Lockout-Tagout procedures physically secure energy sources to prevent accidental equipment activation during maintenance, ensuring worker safety. Remote isolation employs control systems to disconnect energy sources from a distance, reducing the need for direct physical contact and minimizing exposure to hazardous environments. Both methods are essential for effective safety pet protocols, but remote isolation offers enhanced convenience and flexibility in managing equipment risks.
Table of Comparison
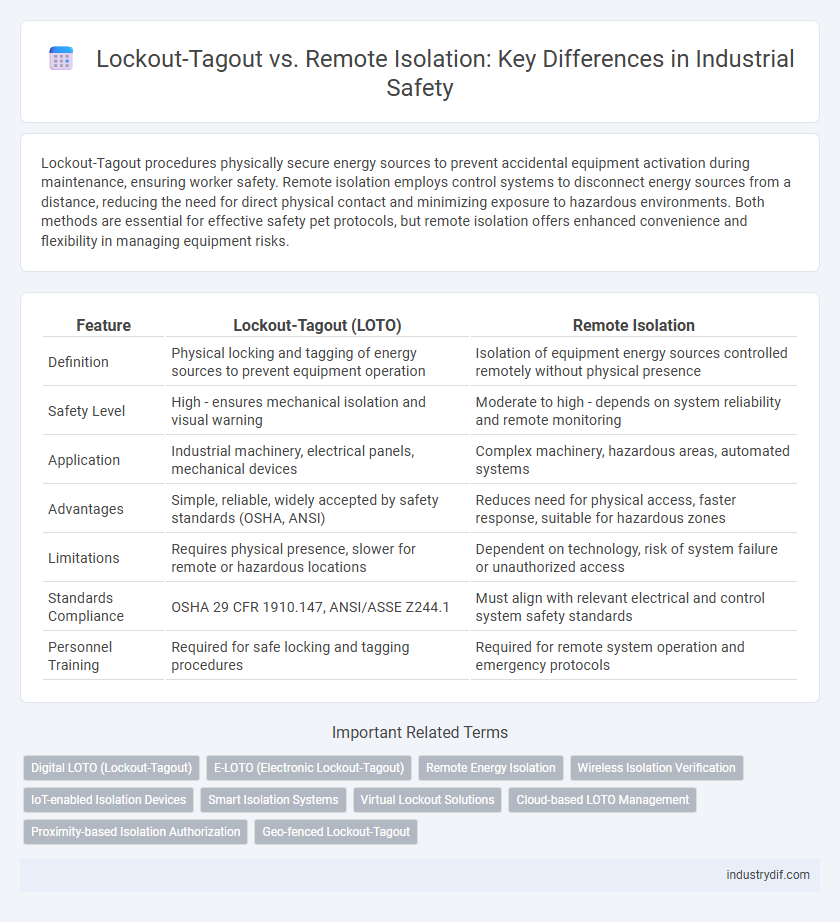
| Feature | Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) | Remote Isolation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical locking and tagging of energy sources to prevent equipment operation | Isolation of equipment energy sources controlled remotely without physical presence |
| Safety Level | High - ensures mechanical isolation and visual warning | Moderate to high - depends on system reliability and remote monitoring |
| Application | Industrial machinery, electrical panels, mechanical devices | Complex machinery, hazardous areas, automated systems |
| Advantages | Simple, reliable, widely accepted by safety standards (OSHA, ANSI) | Reduces need for physical access, faster response, suitable for hazardous zones |
| Limitations | Requires physical presence, slower for remote or hazardous locations | Dependent on technology, risk of system failure or unauthorized access |
| Standards Compliance | OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147, ANSI/ASSE Z244.1 | Must align with relevant electrical and control system safety standards |
| Personnel Training | Required for safe locking and tagging procedures | Required for remote system operation and emergency protocols |
Introduction to Lockout-Tagout and Remote Isolation
Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) is a safety procedure that ensures machines are properly shut off and unable to be started during maintenance by physically locking energy-isolating devices and tagging them with warning labels. Remote isolation involves controlling the shutdown of equipment from a distance, enhancing worker safety by eliminating direct contact with hazardous energy sources. Both methods play critical roles in preventing accidental machine startup and minimizing workplace injuries in industrial environments.
Definition and Core Principles of Lockout-Tagout
Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) is a safety procedure designed to ensure that machines are properly shut off and unable to be started up again prior to the completion of maintenance or repair work. Its core principles include isolating energy sources, applying lockout devices to energy-isolating devices, and tagging them with warning tags to prevent accidental re-energization. LOTO emphasizes physical control over hazardous energy through locks and tags to protect workers from unexpected machine activation, whereas Remote Isolation involves controlling energy sources from a distance, reducing direct exposure but relying more on remote system integrity.
Understanding Remote Isolation Systems
Remote isolation systems enhance lockout-tagout protocols by allowing workers to control hazardous energy sources from a safe distance, reducing exposure risks during maintenance. These systems utilize wireless or wired controls to isolate equipment, ensuring that power, pressure, or chemical flows are securely halted before service. Understanding the functionality and integration of remote isolation devices is crucial for improving safety compliance and minimizing accidental energization incidents.
Key Differences Between Lockout-Tagout and Remote Isolation
Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) requires physically locking and tagging energy sources to prevent accidental activation during maintenance, ensuring worker safety through direct control. Remote Isolation utilizes technology to isolate and control energy sources from a distance, reducing risk by eliminating the need for workers to access hazardous areas. Key differences include the physical presence for LOTO versus remote technology use in isolation, with LOTO offering visible security and Remote Isolation providing enhanced safety through automation and minimized exposure.
Advantages and Limitations of Lockout-Tagout
Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) ensures worker safety by physically isolating energy sources with locks and tags, preventing accidental equipment startup during maintenance. Its advantages include clear visual identification of locked-out equipment and compliance with OSHA regulations, reducing injury risk in hazardous environments. Limitations involve potential human error in applying devices, the time-intensive process, and reduced effectiveness for isolating energy sources that are difficult to access remotely.
Benefits and Challenges of Remote Isolation
Remote isolation enhances worker safety by allowing equipment to be de-energized and isolated from a distance, minimizing direct exposure to hazardous energy sources. This method improves operational efficiency through quicker isolation processes and reduces the risk of human error compared to traditional Lockout-Tagout procedures. Challenges of remote isolation include the need for reliable communication systems, thorough employee training, and potential technological malfunctions that require robust backup protocols.
Safety Compliance and Regulatory Standards
Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) procedures are established under OSHA standard 29 CFR 1910.147 to ensure safety compliance by physically isolating energy sources during maintenance, minimizing risks of accidental machine startup. Remote isolation technologies enhance safety protocols by enabling isolation from a distance, reducing worker exposure to hazardous environments while meeting evolving regulatory standards such as ANSI/ASSE Z244.1. Both methods are critical for regulatory adherence and effective hazard control, with remote isolation offering advanced compliance benefits in complex industrial settings.
Implementing Lockout-Tagout Procedures
Implementing lockout-tagout procedures involves physically isolating energy sources by applying locks and tags to machinery controls, ensuring equipment cannot be activated during maintenance. This method provides a clear visual indicator of ongoing work, significantly reducing the risk of accidental energization. Remote isolation, while useful, does not replace the need for physical lockout-tagout to comply with OSHA safety standards and guarantee worker protection.
Best Practices for Adopting Remote Isolation
Best practices for adopting remote isolation in safety protocols include clearly defining energy sources and ensuring comprehensive training for all personnel involved in lockout-tagout procedures. Implementing robust communication systems and real-time monitoring enhances the effectiveness of remote isolation, reducing risks associated with unexpected equipment energization. Regular audits and updates to isolation devices maintain compliance with industry standards and improve overall workplace safety.
Future Trends in Industrial Safety Isolation Methods
Emerging trends in industrial safety isolation methods emphasize the integration of smart lockout-tagout systems with remote isolation technologies to enhance real-time monitoring and control. Advanced sensor networks and IoT connectivity enable predictive maintenance and reduce human error by automating isolation verification processes. Future safety protocols will prioritize hybrid models combining physical lockout devices with digital remote isolation to maximize efficiency and worker protection.
Related Important Terms
Digital LOTO (Lockout-Tagout)
Digital Lockout-Tagout (Digital LOTO) leverages IoT sensors and cloud-based platforms to enhance safety by enabling real-time remote isolation and monitoring of hazardous equipment, reducing human error and downtime compared to traditional Lockout-Tagout methods. This technology improves compliance tracking, auditability, and worker protection by providing instant status updates and digital authentication, streamlining safety protocols in industrial environments.
E-LOTO (Electronic Lockout-Tagout)
E-LOTO (Electronic Lockout-Tagout) enhances traditional lockout-tagout procedures by enabling remote isolation and real-time monitoring of energy sources, significantly reducing human error and increasing worker safety. Implementing E-LOTO systems integrates electronic controls with automated isolation protocols to ensure compliance with OSHA standards and improve the overall effectiveness of hazardous energy control.
Remote Energy Isolation
Remote energy isolation enhances safety by enabling personnel to control hazardous energy sources from a distance, significantly reducing the risk of accidental exposure during maintenance. Unlike traditional lockout-tagout methods, remote isolation incorporates automated systems and wireless technology to provide secure and reliable energy shutdowns, improving compliance with safety standards.
Wireless Isolation Verification
Wireless isolation verification enhances Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) procedures by enabling real-time remote monitoring and confirmation of equipment isolation status, significantly reducing human error and improving worker safety. Compared to traditional Lockout-Tagout methods, remote isolation utilizing wireless technology ensures continuous verification, minimizes unauthorized re-energization, and supports compliance with OSHA safety standards.
IoT-enabled Isolation Devices
IoT-enabled isolation devices enhance Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) by enabling remote isolation of hazardous energy sources, reducing human exposure and increasing operational safety. These smart systems provide real-time status monitoring and automated lockout controls, optimizing compliance with safety protocols and minimizing downtime.
Smart Isolation Systems
Smart isolation systems enhance safety by integrating Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) procedures with remote isolation technology, enabling real-time control and monitoring of hazardous energy sources. These systems reduce human error and exposure risks by allowing operators to securely isolate equipment remotely, improving compliance with industrial safety standards.
Virtual Lockout Solutions
Virtual lockout solutions enhance safety protocols by enabling remote isolation of hazardous energy sources, reducing the need for physical lockout-tagout procedures and minimizing worker exposure to dangerous environments. These digital systems utilize electronic tags and controlled access to ensure energy isolation verification and compliance with OSHA standards, streamlining maintenance operations while maintaining high safety standards.
Cloud-based LOTO Management
Cloud-based Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) management enhances safety by enabling real-time remote isolation of energy sources, reducing human error and ensuring compliance through centralized digital documentation. Integrating remote isolation with cloud LOTO platforms streamlines hazard control, providing instant access to lockout statuses and audit trails critical for preventing accidental equipment energization.
Proximity-based Isolation Authorization
Lockout-Tagout procedures require physical presence at the equipment to apply locks and tags, ensuring control over energy sources during maintenance, while Remote Isolation leverages technology to authorize isolation from a distance, reducing the need for direct proximity to hazardous areas. Proximity-based isolation authorization enhances safety by minimizing worker exposure to dangerous environments and enabling real-time control verification through electronic systems.
Geo-fenced Lockout-Tagout
Geo-fenced Lockout-Tagout enhances traditional Lockout-Tagout by using GPS technology to create virtual boundaries around hazardous areas, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access machinery within these zones during maintenance. This remote isolation method reduces accidental energization risks and improves compliance by automatically enforcing lockout protocols within designated geo-fenced perimeters.
Lockout-Tagout vs Remote Isolation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com