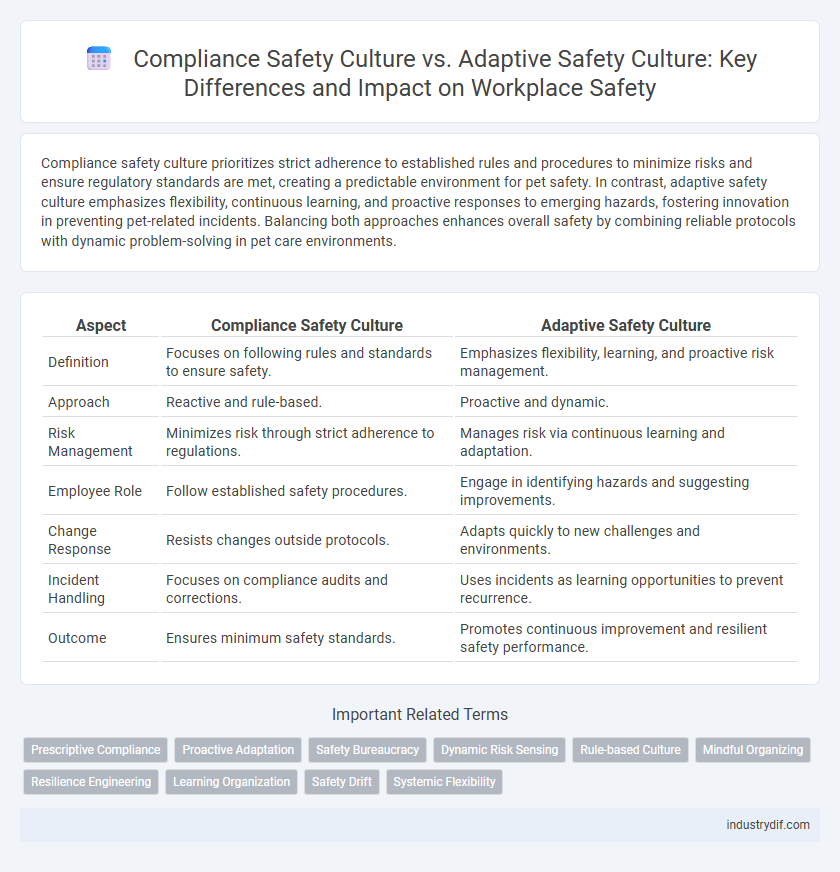
Compliance safety culture prioritizes strict adherence to established rules and procedures to minimize risks and ensure regulatory standards are met, creating a predictable environment for pet safety. In contrast, adaptive safety culture emphasizes flexibility, continuous learning, and proactive responses to emerging hazards, fostering innovation in preventing pet-related incidents. Balancing both approaches enhances overall safety by combining reliable protocols with dynamic problem-solving in pet care environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Compliance Safety Culture | Adaptive Safety Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on following rules and standards to ensure safety. | Emphasizes flexibility, learning, and proactive risk management. |
| Approach | Reactive and rule-based. | Proactive and dynamic. |
| Risk Management | Minimizes risk through strict adherence to regulations. | Manages risk via continuous learning and adaptation. |
| Employee Role | Follow established safety procedures. | Engage in identifying hazards and suggesting improvements. |
| Change Response | Resists changes outside protocols. | Adapts quickly to new challenges and environments. |
| Incident Handling | Focuses on compliance audits and corrections. | Uses incidents as learning opportunities to prevent recurrence. |
| Outcome | Ensures minimum safety standards. | Promotes continuous improvement and resilient safety performance. |
Defining Compliance Safety Culture
Compliance Safety Culture emphasizes strict adherence to established safety policies, regulations, and procedures to minimize risk and ensure organizational accountability. It relies on clearly defined rules and systematic monitoring to enforce consistent safety behavior among employees. This culture prioritizes preventing incidents through conformity, audit-driven performance, and corrective actions based on regulatory standards.
Understanding Adaptive Safety Culture
Adaptive Safety Culture emphasizes flexibility and continuous learning to proactively manage emerging risks, contrasting with Compliance Safety Culture's focus on adhering strictly to established rules and procedures. It fosters open communication, employee empowerment, and real-time problem-solving, enabling organizations to anticipate and respond to dynamic safety challenges. This approach improves resilience by integrating frontline insights and encouraging innovation in safety practices.
Key Differences Between Compliance and Adaptive Approaches
Compliance safety culture emphasizes strict adherence to established rules, regulations, and procedures to prevent incidents and ensure organizational safety standards are met. Adaptive safety culture prioritizes flexibility, learning, and responsiveness to evolving risks, encouraging proactive identification and mitigation of hazards. Key differences include the rigidity of compliance with fixed protocols versus the dynamic, continuous improvement focus of adaptive safety cultures.
Benefits of Compliance Safety Culture
Compliance safety culture ensures adherence to established regulations and standards, reducing the risk of accidents and legal liabilities through consistent enforcement of safety protocols. It fosters a predictable and controlled work environment where employees clearly understand safety expectations and procedures. Organizations with a strong compliance safety culture often experience enhanced accountability and measurable safety performance improvements.
Advantages of Adaptive Safety Culture
Adaptive Safety Culture enhances organizational resilience by promoting continuous learning and flexibility in response to emerging risks. This approach prioritizes proactive hazard identification and real-time decision-making, reducing the likelihood of accidents. Emphasizing employee engagement and innovation, adaptive safety culture fosters a dynamic environment that evolves alongside operational challenges.
Challenges of Implementing Compliance Safety
Implementing a compliance safety culture faces significant challenges such as rigid adherence to rules that can stifle employee initiative and reduce situational awareness. Organizations often struggle with ensuring consistent enforcement and overcoming resistance from workers who perceive compliance as bureaucratic rather than protective. Additionally, maintaining up-to-date training and adapting policies to evolving hazards requires continuous resources and management commitment to avoid superficial compliance.
Barriers to Adopting Adaptive Safety Culture
Barriers to adopting an adaptive safety culture include deeply ingrained compliance-based mindsets that emphasize rule-following over flexibility, limiting organizational responsiveness to dynamic risks. Resistance from leadership and employees often stems from uncertainty and fear of change, hindering proactive learning and real-time hazard mitigation. Insufficient training and lack of systems to capture frontline feedback further obstruct the shift towards a more resilient, adaptive safety environment.
Measuring Safety Performance: Compliance vs Adaptivity
Measuring safety performance in a compliance safety culture primarily involves tracking adherence to established rules, regulations, and procedures through audits, inspections, and incident reports. In contrast, an adaptive safety culture emphasizes continuous learning, real-time feedback, and behavioral indicators to assess how well an organization identifies and responds to emerging risks. Metrics in adaptive cultures focus on flexibility, employee engagement, and proactive risk management rather than solely on compliance percentages or violation counts.
Shifting from Compliance to Adaptive Safety Culture
Shifting from a Compliance Safety Culture to an Adaptive Safety Culture emphasizes proactive engagement, where employees actively identify and mitigate risks beyond regulatory requirements. Adaptive Safety Culture fosters continuous learning and flexibility, enabling organizations to respond effectively to unforeseen safety challenges. This transformation enhances overall workplace safety by prioritizing real-time hazard recognition and collaborative problem-solving over mere adherence to rules.
Best Practices for Fostering a Resilient Safety Culture
Fostering a resilient safety culture requires integrating best practices that emphasize continuous learning, employee engagement, and proactive risk management, striking a balance between Compliance Safety Culture's rule adherence and Adaptive Safety Culture's flexibility. Prioritizing open communication channels and empowering workers to identify hazards cultivates an environment where safety is a shared responsibility, enhancing organizational resilience. Leveraging real-time data analytics and iterative feedback loops supports adaptive improvements, ensuring safety practices evolve alongside emerging risks.
Related Important Terms
Prescriptive Compliance
Prescriptive compliance in safety culture emphasizes strict adherence to predefined rules and regulations, minimizing deviations to reduce risks in highly controlled environments. This approach contrasts with adaptive safety culture, which prioritizes flexibility and proactive learning to respond dynamically to emerging hazards.
Proactive Adaptation
Compliance safety culture emphasizes adherence to established rules and procedures, ensuring consistent risk management through structured protocols. Adaptive safety culture prioritizes proactive adaptation by encouraging continuous learning and flexibility to anticipate and respond to emerging hazards dynamically.
Safety Bureaucracy
Compliance Safety Culture emphasizes rigid adherence to established rules and procedures, often resulting in safety bureaucracy that can hinder flexibility and responsiveness to emerging risks. Adaptive Safety Culture prioritizes continuous learning and proactive risk management, reducing bureaucratic barriers to foster innovation and dynamic safety improvements.
Dynamic Risk Sensing
Compliance Safety Culture emphasizes rigid adherence to established rules and procedures, often limiting responsiveness to emerging hazards, while Adaptive Safety Culture prioritizes dynamic risk sensing through continuous monitoring and real-time feedback to anticipate and mitigate evolving safety threats. Dynamic risk sensing integrates advanced data analytics, employee insights, and environmental scanning to enable proactive adjustments, enhancing overall organizational resilience and reducing incident rates.
Rule-based Culture
Rule-based safety culture emphasizes strict adherence to established protocols and regulations to minimize risks, prioritizing compliance as the foundation for organizational safety. This approach can be less flexible compared to adaptive safety culture, which encourages continuous learning and adjustment in response to changing conditions and emerging hazards.
Mindful Organizing
Compliance Safety Culture emphasizes strict adherence to rules and protocols to prevent accidents, while Adaptive Safety Culture prioritizes Mindful Organizing, encouraging continuous awareness, learning, and flexibility to respond effectively to unexpected risks. Mindful Organizing enhances safety by fostering collective vigilance and proactive problem-solving among teams, leading to improved hazard detection and mitigation.
Resilience Engineering
Compliance Safety Culture emphasizes adherence to established rules and procedures to prevent accidents, limiting flexibility in dynamic environments. Adaptive Safety Culture, grounded in Resilience Engineering, promotes continuous learning, proactive risk management, and the ability to anticipate and respond to unforeseen challenges, enhancing overall organizational safety performance.
Learning Organization
Compliance Safety Culture emphasizes strict adherence to established rules and procedures to minimize risk, promoting consistent safety performance through formal training and enforcement. Adaptive Safety Culture prioritizes continuous learning and flexibility, encouraging employees to identify and respond to emerging hazards dynamically, fostering a proactive learning organization that evolves safety practices in real-time.
Safety Drift
Compliance Safety Culture emphasizes strict adherence to established rules and procedures to minimize safety risks, often preventing deviations through rigid control mechanisms. Adaptive Safety Culture, in contrast, promotes flexibility and continuous learning, enabling organizations to detect and correct safety drift caused by evolving operational conditions and unforeseen challenges.
Systemic Flexibility
Compliance Safety Culture emphasizes strict adherence to established rules and protocols to minimize risks, often limiting flexibility in responding to unforeseen hazards. Adaptive Safety Culture prioritizes systemic flexibility, enabling organizations to learn, evolve, and respond dynamically to complex and changing safety challenges.
Compliance Safety Culture vs Adaptive Safety Culture Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com