Root Cause Analysis identifies the underlying causes of pet safety incidents by systematically investigating each factor contributing to the event. The Bowtie Methodology visually maps out potential hazards, preventive controls, and recovery measures, providing a clear overview of risk management strategies for pet safety. Combining both approaches enhances hazard identification and control, improving overall safety protocols for pets.
Table of Comparison
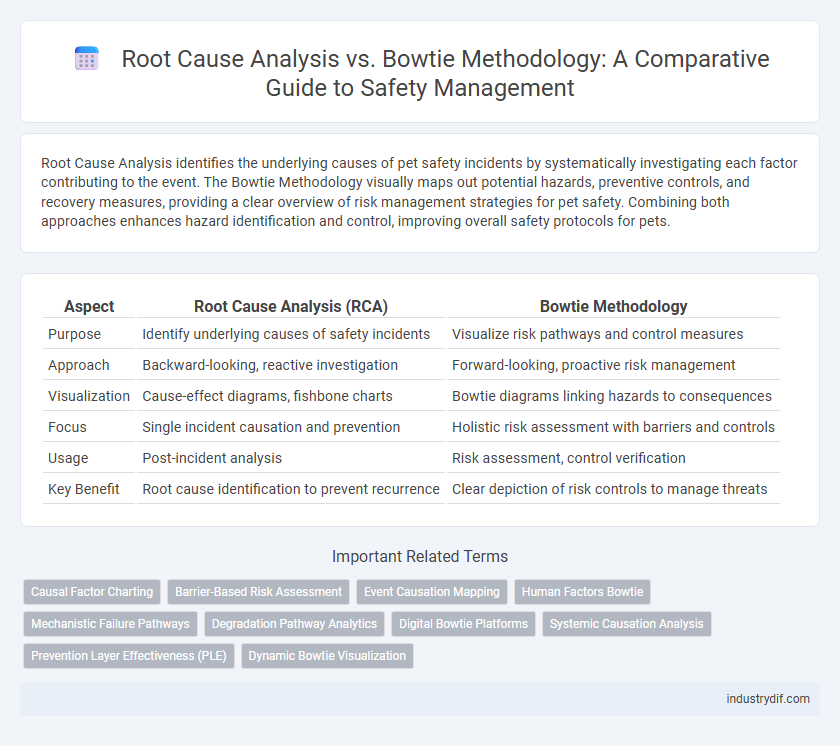
| Aspect | Root Cause Analysis (RCA) | Bowtie Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify underlying causes of safety incidents | Visualize risk pathways and control measures |
| Approach | Backward-looking, reactive investigation | Forward-looking, proactive risk management |
| Visualization | Cause-effect diagrams, fishbone charts | Bowtie diagrams linking hazards to consequences |
| Focus | Single incident causation and prevention | Holistic risk assessment with barriers and controls |
| Usage | Post-incident analysis | Risk assessment, control verification |
| Key Benefit | Root cause identification to prevent recurrence | Clear depiction of risk controls to manage threats |
Introduction to Root Cause Analysis in Safety
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in safety systematically identifies underlying causes of incidents to prevent recurrence and enhance workplace safety. By examining sequence of events and contributing factors, RCA enables organizations to implement targeted corrective actions, reducing risks and improving safety outcomes. Unlike the Bowtie methodology, which visually maps hazards and controls, RCA provides a detailed investigative approach focused specifically on causation and resolution.
Overview of Bowtie Methodology
The Bowtie Methodology provides a visual risk assessment framework that links potential hazards to preventive and mitigative controls, illustrating the pathways from causes to consequences clearly. It integrates fault tree analysis and event tree analysis principles, enabling organizations to identify critical risk control barriers and improve overall safety management. This approach enhances communication across teams by presenting complex safety scenarios in an intuitive, easy-to-understand diagram.
Defining Key Concepts: Root Cause vs Bowtie
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) identifies the fundamental origin of a safety incident by tracing back through cause-and-effect relationships, enabling precise corrective actions. The Bowtie methodology visually maps out hazard pathways, linking potential causes to preventive barriers and consequences, offering a comprehensive risk assessment framework. Defining these key concepts ensures a clear distinction: RCA targets the primary fault leading to failure, while Bowtie integrates cause, controls, and consequences into a unified risk management tool.
Historical Development of Safety Analytical Methods
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) emerged in the 1960s as a systematic approach to identify underlying reasons for failures to prevent recurrence in industrial settings. The Bowtie Methodology, developed in the late 1970s, integrates fault tree analysis and event tree analysis to visually map risk management barriers around a central hazard. Both methods have evolved to enhance safety performance by emphasizing different aspects: RCA focuses on identifying root causes post-incident, while Bowtie provides a proactive risk visualization framework.
Practical Applications in Industrial Safety
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) systematically identifies underlying causes of industrial accidents to prevent recurrence, emphasizing detailed failure investigation and corrective action implementation. The Bowtie Methodology visually maps out hazard controls and potential pathways from causes to consequences, enhancing risk communication and proactive barrier management. Combining RCA's deep diagnostic insights with the Bowtie's comprehensive risk visualization optimizes safety performance in complex industrial environments.
Step-by-Step Process: Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis involves a systematic step-by-step process starting with problem identification, followed by data collection and analysis to uncover underlying causes. Key steps include defining the problem, gathering evidence, categorizing potential causes using tools like the 5 Whys or Fishbone Diagram, and validating root causes through verification and testing. This method ensures targeted corrective actions are implemented to prevent recurrence, enhancing overall safety performance.
Step-by-Step Process: Bowtie Methodology
The Bowtie Methodology involves a visual step-by-step approach starting with identifying a hazard and defining the top event, followed by outlining threats on the left side and consequences on the right. Controls and barriers are then mapped to prevent threats from triggering the top event or to mitigate consequences if the event occurs. This structured process enhances safety management by clearly illustrating risk pathways and control measures in a single diagram.
Strengths and Limitations: Root Cause vs Bowtie
Root Cause Analysis excels in identifying fundamental causes of incidents through systematic investigation, providing detailed insights that help prevent recurrence. The Bowtie Methodology visualizes risk pathways by mapping threats, barriers, and consequences, offering a clear overview of control measures and potential failure points. While Root Cause Analysis is powerful for deep cause identification, it can be time-consuming and reactive, whereas the Bowtie Methodology's strength lies in proactive risk management but may oversimplify complex scenarios.
Case Studies: Industry Examples and Insights
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Bowtie Methodology are pivotal in safety management, each demonstrated through diverse industry case studies. RCA delves into identifying fundamental failure causes, proven effective in manufacturing and healthcare sectors to prevent accident recurrence. Conversely, Bowtie Methodology visualizes risk pathways and controls, extensively applied in oil and gas industries to enhance hazard mitigation and communication.
Selecting the Right Approach for Safety Management
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) identifies underlying causes of safety incidents through systematic investigation, making it ideal for post-incident analysis and corrective action planning. Bowtie Methodology visualizes risk pathways by combining hazard identification with preventive and mitigative controls, enabling proactive management of complex safety risks. Choosing the right approach depends on whether the safety management goal is to investigate past failures or to prevent future incidents through comprehensive risk assessment and control implementation.
Related Important Terms
Causal Factor Charting
Root Cause Analysis identifies underlying causes of safety incidents by systematically tracing contributing factors, while Bowtie Methodology visualizes risk pathways and controls through a bowtie diagram that links hazards to consequences. Causal Factor Charting enhances Root Cause Analysis by mapping out sequences of events and interactions, enabling deeper insight into incident causation and prevention measures.
Barrier-Based Risk Assessment
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) identifies underlying causes of incidents by systematically tracing failures, whereas Bowtie Methodology integrates barrier-based risk assessment to visualize prevention and mitigation controls around a central hazard. Bowtie enables clearer communication of safety barriers and their effectiveness, improving proactive risk management compared to RCA's reactive problem-solving approach.
Event Causation Mapping
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) systematically identifies fundamental causes of safety incidents by tracing back through event sequences, while Bowtie Methodology visually maps risk pathways linking hazards to consequences with barriers. Event Causation Mapping enhances both approaches by detailing interconnected causes and controls, enabling clearer understanding of complex safety failures and prevention strategies.
Human Factors Bowtie
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) identifies underlying causes of incidents by systematically tracing back from the event, while Bowtie Methodology visually maps risk pathways, integrating preventive and mitigative controls with clear representation of hazards, top events, threats, and consequences. The Human Factors Bowtie approach emphasizes cognitive, organizational, and behavioral causes in risk scenarios, enhancing safety management by linking human error precursors directly to barriers and control measures within complex systems.
Mechanistic Failure Pathways
Root Cause Analysis identifies mechanistic failure pathways by tracing back from the observed problem to the underlying causes, enabling targeted corrective actions; Bowtie Methodology, however, visually maps mechanistic failure pathways by illustrating hazards, potential causes, and barriers in a structured diagram that integrates preventive and mitigative controls. Both approaches enhance safety by addressing failure mechanisms, but Bowtie offers a more comprehensive visualization of complex risk scenarios and control measures.
Degradation Pathway Analytics
Root Cause Analysis identifies underlying causes of safety incidents by tracing failure sequences, while Bowtie Methodology visually maps risk scenarios and control measures along degradation pathways to prevent incident escalation. Degradation Pathway Analytics enhances Bowtie by quantifying barrier effectiveness and pinpointing critical control failures, optimizing proactive risk management in safety systems.
Digital Bowtie Platforms
Root Cause Analysis pinpoints underlying issues after an incident occurs, while Bowtie Methodology visually maps potential risk pathways to prevent failures, enhancing real-time hazard control. Digital Bowtie Platforms leverage interactive, data-driven interfaces to integrate risk assessment, incident monitoring, and mitigation strategies, improving organizational safety performance through proactive management.
Systemic Causation Analysis
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) identifies specific failures within a system by tracing discrete incidents to their origin, while Bowtie Methodology maps out potential threat pathways and preventative barriers to visualize and manage risk comprehensively. Bowtie excels in systemic causation analysis by integrating multiple hazard scenarios into a single framework, enabling proactive safety management beyond isolated root causes.
Prevention Layer Effectiveness (PLE)
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) identifies the fundamental causes of incidents to prevent recurrence by addressing specific failures, while Bowtie Methodology visually maps out hazard controls and barriers, emphasizing Prevention Layer Effectiveness (PLE) in maintaining safety integrity. Bowtie offers a proactive assessment of multiple prevention layers' effectiveness, enabling real-time monitoring and continuous improvement, whereas RCA primarily provides reactive insights post-incident.
Dynamic Bowtie Visualization
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) identifies underlying causes of safety incidents by systematically investigating failures, while Bowtie Methodology provides a visual risk management framework linking hazards to controls. Dynamic Bowtie Visualization enhances this process by offering real-time, interactive representation of risk pathways and control barriers, improving hazard awareness and decision-making in complex safety environments.
Root Cause Analysis vs Bowtie Methodology Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com