Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) focuses on observing and reinforcing safe behaviors among employees to reduce accidents, emphasizing individual actions and real-time feedback. The Safety Culture Index measures the overall safety climate within an organization by assessing attitudes, beliefs, and perceptions about safety at all levels. Combining BBS with a strong Safety Culture Index creates a comprehensive approach that enhances both personal responsibility and collective commitment to workplace safety.
Table of Comparison
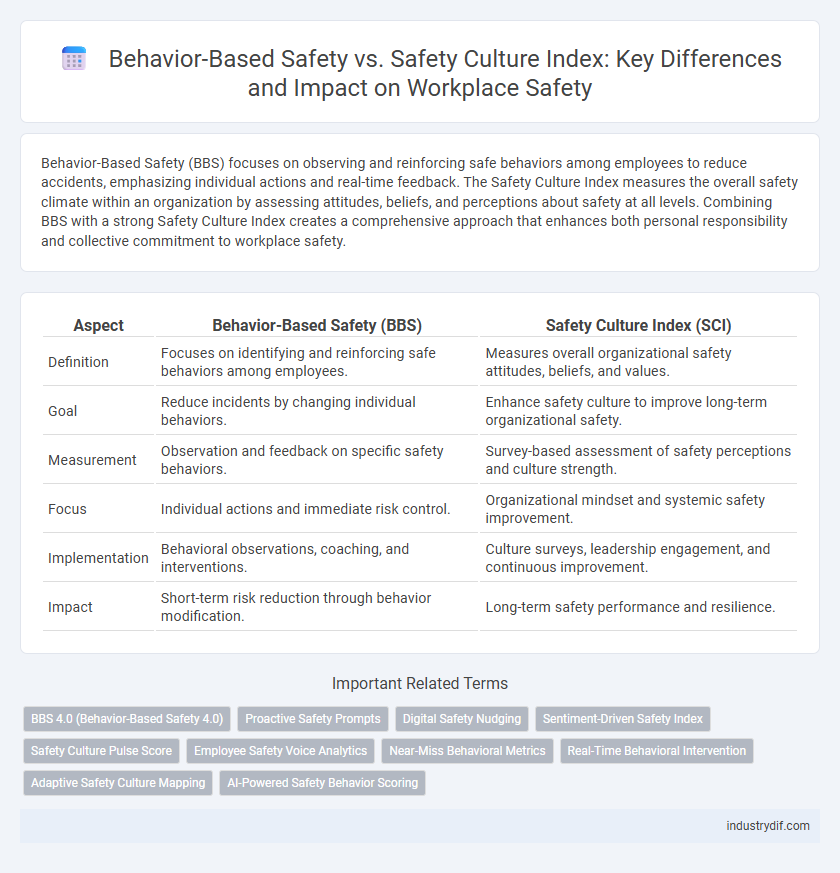
| Aspect | Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) | Safety Culture Index (SCI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on identifying and reinforcing safe behaviors among employees. | Measures overall organizational safety attitudes, beliefs, and values. |
| Goal | Reduce incidents by changing individual behaviors. | Enhance safety culture to improve long-term organizational safety. |
| Measurement | Observation and feedback on specific safety behaviors. | Survey-based assessment of safety perceptions and culture strength. |
| Focus | Individual actions and immediate risk control. | Organizational mindset and systemic safety improvement. |
| Implementation | Behavioral observations, coaching, and interventions. | Culture surveys, leadership engagement, and continuous improvement. |
| Impact | Short-term risk reduction through behavior modification. | Long-term safety performance and resilience. |
Defining Behavior-Based Safety (BBS)
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) is a proactive approach that focuses on identifying and modifying at-risk behaviors to prevent workplace accidents and injuries. By observing employee actions and providing real-time feedback, BBS promotes safe practices and reinforces positive behaviors. This method relies heavily on data-driven insights and continuous employee engagement to enhance overall safety performance compared to broader measures like the Safety Culture Index.
Understanding the Safety Culture Index
The Safety Culture Index measures an organization's overall safety mindset by evaluating employee attitudes, perceptions, and behaviors toward risk and compliance. Unlike Behavior-Based Safety, which targets specific unsafe actions, the Safety Culture Index provides a comprehensive assessment of how deeply safety values are embedded within the workplace environment. Organizations use this index to identify cultural strengths and weaknesses, enabling targeted interventions that support long-term improvements in safety performance.
Key Differences Between BBS and Safety Culture Index
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) focuses on identifying and modifying employees' actions to reduce accidents, relying on observable behaviors and immediate feedback. The Safety Culture Index measures the overall organizational safety climate, assessing attitudes, perceptions, and values that influence safety performance on a broader scale. Key differences include BBS targeting individual behavior change, while the Safety Culture Index evaluates systemic cultural factors driving long-term safety improvements.
Core Principles of Behavior-Based Safety
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) centers on identifying and modifying unsafe behaviors through positive reinforcement and continuous observation, emphasizing employee involvement and real-time feedback. Core principles include clear behavior definition, frequent safety observations, constructive feedback, and behavioral data analysis to reduce incidents. In contrast, the Safety Culture Index evaluates organizational attitudes and values towards safety, providing a broader measurement of safety climate beyond individual behaviors.
Components of a Robust Safety Culture
A robust safety culture integrates clear communication, continuous employee engagement, and leadership commitment to prioritize workplace safety. Behavior-Based Safety emphasizes observable actions and feedback to reduce risks, while the Safety Culture Index provides measurable insights into organizational attitudes and values toward safety. Combining these components fosters a proactive environment where safety is embedded in decision-making and daily practices.
Measuring Safety Performance: BBS vs Safety Culture Index
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) measures safety performance by analyzing individual employee behaviors and adherence to safety protocols through direct observations and feedback. The Safety Culture Index evaluates the collective attitudes, beliefs, and perceptions about safety within an organization, using surveys and assessments to gauge overall safety climate. While BBS provides granular data on specific behaviors, the Safety Culture Index offers a broader understanding of organizational safety mindset and its impact on incident rates.
Benefits and Limitations of Behavior-Based Safety
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) programs enhance workplace safety by identifying and modifying risky behaviors through observation and feedback, leading to a measurable reduction in incidents and improved employee engagement. The main benefit of BBS lies in its proactive approach, focusing on human factors to prevent accidents before they occur; however, it can be limited by potential observer bias and a narrow emphasis on individual behavior rather than systemic safety issues. Unlike the broader Safety Culture Index, which evaluates organizational attitudes and structures, BBS provides targeted actions but may overlook deeper cultural drivers influencing safety performance.
Advantages and Challenges of Using Safety Culture Index
The Safety Culture Index offers a comprehensive, data-driven approach to measuring organizational safety attitudes, enabling targeted interventions that enhance overall workplace safety. Its advantages include the ability to benchmark progress over time and foster employee engagement through transparent feedback mechanisms. Challenges arise from the complexity of accurately capturing cultural nuances and the potential for misinterpretation of survey data without proper contextual analysis.
Integrating BBS and Safety Culture Index for Maximum Impact
Integrating Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) with the Safety Culture Index enhances workplace risk management by combining observational behavior data with cultural assessment metrics. This integration allows organizations to identify critical behavioral patterns alongside underlying cultural factors that contribute to unsafe practices. Leveraging both tools together drives comprehensive safety improvements, reduces incident rates, and fosters a proactive safety environment.
Choosing the Right Safety Approach for Your Organization
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) focuses on observing and modifying individual actions to reduce workplace accidents, while the Safety Culture Index measures the overall safety attitudes and behaviors within an organization. Selecting the right safety approach depends on the organization's specific needs, risk level, and existing safety maturity, with BBS being effective for targeted behavioral improvements and the Safety Culture Index providing a broader cultural assessment. Integrating both strategies can enhance safety performance by addressing immediate behaviors and underlying cultural factors.
Related Important Terms
BBS 4.0 (Behavior-Based Safety 4.0)
Behavior-Based Safety 4.0 (BBS 4.0) integrates real-time data analytics and IoT technology to proactively identify and mitigate workplace hazards, enhancing employee engagement through personalized behavioral interventions. Unlike the Safety Culture Index, which measures organizational attitudes toward safety, BBS 4.0 actively modifies behaviors using behavioral science and advanced monitoring tools to reduce incidents and promote a sustainable safety environment.
Proactive Safety Prompts
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) emphasizes proactive safety prompts by identifying and modifying at-risk behaviors through direct observation and feedback, reducing incidents before they occur. In contrast, the Safety Culture Index evaluates the overall safety mindset of an organization, providing data-driven insights but less immediate behavioral intervention.
Digital Safety Nudging
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) leverages digital safety nudging to reinforce safe behaviors through targeted, real-time feedback and data-driven interventions, increasing employee engagement and reducing incidents. The Safety Culture Index incorporates these digital nudges to quantitatively assess organizational safety attitudes and predict risk patterns, enhancing proactive safety management.
Sentiment-Driven Safety Index
Sentiment-Driven Safety Index enhances traditional Behavior-Based Safety by integrating employee emotions and perceptions to predict safety risks more accurately. This approach leverages real-time sentiment analysis from surveys and feedback, offering deeper insights compared to the quantitative metrics used in Safety Culture Index assessments.
Safety Culture Pulse Score
Safety Culture Pulse Score quantifies employee perceptions and engagement levels in safety practices, offering real-time insights into organizational safety climate. Unlike Behavior-Based Safety which targets individual actions, the Pulse Score emphasizes collective cultural factors impacting overall safety performance.
Employee Safety Voice Analytics
Behavior-Based Safety emphasizes identifying and modifying unsafe employee actions through real-time observations, while the Safety Culture Index measures overall organizational safety attitudes and practices. Employee Safety Voice Analytics leverages data from worker feedback and communication patterns to enhance both behavior interventions and culture assessments by pinpointing hidden safety concerns and trends.
Near-Miss Behavioral Metrics
Behavior-Based Safety emphasizes identifying and modifying unsafe behaviors through near-miss behavioral metrics to prevent incidents before they occur, while the Safety Culture Index evaluates the overall organizational attitudes and perceptions towards safety, incorporating near-miss reporting as a key indicator of proactive safety engagement. Near-miss behavioral metrics provide actionable data that directly influence behavior change, enhancing the accuracy and effectiveness of both safety management approaches.
Real-Time Behavioral Intervention
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) emphasizes Real-Time Behavioral Intervention by identifying and correcting unsafe actions on the spot, enhancing immediate risk reduction. The Safety Culture Index, while measuring overall organizational safety attitudes, lacks the dynamic responsiveness of BBS in addressing unsafe behaviors as they occur.
Adaptive Safety Culture Mapping
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) emphasizes identifying and modifying unsafe actions through direct observation and feedback, while Safety Culture Index (SCI) provides a quantifiable measure of organizational safety attitudes and beliefs. Adaptive Safety Culture Mapping integrates BBS data with SCI metrics to dynamically assess and improve a company's safety culture, enabling targeted interventions that evolve with changing workplace behaviors and environmental conditions.
AI-Powered Safety Behavior Scoring
AI-powered Safety Behavior Scoring enhances Behavior-Based Safety programs by utilizing real-time data analytics to identify risk patterns and predict unsafe actions, enabling proactive intervention. Integrating this technology with the Safety Culture Index offers a dynamic measurement of organizational safety attitudes, driving continuous improvement in workplace safety performance.
Behavior-Based Safety vs Safety Culture Index Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com