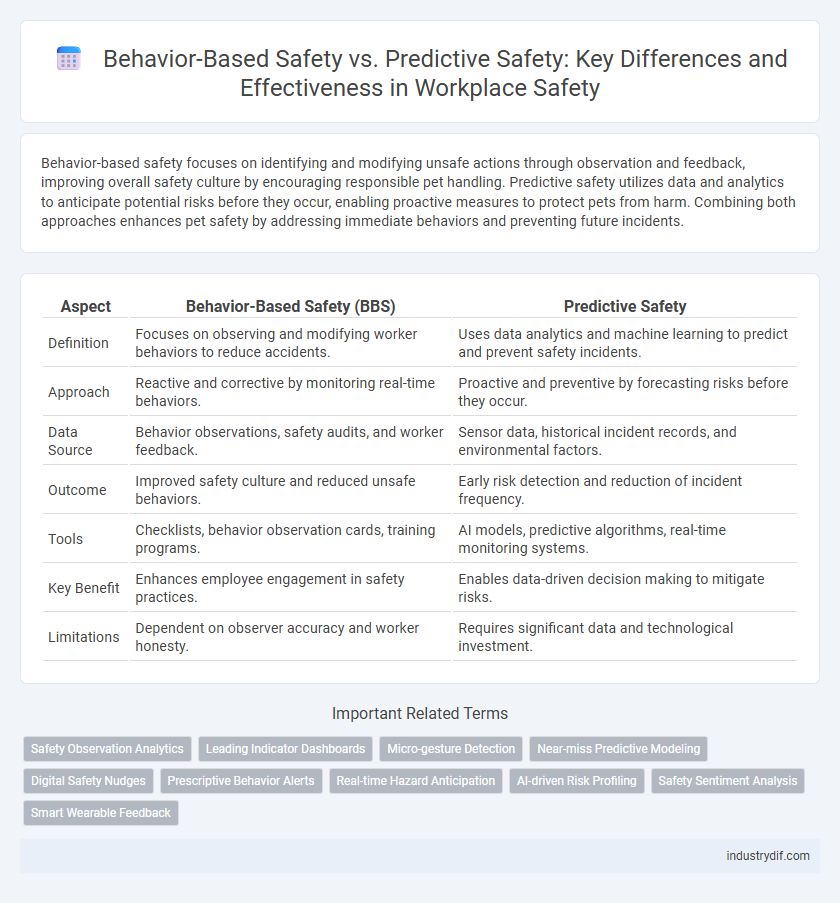
Behavior-based safety focuses on identifying and modifying unsafe actions through observation and feedback, improving overall safety culture by encouraging responsible pet handling. Predictive safety utilizes data and analytics to anticipate potential risks before they occur, enabling proactive measures to protect pets from harm. Combining both approaches enhances pet safety by addressing immediate behaviors and preventing future incidents.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) | Predictive Safety |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on observing and modifying worker behaviors to reduce accidents. | Uses data analytics and machine learning to predict and prevent safety incidents. |
| Approach | Reactive and corrective by monitoring real-time behaviors. | Proactive and preventive by forecasting risks before they occur. |
| Data Source | Behavior observations, safety audits, and worker feedback. | Sensor data, historical incident records, and environmental factors. |
| Outcome | Improved safety culture and reduced unsafe behaviors. | Early risk detection and reduction of incident frequency. |
| Tools | Checklists, behavior observation cards, training programs. | AI models, predictive algorithms, real-time monitoring systems. |
| Key Benefit | Enhances employee engagement in safety practices. | Enables data-driven decision making to mitigate risks. |
| Limitations | Dependent on observer accuracy and worker honesty. | Requires significant data and technological investment. |
Understanding Behavior-Based Safety: Core Principles
Behavior-Based Safety focuses on identifying and reinforcing safe behaviors through direct observation and feedback, emphasizing employee participation and behavioral change to reduce workplace incidents. Core principles include proactive hazard identification, continuous performance monitoring, and positive reinforcement to promote a safety culture. This approach relies on data-driven insights into human actions to prevent accidents and improve overall organizational safety.
Introduction to Predictive Safety: Definitions and Scope
Predictive Safety utilizes data analytics and machine learning algorithms to forecast potential workplace hazards before they occur, enabling proactive risk management. Unlike Behavior-Based Safety, which focuses on observing and modifying employee behaviors, Predictive Safety integrates real-time sensor data, historical incident records, and environmental factors to identify patterns and predict safety incidents. This approach broadens the scope of traditional safety measures by leveraging technology to anticipate risks and implement preventive actions, enhancing overall workplace safety performance.
Key Differences Between Behavior-Based and Predictive Safety
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) emphasizes observing and modifying employee actions to prevent accidents by identifying unsafe behaviors and promoting safe practices in real-time. Predictive Safety relies on data analysis, leveraging historical incident reports, sensor data, and risk models to forecast potential hazards before they occur. The key difference lies in BBS targeting human behavior through direct observation and feedback, while Predictive Safety uses technology-driven analytics to proactively mitigate risks.
The Role of Data in Behavior-Based Safety Programs
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) programs rely heavily on data collection from employee actions and observations to identify risk patterns and unsafe behaviors in real-time. Data analytics in BBS enables targeted interventions that improve worker compliance and reduce incidents by focusing on behavioral trends instead of just outcomes. Integrating comprehensive behavior data enhances the precision and effectiveness of safety strategies, driving continuous improvement in workplace safety culture.
Leveraging Predictive Analytics for Workplace Safety
Leveraging predictive analytics in workplace safety enhances hazard identification by analyzing historical incident data and real-time sensor inputs to forecast potential risks before they manifest. This data-driven approach optimizes resource allocation for safety interventions, reducing workplace accidents more effectively than traditional behavior-based safety programs. Advanced predictive models enable organizations to implement proactive measures, fostering a safer work environment with decreased injury rates and improved compliance.
Strengths and Limitations of Behavior-Based Safety Approaches
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) emphasizes observing and modifying individual worker behaviors to reduce accidents, leveraging real-time feedback and employee engagement to foster a proactive safety culture. Strengths of BBS include its ability to increase hazard awareness and promote safe practices through continuous monitoring and reinforcement of positive actions. Limitations arise from its focus on individual behavior, often neglecting systemic issues, equipment failures, and organizational factors that also contribute to workplace incidents.
Predictive Safety: Benefits and Implementation Challenges
Predictive Safety leverages advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms to proactively identify potential hazards before incidents occur, enhancing overall workplace safety. Key benefits include improved risk mitigation, reduced accident rates, and optimized resource allocation for safety interventions. Implementation challenges involve data quality management, integration with existing safety systems, and the need for skilled personnel to interpret predictive insights effectively.
Integrating Behavior-Based and Predictive Safety Strategies
Integrating behavior-based safety (BBS) and predictive safety strategies enhances workplace risk management by combining real-time behavioral observations with data-driven hazard forecasting. BBS focuses on modifying unsafe behaviors through employee engagement and feedback, while predictive safety leverages advanced analytics and machine learning to anticipate potential incidents before they occur. This integrated approach improves accident prevention, fosters a proactive safety culture, and optimizes resource allocation for maximum impact.
Case Studies: Behavior-Based Safety vs Predictive Safety Outcomes
Case studies comparing Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) and Predictive Safety reveal distinct outcomes affecting workplace incident rates. BBS initiatives typically result in improved employee compliance and reduced unsafe behaviors by reinforcing positive actions through observation and feedback. Predictive Safety, leveraging data analytics and machine learning, identifies potential hazards before incidents occur, demonstrating significant reductions in accidents through proactive interventions.
Future Trends in Industrial Safety: From Behavior to Prediction
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) emphasizes identifying and modifying unsafe behaviors through observation and feedback, while Predictive Safety leverages data analytics and machine learning to forecast and prevent incidents before they occur. Future trends in industrial safety point towards integrating real-time sensor data with AI-driven predictive models to enhance hazard detection and risk mitigation. This shift from reactive behavior monitoring to proactive prediction aims to reduce workplace accidents by anticipating potential failures and enabling timely interventions.
Related Important Terms
Safety Observation Analytics
Behavior-Based Safety relies on direct safety observation analytics to identify at-risk behaviors and implement corrective actions, enhancing workplace compliance and reducing incidents. Predictive Safety leverages advanced data analytics and machine learning to analyze safety observation trends, forecasting potential hazards before they manifest and enabling proactive risk mitigation.
Leading Indicator Dashboards
Leading Indicator Dashboards in Behavior-Based Safety emphasize real-time observations and employee engagement metrics to proactively reduce workplace risks, while Predictive Safety dashboards leverage data analytics and machine learning to forecast potential incidents before they occur. Integrating behavior-driven insights with predictive algorithms enhances the precision of hazard identification and facilitates timely interventions.
Micro-gesture Detection
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) relies on observing and correcting visible actions to prevent accidents, while Predictive Safety utilizes advanced technologies such as micro-gesture detection to identify subtle, often unconscious movements that signal potential risks. Micro-gesture detection enhances safety programs by providing real-time analysis of fine motor patterns, enabling early intervention before hazardous behaviors escalate.
Near-miss Predictive Modeling
Behavior-Based Safety focuses on observing and modifying worker behaviors to prevent incidents, while Predictive Safety utilizes near-miss predictive modeling by analyzing data patterns from near-miss events to forecast and mitigate potential hazards before they escalate. Near-miss predictive modeling enhances safety programs by identifying hidden risks in real-time, enabling proactive interventions that reduce workplace accidents and improve overall safety performance.
Digital Safety Nudges
Behavior-Based Safety relies on observing and modifying worker actions through real-time feedback, while Predictive Safety employs data analytics and machine learning to anticipate hazards before incidents occur. Digital Safety Nudges enhance both approaches by delivering timely, personalized alerts that encourage safer behaviors and prevent risks based on predictive insights.
Prescriptive Behavior Alerts
Prescriptive behavior alerts in behavior-based safety systems provide real-time guidance to employees by identifying unsafe actions and recommending corrective measures to prevent accidents. Predictive safety leverages data analytics to forecast potential risks, but integrating prescriptive alerts ensures immediate behavioral adjustments, enhancing overall workplace safety performance.
Real-time Hazard Anticipation
Behavior-Based Safety relies on observing employee actions to identify risks, while Predictive Safety uses real-time data analytics and machine learning algorithms for proactive hazard anticipation. Real-time hazard anticipation in Predictive Safety enhances workplace safety by predicting potential incidents before they occur, reducing accident rates significantly.
AI-driven Risk Profiling
Behavior-Based Safety emphasizes monitoring employee actions to prevent accidents, while Predictive Safety leverages AI-driven risk profiling to analyze data patterns, anticipate hazards, and proactively mitigate risks before incidents occur. AI-powered algorithms process historical safety data and real-time inputs to generate precise risk assessments, enhancing workplace safety management and reducing injury rates.
Safety Sentiment Analysis
Behavior-Based Safety leverages direct observation of worker actions to identify and mitigate unsafe behaviors, while Predictive Safety employs data analytics and machine learning to forecast potential hazards; incorporating Safety Sentiment Analysis enhances these approaches by interpreting employee feedback and emotions to uncover hidden risks and improve proactive safety interventions. Integrating real-time sentiment insights with behavioral and predictive data optimizes safety performance by addressing both observable actions and underlying workforce attitudes.
Smart Wearable Feedback
Behavior-Based Safety emphasizes real-time observation and feedback to modify worker actions and reduce incidents, while Predictive Safety leverages data analytics and smart wearable feedback to anticipate and prevent hazards before they occur. Smart wearables equipped with sensors monitor physiological and environmental conditions, delivering immediate alerts and personalized safety recommendations to enhance proactive risk management.
Behavior-Based Safety vs Predictive Safety Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com