Emergency drills involve hands-on practice where pets and their owners simulate real-life scenarios to reinforce safety protocols, ensuring quick and effective responses during actual emergencies. Tabletop exercises are discussion-based sessions that allow participants to mentally walk through emergency plans, identify potential gaps, and improve decision-making without physical activity. Both methods enhance preparedness, but combining practical drills with strategic discussions creates the most comprehensive safety approach for pets.
Table of Comparison
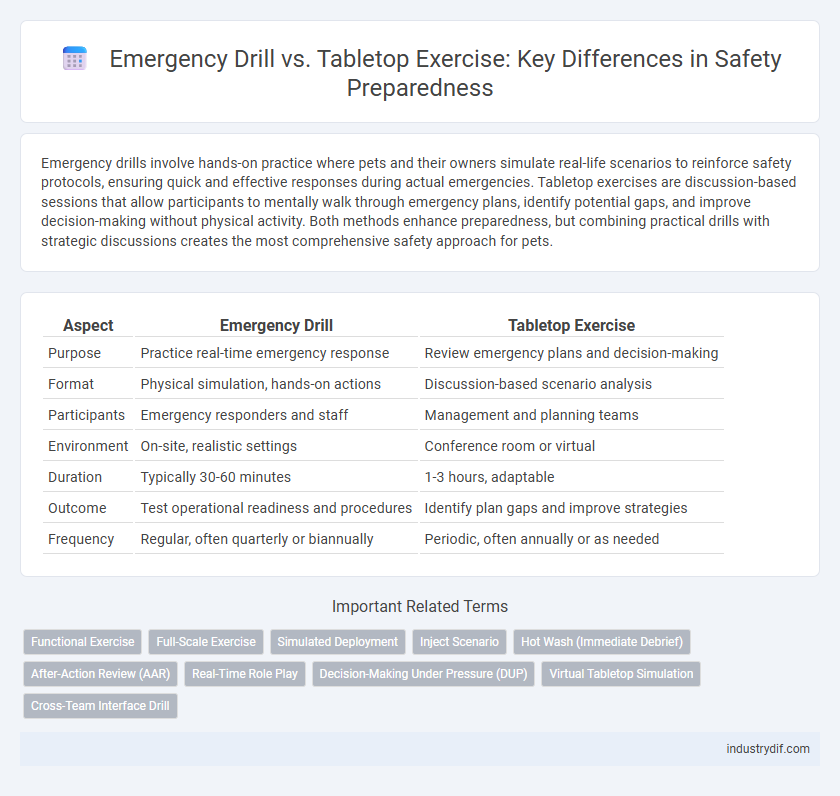
| Aspect | Emergency Drill | Tabletop Exercise |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Practice real-time emergency response | Review emergency plans and decision-making |
| Format | Physical simulation, hands-on actions | Discussion-based scenario analysis |
| Participants | Emergency responders and staff | Management and planning teams |
| Environment | On-site, realistic settings | Conference room or virtual |
| Duration | Typically 30-60 minutes | 1-3 hours, adaptable |
| Outcome | Test operational readiness and procedures | Identify plan gaps and improve strategies |
| Frequency | Regular, often quarterly or biannually | Periodic, often annually or as needed |
Understanding Emergency Drills and Tabletop Exercises
Emergency drills simulate real-life emergency situations to test response skills and coordination under pressure, enhancing readiness through practice. Tabletop exercises are discussion-based sessions where participants walk through emergency scenarios to evaluate plans, roles, and decision-making processes without physical deployment. Both methods are essential for comprehensive safety preparedness, with drills emphasizing action and tabletop exercises focusing on strategic thinking and communication.
Core Objectives: Emergency Drills vs Tabletop Exercises
Emergency drills prioritize hands-on practice of evacuation procedures and real-time response skills to ensure employee readiness during actual emergencies. Tabletop exercises focus on strategic decision-making and communication through scenario-based discussions to evaluate roles, policies, and coordination among team members. Both methods aim to identify gaps in emergency plans but differ in approach: drills test physical execution, while tabletop exercises assess cognitive preparedness and interdepartmental collaboration.
Key Differences in Execution
Emergency drills involve full-scale, physical enactments of emergency scenarios with personnel actively engaging in tasks such as evacuation, equipment use, and communication, providing hands-on experience and testing real-time response capabilities. Tabletop exercises are discussion-based sessions where team members review procedures, roles, and decision-making strategies without physical movement, emphasizing coordination, communication, and strategic planning in a controlled environment. The key difference in execution lies in the immersive, action-oriented nature of emergency drills versus the collaborative, analytical approach of tabletop exercises.
Scenario Planning: Realism vs Simulation
Emergency drills prioritize realism by physically simulating emergency scenarios, enabling participants to practice real-time responses and test equipment effectiveness under stress. Tabletop exercises emphasize scenario planning through discussion-based simulations, allowing teams to explore decision-making processes and identify procedural gaps without physical enactment. Balancing these approaches enhances preparedness by combining practical response skills with strategic analysis of potential emergency outcomes.
Team Participation Requirements
Emergency drills require full team participation, involving hands-on engagement with physical scenarios to practice response actions in real time. Tabletop exercises involve key team members discussing responses in a simulated environment, focusing on decision-making and communication without physical deployment. Effective safety programs integrate both methods to enhance preparedness through active involvement and strategic planning.
Measuring Effectiveness: Metrics and Outcomes
Emergency drills provide quantifiable data through response time, participant adherence to protocols, and equipment functionality, offering measurable insights into operational readiness. Tabletop exercises emphasize decision-making quality, communication flow, and scenario-based problem-solving, assessed via participant feedback and facilitator evaluations. Combining metrics from both methods yields a comprehensive view of safety preparedness and organizational resilience.
Advantages and Limitations of Emergency Drills
Emergency drills offer hands-on experience by simulating real-life scenarios, enhancing employee readiness and response efficiency in emergencies. They allow identification of practical issues in procedures and equipment but can be resource-intensive and disruptive to regular operations. Limitations include logistical challenges, potential stress to participants, and difficulty in replicating every possible emergency situation accurately.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Tabletop Exercises
Tabletop exercises excel at fostering collaborative decision-making and improving communication among team members without the need for physical deployment, making them cost-effective and flexible for scenario testing. However, their limitations include the lack of real-time stress simulation and hands-on practice, which can reduce the effectiveness of muscle memory and operational readiness. These exercises are best suited for strategic planning and identifying procedural gaps rather than testing physical response capabilities.
Integrating Both Methods into Safety Programs
Integrating emergency drills and tabletop exercises into safety programs enhances organizational preparedness by combining practical response skills with strategic decision-making processes. Emergency drills simulate real-world scenarios to improve reaction times and operational coordination, while tabletop exercises facilitate critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving among stakeholders. Together, these methods create a comprehensive safety strategy that boosts readiness, reduces risks, and ensures effective crisis management.
Best Practices for Emergency Preparedness Training
Emergency drills provide hands-on practice of response procedures, enhancing muscle memory and real-time decision-making under stress. Tabletop exercises focus on scenario-based discussions, improving communication, coordination, and problem-solving among team members without physical enactment. Combining both methods ensures comprehensive emergency preparedness by addressing practical skills and strategic planning.
Related Important Terms
Functional Exercise
A functional exercise simulates real-life emergency scenarios to test the coordination, communication, and response capabilities of safety teams without full deployment of resources. Unlike tabletop exercises that focus on discussion and decision-making, functional exercises provide hands-on experience in managing incidents, enhancing preparedness and identifying operational gaps.
Full-Scale Exercise
A Full-Scale Exercise in safety emergency preparedness tests the entire response system by simulating real-life scenarios with actual personnel, equipment, and resources to evaluate coordination and operational effectiveness. Unlike Emergency Drills that focus on specific functions, or Tabletop Exercises that involve discussion-based problem-solving, Full-Scale Exercises provide comprehensive validation of emergency plans through realistic, hands-on practice.
Simulated Deployment
Emergency drills involve the simulated deployment of personnel and equipment in real-time scenarios to test physical responses and operational readiness. Tabletop exercises focus on strategic decision-making and communication through discussion-based simulations without actual deployment of resources.
Inject Scenario
Inject scenarios in emergency drills simulate real-time incidents with physical actions, enhancing hands-on preparedness and response coordination. Tabletop exercises use inject scenarios as discussion prompts to evaluate decision-making and communication strategies without physical deployment.
Hot Wash (Immediate Debrief)
Emergency drills involve full-scale, hands-on practice of response procedures, while tabletop exercises simulate scenarios through discussion; the Hot Wash immediately following both is crucial for capturing real-time feedback, identifying gaps, and enhancing future safety protocols. This immediate debrief ensures lessons learned are fresh, enabling swift improvements in emergency preparedness and response effectiveness.
After-Action Review (AAR)
Emergency Drill After-Action Reviews (AAR) analyze real-time response effectiveness, operational gaps, and participant coordination under simulated stress conditions. Tabletop Exercise AARs emphasize decision-making processes, communication flow, and procedural clarity through scenario-based discussions, enabling identification of policy improvements without physical deployment.
Real-Time Role Play
Emergency drills involve real-time role play where participants physically enact their responses to simulated crises, enhancing muscle memory and situational awareness. Tabletop exercises focus on discussion-based problem solving without physical enactment, relying on scenario exploration and decision-making processes.
Decision-Making Under Pressure (DUP)
Emergency drills enhance Decision-Making Under Pressure (DUP) by simulating real-time scenarios that require rapid, practical responses, thereby improving reflexive actions and situational awareness. Tabletop exercises advance DUP through collaborative problem-solving and strategic planning, allowing participants to analyze responses and decision pathways without physical execution.
Virtual Tabletop Simulation
Virtual tabletop simulations enhance emergency preparedness by enabling realistic scenario-based training without physical presence, improving decision-making and communication among stakeholders. These simulations offer cost-effective, scalable solutions compared to traditional emergency drills by providing interactive environments to test response strategies and identify weaknesses.
Cross-Team Interface Drill
Emergency drills simulate real-life scenarios requiring physical response and coordination among teams, enhancing readiness through active engagement and practical application of protocols. Tabletop exercises focus on discussion-based problem-solving to assess communication and decision-making processes, making cross-team interface drills essential for identifying gaps in interdepartmental collaboration and improving overall emergency response effectiveness.
Emergency Drill vs Tabletop Exercise Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com