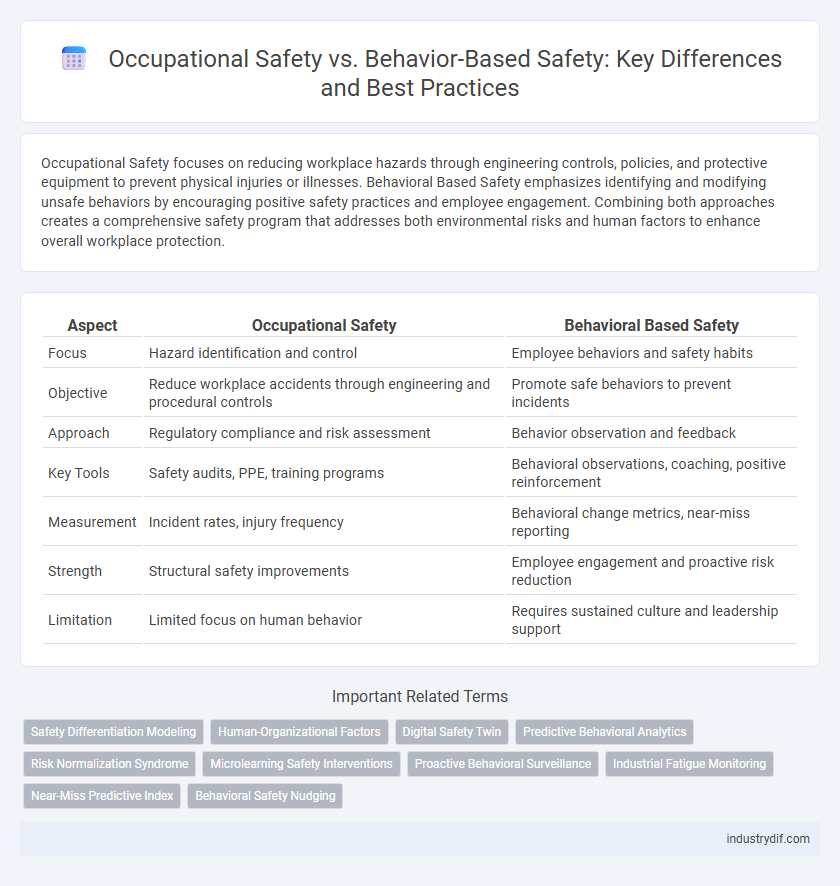
Occupational Safety focuses on reducing workplace hazards through engineering controls, policies, and protective equipment to prevent physical injuries or illnesses. Behavioral Based Safety emphasizes identifying and modifying unsafe behaviors by encouraging positive safety practices and employee engagement. Combining both approaches creates a comprehensive safety program that addresses both environmental risks and human factors to enhance overall workplace protection.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Occupational Safety | Behavioral Based Safety |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Hazard identification and control | Employee behaviors and safety habits |
| Objective | Reduce workplace accidents through engineering and procedural controls | Promote safe behaviors to prevent incidents |
| Approach | Regulatory compliance and risk assessment | Behavior observation and feedback |
| Key Tools | Safety audits, PPE, training programs | Behavioral observations, coaching, positive reinforcement |
| Measurement | Incident rates, injury frequency | Behavioral change metrics, near-miss reporting |
| Strength | Structural safety improvements | Employee engagement and proactive risk reduction |
| Limitation | Limited focus on human behavior | Requires sustained culture and leadership support |
Understanding Occupational Safety: Definitions and Scope
Occupational safety encompasses the policies, procedures, and practices designed to prevent workplace injuries and illnesses, ensuring a secure environment for employees across various industries. It includes hazard identification, risk assessment, and compliance with regulatory standards such as OSHA to maintain health and safety protocols. Understanding the scope of occupational safety involves recognizing the roles of engineering controls, personal protective equipment, and safety training in mitigating workplace hazards.
Introduction to Behavioral Based Safety (BBS)
Behavioral Based Safety (BBS) focuses on identifying and modifying unsafe behaviors in the workplace to prevent accidents and injuries. Unlike traditional Occupational Safety which emphasizes compliance with safety regulations and hazard controls, BBS leverages observation, feedback, and positive reinforcement to encourage safer employee actions. Implementing BBS programs results in measurable improvements in safety culture and reduction of incident rates by addressing the root human factors contributing to workplace hazards.
Key Differences Between Occupational Safety and BBS
Occupational Safety primarily focuses on compliance with established regulations, hazard identification, and implementation of engineering controls to minimize workplace risks. Behavioral Based Safety (BBS) emphasizes observing and influencing employee behaviors to prevent accidents by promoting safe practices and reinforcing positive actions. The key difference lies in Occupational Safety targeting systemic controls, while BBS centers on modifying human behavior to enhance overall safety culture.
Core Principles of Occupational Safety Programs
Occupational Safety programs center on hazard identification, risk assessment, and implementing engineering controls to prevent workplace injuries, emphasizing compliance with regulatory standards such as OSHA guidelines. Behavioral Based Safety focuses on modifying employee behaviors through observation and feedback to reduce at-risk actions, promoting a safety culture driven by individual responsibility. Core principles of Occupational Safety include systematic hazard control, comprehensive training, and continuous monitoring to ensure a safe work environment.
Fundamental Concepts of Behavioral Based Safety
Behavioral Based Safety (BBS) centers on identifying and modifying employee behaviors to prevent workplace accidents, emphasizing proactive risk reduction rather than reactive measures. Core concepts include observation, feedback, and positive reinforcement to encourage safe work practices and enhance hazard recognition. This approach contrasts with traditional Occupational Safety, which often focuses more on compliance and engineering controls rather than behavioral interventions.
Role of Management in Occupational vs. Behavioral Safety
Management in Occupational Safety establishes formal policies, ensures regulatory compliance, and allocates resources to maintain a safe work environment through systematic hazard identification and controls. In Behavioral Based Safety, management plays a pivotal role in fostering a safety culture by promoting employee engagement, providing behavior-focused training, and reinforcing positive safety behaviors. Leadership commitment and active involvement are critical in both approaches to effectively minimize workplace injuries and enhance overall safety performance.
Measuring Success: Safety Metrics and KPIs
Measuring success in Occupational Safety relies heavily on lagging indicators such as the Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR) and Lost Time Injury Frequency Rate (LTIFR), which quantify the occurrence of accidents after they happen. Behavioral Based Safety focuses on leading indicators like the frequency of safe behaviors observed and near-miss reporting rates to proactively reduce hazards before incidents occur. Combining lagging and leading safety metrics and KPIs creates a comprehensive approach to evaluating and improving workplace safety performance.
Common Challenges in Implementing Occupational Safety and BBS
Implementing Occupational Safety and Behavioral Based Safety (BBS) programs often faces common challenges such as employee resistance, inconsistent management commitment, and difficulty in accurately measuring behavior changes. Both approaches require continuous training and clear communication to ensure adherence to safety protocols and foster a culture of accountability. Addressing these issues through stakeholder engagement and robust monitoring systems enhances program effectiveness and reduces workplace incidents.
Integration Strategies: Blending Occupational and Behavioral Approaches
Effective integration strategies blend Occupational Safety's regulatory compliance and hazard control with Behavioral Based Safety's focus on employee behavior and mindset to create a comprehensive safety culture. Implementing data-driven hazard assessments alongside behavior observation tools enhances risk identification and proactive prevention. Training programs that combine technical safety protocols with behavioral reinforcement improve overall workplace safety performance and reduce incident rates.
Future Trends in Workplace Safety Practices
Future trends in workplace safety practices emphasize integrating Occupational Safety Management Systems with Behavioral Based Safety approaches to create comprehensive risk reduction strategies. Advancements in AI-powered monitoring and wearable technology enable real-time hazard detection and personalized behavioral feedback, significantly enhancing proactive incident prevention. Increasing adoption of data analytics and employee engagement platforms fosters a culture of continuous safety improvement by aligning organizational policies with individual safety behaviors.
Related Important Terms
Safety Differentiation Modeling
Occupational Safety focuses on compliance with regulations, hazard identification, and implementation of engineering controls to minimize workplace risks, while Behavioral Based Safety emphasizes modifying employee behaviors through observation and feedback to prevent incidents. Safety Differentiation Modeling integrates these approaches by analyzing both systemic hazards and individual actions to create a holistic risk reduction strategy.
Human-Organizational Factors
Occupational Safety prioritizes structured policies and regulatory compliance to mitigate workplace hazards, while Behavioral Based Safety emphasizes modifying individual behaviors through observation and feedback, targeting human-organizational factors such as communication, leadership, and workplace culture. Integrating these approaches enhances safety performance by addressing both systemic risk controls and employee behavioral patterns that influence accident prevention.
Digital Safety Twin
Occupational Safety traditionally centers on compliance and hazard control, while Behavioral Based Safety emphasizes employee behavior to prevent accidents; integrating Digital Safety Twin technology enhances both approaches by simulating real-time safety scenarios and predicting risk factors with precise data analytics. This advanced digital model enables proactive interventions, reducing workplace incidents by continuously monitoring behavioral patterns and environmental conditions.
Predictive Behavioral Analytics
Predictive Behavioral Analytics in Occupational Safety utilizes data-driven insights to forecast unsafe behaviors and prevent incidents before they occur, enhancing overall workplace risk management. This approach surpasses traditional Behavioral Based Safety methods by integrating real-time monitoring and advanced algorithms to proactively identify potential hazards and improve safety compliance.
Risk Normalization Syndrome
Risk Normalization Syndrome occurs when workers become desensitized to hazards through repeated exposure, undermining both Occupational Safety protocols and Behavioral Based Safety (BBS) initiatives that rely on consistent hazard recognition. Addressing this syndrome requires integrating real-time risk assessments and behavioral interventions to maintain vigilance and prevent complacency in safety practices.
Microlearning Safety Interventions
Occupational Safety emphasizes hazard identification and compliance with safety regulations, while Behavioral-Based Safety focuses on modifying employee behaviors to prevent accidents. Microlearning safety interventions enable targeted, bite-sized training modules that improve retention and reinforce safe practices effectively in both approaches.
Proactive Behavioral Surveillance
Proactive behavioral surveillance in occupational safety emphasizes real-time observation and modification of worker behaviors to prevent incidents before they occur, leveraging behavioral-based safety principles. This approach integrates data-driven risk assessments with employee engagement, fostering a culture of continuous safety improvement and reducing workplace hazards more effectively than traditional compliance-focused methods.
Industrial Fatigue Monitoring
Industrial fatigue monitoring is a critical component of Occupational Safety, utilizing real-time data and wearable technology to identify worker fatigue levels and prevent accidents caused by decreased alertness. Behavioral Based Safety complements this approach by promoting worker awareness and proactive behaviors, thus reducing fatigue-related incidents through continuous observation and feedback.
Near-Miss Predictive Index
Occupational Safety emphasizes compliance with regulations and hazard control, while Behavioral Based Safety (BBS) focuses on modifying employee behavior to reduce incidents; the Near-Miss Predictive Index leverages behavioral data to predict and prevent potential accidents before they occur. Integrating Near-Miss Predictive Index within BBS programs enhances proactive risk management by identifying patterns and enabling targeted interventions.
Behavioral Safety Nudging
Behavioral Safety Nudging leverages subtle cues and prompts to influence workers' actions toward safer behaviors, enhancing compliance without direct enforcement. This approach contrasts with traditional Occupational Safety measures by prioritizing psychological motivators and real-time feedback to reduce workplace incidents effectively.
Occupational Safety vs Behavioral Based Safety Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com