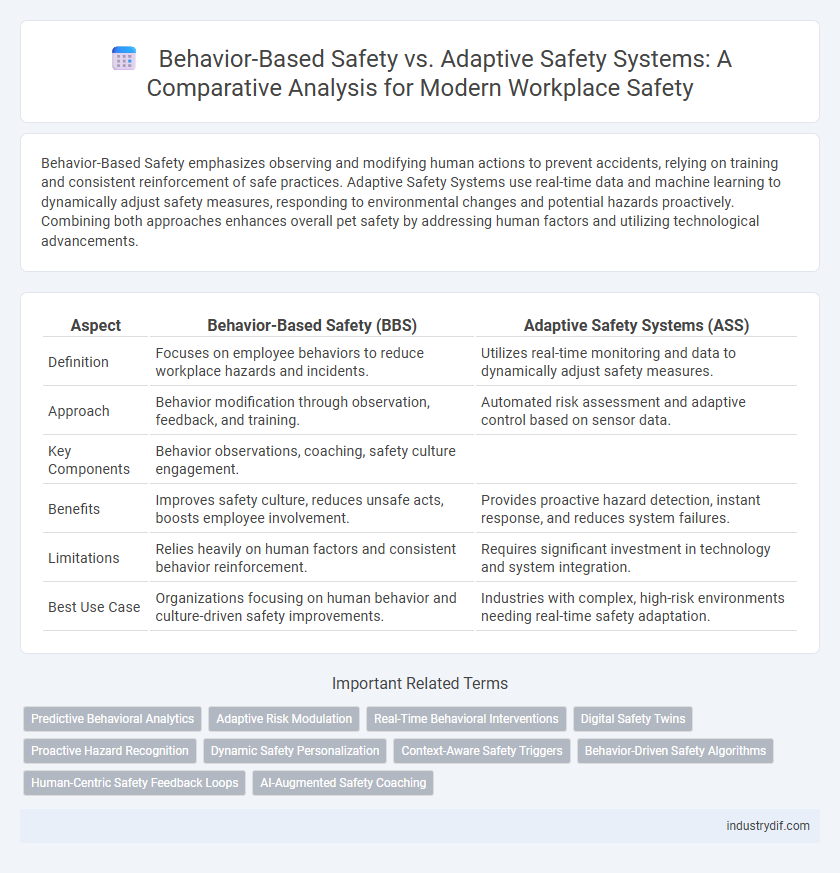
Behavior-Based Safety emphasizes observing and modifying human actions to prevent accidents, relying on training and consistent reinforcement of safe practices. Adaptive Safety Systems use real-time data and machine learning to dynamically adjust safety measures, responding to environmental changes and potential hazards proactively. Combining both approaches enhances overall pet safety by addressing human factors and utilizing technological advancements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) | Adaptive Safety Systems (ASS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on employee behaviors to reduce workplace hazards and incidents. | Utilizes real-time monitoring and data to dynamically adjust safety measures. |
| Approach | Behavior modification through observation, feedback, and training. | Automated risk assessment and adaptive control based on sensor data. |
| Key Components | Behavior observations, coaching, safety culture engagement. | |
| Benefits | Improves safety culture, reduces unsafe acts, boosts employee involvement. | Provides proactive hazard detection, instant response, and reduces system failures. |
| Limitations | Relies heavily on human factors and consistent behavior reinforcement. | Requires significant investment in technology and system integration. |
| Best Use Case | Organizations focusing on human behavior and culture-driven safety improvements. | Industries with complex, high-risk environments needing real-time safety adaptation. |
Introduction to Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) and Adaptive Safety Systems
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) focuses on identifying and reinforcing safe behaviors through observation and feedback to reduce workplace accidents. Adaptive Safety Systems leverage real-time data and machine learning algorithms to dynamically adjust safety protocols and prevent incidents. Both approaches enhance risk management but differ in their reliance on human behavior monitoring versus automated system responsiveness.
Core Principles of Behavior-Based Safety
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) relies on observing and reinforcing safe behaviors among employees to prevent accidents and injuries in the workplace. Core principles include identifying critical safety behaviors, providing positive feedback, and engaging workers in safety discussions to foster accountability and continuous improvement. BBS emphasizes proactive safety culture by addressing human factors and encouraging consistent safe practices through behavior modification.
Fundamentals of Adaptive Safety Systems
Adaptive Safety Systems utilize real-time data and machine learning algorithms to continuously monitor and adjust safety measures, enhancing risk mitigation beyond static protocols. These systems integrate sensor networks and predictive analytics to identify hazards dynamically, improving response times and reducing incident rates. Unlike traditional Behavior-Based Safety approaches that rely on human observation and compliance, Adaptive Safety Systems offer scalable, automated solutions that evolve with changing environments and operational conditions.
Key Differences Between BBS and Adaptive Safety
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) focuses on observing and modifying employee behaviors to prevent workplace accidents through training and feedback, emphasizing human factors and proactive hazard identification. Adaptive Safety Systems leverage real-time data, sensors, and AI algorithms to dynamically adjust safety protocols and mitigate risks based on changing environmental conditions and operational contexts. The key difference lies in BBS prioritizing behavioral modification while Adaptive Safety Systems integrate technology-driven, automated responses for continuous safety management.
Advantages of Behavior-Based Safety Approaches
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) approaches emphasize proactive identification and modification of unsafe behaviors, leading to sustained improvements in workplace safety culture and employee engagement. BBS leverages real-time feedback and positive reinforcement to reduce accident rates more effectively than purely technical safety systems. This method enhances organizational commitment to safety by fostering personal accountability and continuous behavioral risk assessment.
Benefits of Adaptive Safety Systems
Adaptive Safety Systems dynamically respond to real-time data and changing environmental conditions, significantly reducing workplace accidents through proactive hazard mitigation. These systems leverage advanced technologies such as AI, IoT sensors, and machine learning to predict and prevent unsafe behaviors before incidents occur. Enhanced situational awareness and continuous safety optimization contribute to improved compliance and overall operational efficiency.
Implementation Challenges in BBS and Adaptive Safety
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) implementation faces challenges such as employee resistance, inconsistent observation methods, and difficulty maintaining long-term engagement. Adaptive Safety Systems encounter obstacles in integrating real-time data analytics, ensuring system reliability, and managing the complexity of automated responses. Both approaches require significant organizational commitment and continuous training to address human factors and technological adaptation effectively.
Selecting the Right Safety System for Your Industry
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) emphasizes employee engagement and observation to reduce workplace hazards through cultural change, while Adaptive Safety Systems incorporate real-time data and automated responses to dynamically manage risk. Selecting the right safety system depends on industry-specific factors such as hazard complexity, operational environment, and workforce behavior patterns. Industries with highly variable risk conditions benefit more from Adaptive Safety Systems, whereas environments prioritizing human factors and proactive behaviors gain from Behavior-Based Safety programs.
Integrating BBS with Adaptive Safety Technologies
Integrating Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) with Adaptive Safety Technologies enhances workplace hazard prevention by combining human behavioral insights with real-time risk data from IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics. This synergy enables dynamic safety interventions tailored to individual actions and environmental conditions, significantly reducing incidents and improving compliance. Leveraging wearable devices and automated feedback loops creates a proactive safety culture by continuously adapting to evolving workplace risks.
Future Trends in Industrial Safety Systems
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) emphasizes employee actions and proactive training to reduce workplace incidents, while Adaptive Safety Systems integrate real-time data and AI to predict and mitigate hazards dynamically. Future trends in industrial safety systems center on combining BBS insights with machine learning algorithms, enabling continuous improvement and personalized safety interventions. Advanced sensor technologies and IoT connectivity will drive these hybrid systems, fostering smarter, more responsive safety environments.
Related Important Terms
Predictive Behavioral Analytics
Predictive Behavioral Analytics in Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) leverages real-time data to identify patterns of unsafe behavior before incidents occur, enhancing proactive risk mitigation. Adaptive Safety Systems integrate these analytics with automated responses to dynamically adjust safety protocols based on evolving worker behavior and environmental conditions.
Adaptive Risk Modulation
Adaptive Risk Modulation in Adaptive Safety Systems continuously adjusts safety protocols based on real-time data and environmental changes, enhancing hazard prediction and prevention compared to the static nature of Behavior-Based Safety approaches. This dynamic adaptation improves workplace safety by proactively mitigating risks through intelligent system responses tailored to evolving operational conditions.
Real-Time Behavioral Interventions
Behavior-Based Safety employs real-time behavioral interventions by monitoring and analyzing employee actions to reduce incidents and reinforce safe practices on-site. Adaptive Safety Systems leverage real-time data and machine learning to dynamically adjust safety protocols, enhancing proactive hazard mitigation through continuous behavioral feedback.
Digital Safety Twins
Behavior-Based Safety emphasizes monitoring and modifying human actions to prevent accidents, whereas Adaptive Safety Systems leverage real-time data and machine learning to dynamically adjust safety protocols; Digital Safety Twins integrate these approaches by creating virtual replicas of physical environments that simulate safety scenarios, enabling predictive risk analysis and proactive hazard mitigation. This fusion enhances workplace safety through continuous behavioral insights and adaptive responses, reducing incidents more effectively than traditional methods.
Proactive Hazard Recognition
Behavior-Based Safety emphasizes proactive hazard recognition by analyzing worker actions and reinforcing safe behaviors to prevent incidents before they occur. Adaptive Safety Systems leverage real-time data and machine learning algorithms to dynamically identify and mitigate emerging risks, enhancing hazard detection efficiency.
Dynamic Safety Personalization
Behavior-Based Safety relies on monitoring and modifying employee actions to reduce risks, while Adaptive Safety Systems utilize real-time data and artificial intelligence to dynamically personalize safety measures tailored to individual behaviors and environmental conditions. This dynamic safety personalization enhances hazard detection and risk mitigation by continuously adjusting safety protocols to the evolving workplace context.
Context-Aware Safety Triggers
Behavior-Based Safety relies on observing and modifying worker actions to prevent incidents, whereas Adaptive Safety Systems utilize real-time data and machine learning algorithms to detect hazards dynamically. Context-aware safety triggers enhance these systems by integrating environmental variables and worker conditions, enabling proactive risk mitigation tailored to specific operational contexts.
Behavior-Driven Safety Algorithms
Behavior-Driven Safety Algorithms leverage real-time data to analyze and predict risky behaviors, enhancing proactive hazard prevention in workplaces. These algorithms improve safety outcomes by continuously adapting interventions based on employee actions and environmental changes, surpassing traditional Behavior-Based Safety and static Adaptive Safety Systems.
Human-Centric Safety Feedback Loops
Behavior-Based Safety emphasizes continuous observation and real-time feedback to modify employee actions, fostering proactive risk reduction through human-centric safety feedback loops. Adaptive Safety Systems integrate sensor data and AI-driven analytics to dynamically adjust safety protocols, enhancing responsiveness by combining technological inputs with human behavior insights for optimal hazard prevention.
AI-Augmented Safety Coaching
Behavior-Based Safety integrates AI-augmented safety coaching to analyze employee actions and provide real-time feedback, reducing human error and promoting proactive risk mitigation. Adaptive Safety Systems leverage machine learning to dynamically adjust safety protocols based on contextual data, enhancing workplace hazard prevention through continuous learning and personalized interventions.
Behavior-Based Safety vs Adaptive Safety Systems Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com