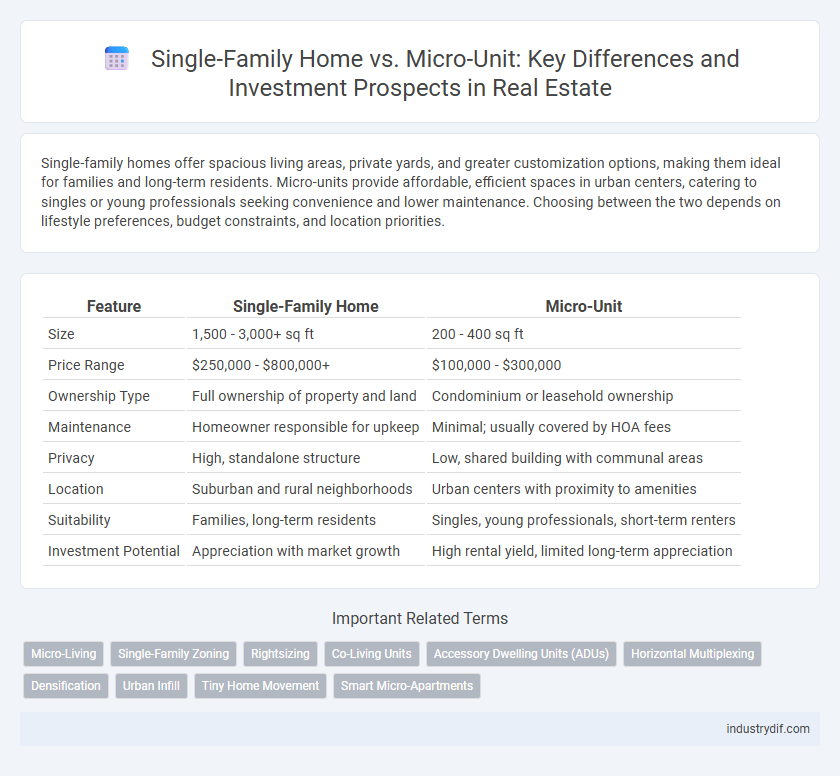
| Feature | Single-Family Home | Micro-Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 1,500 - 3,000+ sq ft | 200 - 400 sq ft |
| Price Range | $250,000 - $800,000+ | $100,000 - $300,000 |
| Ownership Type | Full ownership of property and land | Condominium or leasehold ownership |
| Maintenance | Homeowner responsible for upkeep | Minimal; usually covered by HOA fees |
| Privacy | High, standalone structure | Low, shared building with communal areas |
| Location | Suburban and rural neighborhoods | Urban centers with proximity to amenities |
| Suitability | Families, long-term residents | Singles, young professionals, short-term renters |
| Investment Potential | Appreciation with market growth | High rental yield, limited long-term appreciation |
Single-Family Home vs Micro-Unit: Key Differences
Single-family homes offer more space, privacy, and a yard, making them ideal for families or those seeking long-term stability. Micro-units prioritize affordability and location efficiency, often situated in urban centers with limited square footage and shared amenities. The choice hinges on lifestyle preferences, budget constraints, and the need for space versus convenience.
Space Utilization and Layout Comparison
Single-family homes offer expansive floor plans that provide distinct living, dining, and sleeping areas, maximizing privacy and comfort through separate rooms and ample storage. Micro-units optimize limited square footage by employing multifunctional furniture, open layouts, and vertical storage solutions, enhancing functionality within compact spaces. While single-family homes emphasize spaciousness and individual zones, micro-units prioritize efficient space utilization through smart design and minimalistic layouts.
Cost Analysis: Purchase Price and Rent
Single-family homes typically have higher purchase prices, averaging $350,000 to $450,000 depending on location, while micro-units can cost between $100,000 and $200,000, making them appealing for budget-conscious buyers. Rent for single-family homes ranges from $1,800 to $2,500 per month, whereas micro-unit rents are significantly lower, usually between $800 and $1,200, offering affordability in high-demand urban areas. Investors often consider micro-units for higher rental yield per square foot despite the lower overall rent, while single-family homes provide long-term asset stability and potential appreciation.
Location Trends for Single-Family Homes and Micro-Units
Single-family homes are predominantly located in suburban and rural areas where land availability supports larger properties and family-oriented communities, appealing to buyers seeking space and privacy. Micro-units concentrate in urban centers with high population density, offering affordable, compact living spaces near transit hubs and employment opportunities. Recent trends show increasing micro-unit developments in downtown districts, responding to demand for efficient housing among young professionals and students.
Target Demographics and Buyer Profiles
Single-family homes attract families, professionals, and those seeking more space, privacy, and long-term investment stability, often located in suburban or residential neighborhoods ideal for raising children. Micro-units appeal primarily to young professionals, students, and urban dwellers prioritizing affordability, convenience, and proximity to city amenities, especially in high-density metropolitan areas. Understanding these distinct buyer profiles helps investors and developers tailor properties to meet specific lifestyle preferences and market demands.
Investment Potential and ROI Insights
Single-family homes generally offer stable rental income and higher long-term appreciation, making them a solid investment for consistent ROI in residential real estate markets. Micro-units attract urban professionals and students with lower entry costs and higher rental yield percentages, ideal for investors seeking quicker returns in densely populated areas. Analyzing local demand, occupancy rates, and maintenance expenses is crucial to maximizing investment potential across both housing types.
Lifestyle and Amenities Offered
Single-family homes provide expansive living spaces, private yards, and greater customization options, catering to families seeking privacy and outdoor amenities. Micro-units offer compact, efficient layouts with shared communal spaces and proximity to urban conveniences, ideal for professionals valuing location and minimal maintenance. Lifestyle preferences often dictate the choice, balancing privacy and space against accessibility and community-focused amenities.
Maintenance and Property Management Considerations
Single-family homes typically require higher maintenance costs due to larger spaces and outdoor upkeep, whereas micro-units benefit from lower maintenance expenses and simpler property management. Property managers often face fewer tenant turnover issues with single-family homes, while micro-units may experience higher tenant turnover rates, necessitating more frequent leasing and inspections. Efficient maintenance scheduling and streamlined property management software are essential for optimizing operations across both housing types.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Factors
Single-family homes typically consume more energy due to larger square footage and less efficient use of space, whereas micro-units promote sustainability by minimizing resource consumption and maximizing energy efficiency per square foot. Advanced insulation, smart home technologies, and energy-efficient appliances are easier to implement effectively in compact micro-unit designs, reducing carbon footprints significantly. Urban micro-units also support reduced land use and lower transportation emissions, contributing to holistic environmental benefits compared to sprawling single-family residences.
Future Trends in Residential Housing Choices
Future residential housing trends indicate a growing preference for micro-units in urban areas due to increasing demand for affordable, space-efficient living solutions. Single-family homes continue to attract buyers seeking privacy, outdoor space, and long-term investment value, particularly in suburban and exurban markets. Technology integration and sustainable building practices are shaping both housing types, with smart home features and energy efficiency becoming standard expectations.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Living
Micro-units in real estate maximize urban living efficiency by offering compact, affordable spaces designed for minimalistic lifestyles and reduced utility costs. With features like multi-functional furniture and proximity to amenities, micro-living appeals to young professionals seeking convenience and lower housing expenses compared to traditional single-family homes.
Single-Family Zoning
Single-family zoning restricts land use to detached houses, limiting the development of micro-units and contributing to lower density in suburban neighborhoods. This regulatory framework often increases property values and preserves community character but reduces housing supply flexibility and affordability options.
Rightsizing
Single-family homes offer spacious living and private outdoor areas, ideal for families seeking stability, while micro-units prioritize efficient use of space and affordability, appealing to urban dwellers looking to rightsize without compromising location. Choosing between the two depends on lifestyle needs and the desire to balance square footage with cost and convenience.
Co-Living Units
Single-family homes offer privacy and space ideal for families, whereas micro-units in co-living arrangements maximize affordability and social interaction, catering to urban professionals and students. Co-living units optimize square footage through shared amenities, fostering community living while reducing individual housing costs compared to traditional single-family residences.
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs)
Single-family homes offer spacious living with potential for accessory dwelling units (ADUs) that enhance property value and provide rental income opportunities, while micro-units prioritize compact, efficient living often in urban areas with limited room for ADUs. ADUs in single-family properties support multigenerational housing and zoning flexibility, contrasting with micro-units' inherent space constraints that limit such additions.
Horizontal Multiplexing
Single-family homes offer expansive living spaces with private yards, catering to families seeking privacy and personalization, while micro-units maximize urban density through horizontal multiplexing by efficiently dividing available land into multiple compact residences. Horizontal multiplexing optimizes land use by enabling developers to create multiple, affordable housing units on a single plot, addressing urban housing shortages without vertical high-rise construction.
Densification
Single-family homes offer spacious living with private yards, but micro-units maximize urban land use by increasing housing density in high-demand areas. Emphasizing densification, micro-units address housing shortages and reduce urban sprawl by accommodating more residents per square foot.
Urban Infill
Urban infill development benefits from micro-units by maximizing land use efficiency and providing affordable housing options within city cores, whereas single-family homes contribute to neighborhood stability and offer more living space but require larger plots. Choosing between these housing types depends on urban density goals, infrastructure capacity, and community preferences for compact, sustainable living versus traditional, spacious residential environments.
Tiny Home Movement
Single-family homes offer spacious living and privacy, appealing to traditional buyers seeking long-term family space, whereas micro-units cater to urban dwellers prioritizing affordability and minimal maintenance. The Tiny Home Movement emphasizes sustainability and efficient use of space, driving increased interest in micro-units as eco-friendly alternatives in high-demand real estate markets.
Smart Micro-Apartments
Smart micro-apartments optimize urban living with compact, multifunctional designs and advanced technology, maximizing space efficiency compared to traditional single-family homes. These micro-units provide affordable housing solutions in high-demand city centers, appealing to young professionals and minimalists seeking connectivity and convenience.
Single-Family Home vs Micro-Unit Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com