Gas detectors provide targeted detection of specific hazardous gases, ensuring immediate alerts for potential leaks or toxic exposures in pet environments. Real-time air quality monitoring offers continuous analysis of multiple pollutants, delivering comprehensive insights into overall air health to maintain safer conditions for pets. Combining both technologies enhances pet safety by addressing acute gas threats and broader air quality concerns effectively.
Table of Comparison
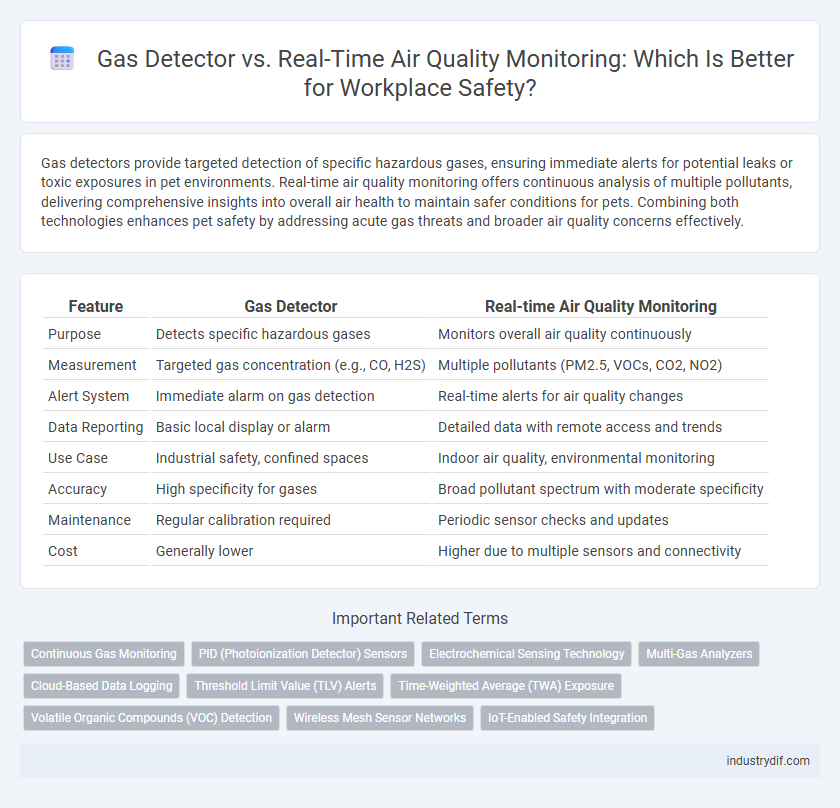
| Feature | Gas Detector | Real-time Air Quality Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects specific hazardous gases | Monitors overall air quality continuously |
| Measurement | Targeted gas concentration (e.g., CO, H2S) | Multiple pollutants (PM2.5, VOCs, CO2, NO2) |
| Alert System | Immediate alarm on gas detection | Real-time alerts for air quality changes |
| Data Reporting | Basic local display or alarm | Detailed data with remote access and trends |
| Use Case | Industrial safety, confined spaces | Indoor air quality, environmental monitoring |
| Accuracy | High specificity for gases | Broad pollutant spectrum with moderate specificity |
| Maintenance | Regular calibration required | Periodic sensor checks and updates |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to multiple sensors and connectivity |
Introduction to Gas Detection and Air Quality Monitoring
Gas detectors are specialized devices designed to identify the presence of hazardous gases such as carbon monoxide, methane, and hydrogen sulfide to prevent toxic exposure and explosive risks. Real-time air quality monitoring systems provide continuous data on multiple pollutants, including particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and ozone levels, enabling comprehensive environmental health assessment. Both technologies are essential for workplace safety and environmental compliance, with gas detectors targeting immediate gas leaks and air quality monitors assessing broader atmospheric conditions.
Key Functions of Gas Detectors
Gas detectors primarily identify specific hazardous gases such as carbon monoxide, methane, and hydrogen sulfide through sensors calibrated for those substances, enabling immediate alerts for dangerous concentrations. These devices are essential for pinpointing gas leaks and preventing toxic exposure or explosions in confined spaces where gas accumulation risks are high. Unlike broad-spectrum air quality monitors, gas detectors focus on precise detection thresholds for combustion and toxic gases, making them vital for industrial safety and workplace compliance.
Real-Time Air Quality Monitoring: An Overview
Real-time air quality monitoring provides continuous data on pollutants, enabling immediate identification of hazardous conditions and timely response to ensure workplace safety. Advanced sensors detect a broad spectrum of contaminants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter (PM2.5/PM10), carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide, delivering comprehensive environmental insights. Integration with digital platforms allows for remote monitoring, data analysis, and predictive maintenance, enhancing overall safety management and regulatory compliance.
Types of Gases Detected in Industrial Settings
Gas detectors primarily identify specific hazardous gases such as carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), oxygen (O2) levels, and combustible gases like methane (CH4) in industrial environments. Real-time air quality monitoring systems offer broader detection capabilities, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and ozone (O3), providing comprehensive environmental data. Both technologies play critical roles in ensuring worker safety by continuously tracking different types of airborne contaminants based on industrial requirements.
Technology Behind Gas Detectors
Gas detectors operate using electrochemical sensors, catalytic sensors, or infrared technology to identify specific toxic or combustible gases, enabling rapid detection and alerting for hazardous conditions. Real-time air quality monitoring systems integrate multiple sensor types and advanced data analytics to continuously assess a broader range of pollutants, including particulate matter, volatile organic compounds, and environmental gases. The core technology behind gas detectors prioritizes precision in detecting targeted gases at low concentrations, providing critical safety alerts in confined or industrial spaces.
Advantages of Real-Time Air Quality Monitoring Systems
Real-time air quality monitoring systems provide continuous data on various pollutants such as carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, and particulate matter, enabling immediate detection and response to hazardous conditions. Unlike traditional gas detectors limited to specific gases, these advanced systems offer comprehensive environmental insights and predictive analytics for proactive safety management. Integration with IoT platforms enhances remote monitoring capabilities, ensuring timely alerts and reducing occupational health risks effectively.
Calibration and Maintenance Requirements
Gas detectors require frequent calibration using certified gas mixtures to ensure sensor accuracy and prevent false alarms, with maintenance involving sensor replacement and functionality checks. Real-time air quality monitoring systems utilize advanced sensors calibrated less often due to self-diagnostic features and remote calibration capabilities, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Regular maintenance protocols for both technologies enhance workplace safety by ensuring reliable detection of hazardous gases and airborne contaminants.
Data Accuracy and Response Time Comparison
Gas detectors provide targeted detection of specific hazardous gases with fast response times, typically within seconds, ensuring immediate alerts for potential threats. Real-time air quality monitoring systems offer comprehensive data on multiple pollutants with continuous, high-resolution measurements, enhancing overall accuracy through integrated sensor networks and advanced algorithms. While gas detectors excel in rapid response to specific toxic gases, real-time monitoring delivers broader environmental insights, crucial for long-term safety management and regulatory compliance.
Industry Applications: Use Cases and Compliance
Gas detectors provide critical point-source detection of hazardous gases, essential for confined spaces and leak identification in industries such as oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, and mining. Real-time air quality monitoring systems offer continuous data on multiple pollutants, enabling compliance with OSHA, EPA, and ISO 45001 standards across manufacturing plants and construction sites. Integrating both technologies enhances workplace safety by ensuring early detection, regulatory adherence, and proactive risk management.
Selecting the Right Solution: Factors to Consider
When selecting between gas detectors and real-time air quality monitoring systems, consider factors such as the types of gases or pollutants to be detected, the required detection sensitivity, and the environment's specific safety risks. Gas detectors excel in identifying hazardous gas leaks like carbon monoxide or methane, while air quality monitors provide comprehensive data on pollutants such as particulate matter, VOCs, and ozone. Choosing the right solution depends on balancing real-time data needs, detection accuracy, maintenance requirements, and compliance with industry safety standards like OSHA or NIOSH.
Related Important Terms
Continuous Gas Monitoring
Continuous gas monitoring with gas detectors provides real-time detection of hazardous gases, ensuring immediate alerts and preventing exposure to toxic or combustible substances. Real-time air quality monitoring offers comprehensive data on multiple pollutants, enabling proactive safety management in industrial and environmental settings.
PID (Photoionization Detector) Sensors
PID (Photoionization Detector) sensors in gas detectors provide rapid identification of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) but offer limited continuous data compared to real-time air quality monitoring systems. Real-time monitoring with PID sensors enables ongoing assessment of pollutant levels, enhancing safety through immediate alerts and comprehensive exposure tracking.
Electrochemical Sensing Technology
Electrochemical sensing technology in gas detectors provides precise measurement of toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide, offering high sensitivity and selectivity crucial for industrial safety. Real-time air quality monitoring systems integrate electrochemical sensors to continuously track multiple gas concentrations, enabling immediate hazard detection and proactive risk management in occupational environments.
Multi-Gas Analyzers
Multi-gas analyzers provide comprehensive safety by detecting various hazardous gases simultaneously, offering real-time air quality monitoring crucial for industrial environments. These devices enhance workplace safety beyond traditional gas detectors by continuously measuring oxygen, combustible gases, and toxic gases, ensuring prompt hazard identification and response.
Cloud-Based Data Logging
Cloud-based data logging in gas detectors offers real-time air quality monitoring with remote accessibility, enabling instant alerts and historical data analysis for enhanced workplace safety. This integration improves regulatory compliance and supports proactive hazard management by centralizing air quality metrics across multiple locations.
Threshold Limit Value (TLV) Alerts
Gas detectors provide critical Threshold Limit Value (TLV) alerts by instantly signaling hazardous gas concentrations to prevent exposure, while real-time air quality monitoring offers continuous, comprehensive data on multiple pollutants, enhancing workplace safety through proactive environmental management. Employing both technologies ensures immediate hazard detection and long-term air quality tracking for optimized protective measures.
Time-Weighted Average (TWA) Exposure
Gas detectors primarily monitor specific hazardous gases, providing instant alerts for concentrations exceeding preset limits, while real-time air quality monitoring systems continuously track multiple airborne pollutants and calculate Time-Weighted Average (TWA) exposure to assess long-term health risks. TWA exposure metrics are critical for occupational safety, helping ensure compliance with regulatory standards by measuring average contaminant levels over an entire work shift.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) Detection
Gas detectors specifically target volatile organic compounds (VOCs) by providing threshold-limit alerts to prevent toxic exposure, while real-time air quality monitoring continuously measures VOC concentrations to offer comprehensive environmental data and trend analysis. Integrating both technologies enhances workplace safety by combining immediate hazard detection with long-term air quality management for VOCs.
Wireless Mesh Sensor Networks
Wireless mesh sensor networks enhance gas detector systems by enabling real-time air quality monitoring with seamless data transmission and robust network reliability. These networks provide scalable coverage, ensuring early detection of hazardous gases and continuous environmental analysis for improved workplace safety.
IoT-Enabled Safety Integration
IoT-enabled gas detectors provide instant alerts for hazardous gas levels, enhancing workplace safety by enabling rapid response and reducing exposure risks. Real-time air quality monitoring systems integrate multiple sensors through IoT platforms, offering comprehensive environmental data that supports proactive safety measures and regulatory compliance.
Gas Detector vs Real-time Air Quality Monitoring Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com