Psychology examines how humans perceive and interpret beauty through cognitive processes, emotions, and social influences. Neuroaesthetics explores the neural mechanisms underlying aesthetic experience, identifying brain regions activated by art and sensory stimuli. Together, these fields provide complementary insights into the relationship between brain function and the perception of beauty.
Table of Comparison
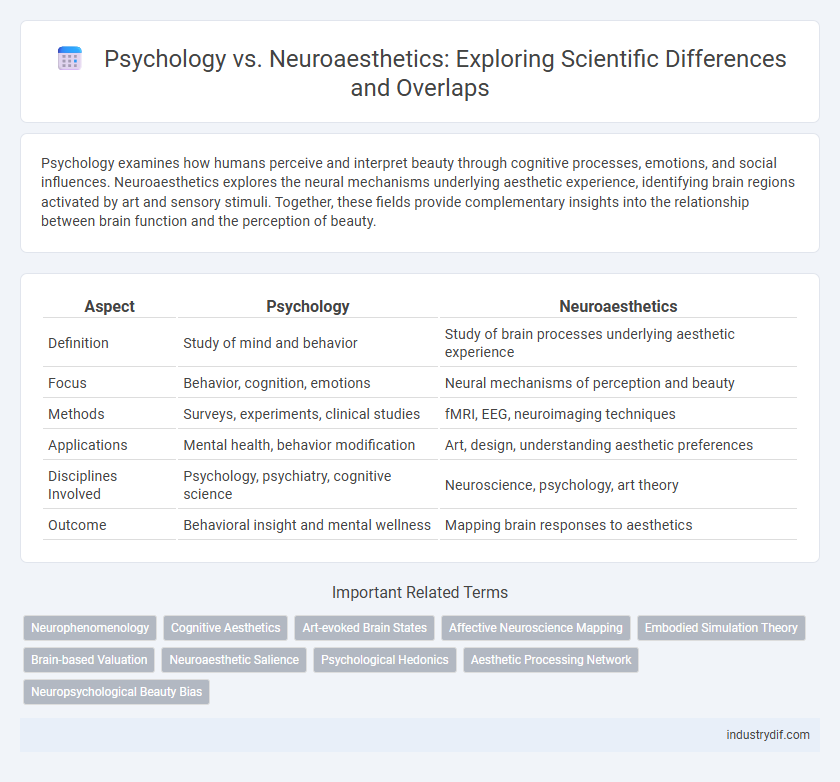
| Aspect | Psychology | Neuroaesthetics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of mind and behavior | Study of brain processes underlying aesthetic experience |
| Focus | Behavior, cognition, emotions | Neural mechanisms of perception and beauty |
| Methods | Surveys, experiments, clinical studies | fMRI, EEG, neuroimaging techniques |
| Applications | Mental health, behavior modification | Art, design, understanding aesthetic preferences |
| Disciplines Involved | Psychology, psychiatry, cognitive science | Neuroscience, psychology, art theory |
| Outcome | Behavioral insight and mental wellness | Mapping brain responses to aesthetics |
Defining Psychology and Neuroaesthetics
Psychology studies human behavior and mental processes through cognitive, emotional, and social perspectives, analyzing how individuals perceive, think, and respond to stimuli. Neuroaesthetics investigates the neural mechanisms underlying aesthetic experiences by examining brain activity related to perception, emotion, and creativity in response to art and beauty. The integration of psychology and neuroaesthetics enhances understanding of how neural processes influence subjective experiences and artistic appreciation.
Historical Evolution of Both Disciplines
Psychology emerged as a formal discipline in the late 19th century, focusing on studying human behavior and mental processes through experimental methods. Neuroaesthetics, a more recent interdisciplinary field developed in the early 21st century, investigates the neural mechanisms underlying artistic experience and aesthetic appreciation using neuroimaging techniques. The historical evolution of psychology provided foundational theories of perception and cognition that neuroaesthetics has expanded by integrating neuroscience to explore the brain's role in art perception and creativity.
Core Concepts in Psychology
Core concepts in psychology encompass cognition, perception, emotion, and behavior, providing a comprehensive framework to understand human mental processes. Neuroaesthetics, by contrast, integrates these psychological principles with neuroscience to explore how brain activity influences aesthetic experience and artistic appreciation. This interdisciplinary approach enriches traditional psychology by linking subjective aesthetic responses to neural mechanisms.
Foundational Principles of Neuroaesthetics
Neuroaesthetics explores the neural mechanisms underlying aesthetic experiences, emphasizing brain regions such as the orbitofrontal cortex and the reward system involved in perceiving beauty and art. Unlike traditional psychology that centers on behavioral and cognitive processes, neuroaesthetics integrates neuroscience tools like fMRI and EEG to investigate how sensory inputs trigger emotional and cognitive responses. Foundational principles include the coupling of sensory perception with emotional valuation and the role of neural plasticity in shaping aesthetic preferences over time.
Research Methodologies: Psychology vs Neuroaesthetics
Psychology research methodologies often utilize experimental designs, surveys, and behavioral observations to explore cognitive, emotional, and social processes. Neuroaesthetics employs neuroimaging techniques such as fMRI, EEG, and PET scans to investigate the neural correlates of aesthetic experiences and artistic perception. Combining quantitative data from psychology with neurobiological measures enhances understanding of human perception, creativity, and aesthetic appreciation.
Brain Mechanisms in Perception and Cognition
Psychology explores perception and cognition through behavioral observations and cognitive processes, emphasizing how mental functions influence human experience. Neuroaesthetics investigates the neural mechanisms underlying aesthetic appreciation, using brain imaging to reveal how sensory input and emotional responses interact in specific brain regions like the orbitofrontal cortex and insula. Integrating psychological theories with neuroaesthetic findings enhances understanding of the brain's role in processing and interpreting sensory stimuli in artistic and natural environments.
Emotional Response to Art: Comparative Perspectives
Psychology examines emotional responses to art through cognitive appraisal and individual differences, emphasizing factors such as memory, personality, and cultural background. Neuroaesthetics investigates these responses by measuring neural activity in brain regions like the amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex, providing insights into the biological basis of aesthetic experience. Comparative studies reveal that integrating psychological theories with neuroimaging data enhances understanding of how emotional engagement with art varies across populations.
Applications in Clinical and Therapeutic Settings
Psychology applies cognitive-behavioral techniques and psychotherapy to address mental health disorders, enhancing emotional regulation and resilience. Neuroaesthetics investigates how aesthetic experiences engage neural circuits, informing therapeutic interventions such as art therapy and music therapy to improve brain plasticity and emotional well-being. Integrating neuroaesthetic insights with psychological practices offers innovative treatment approaches for anxiety, depression, and trauma recovery in clinical settings.
Current Trends and Future Directions
Current trends in psychology emphasize cognitive and emotional processes underlying aesthetic experiences, employing neuroimaging to map brain activity patterns. Neuroaesthetics integrates these insights by exploring neural correlates of art perception, creativity, and sensory integration, leveraging advances in fMRI and EEG technologies. Future directions include developing personalized neuroaesthetic interventions for mental health and enhancing artificial intelligence models to simulate human aesthetic appreciation.
Bridging Psychology and Neuroaesthetics: Interdisciplinary Insights
Bridging psychology and neuroaesthetics reveals how cognitive processes and neural mechanisms interact to shape aesthetic experiences. Integrating psychological theories of perception, emotion, and memory with neuroimaging data uncovers the brain regions responsible for art appreciation and creativity. This interdisciplinary approach advances understanding of human responses to visual stimuli, informing therapeutic applications and enhancing artistic innovation.
Related Important Terms
Neurophenomenology
Neurophenomenology bridges Psychology and Neuroaesthetics by integrating first-person subjective experiences with neurobiological data, enhancing the understanding of aesthetic perception. This interdisciplinary approach employs phenomenological methods alongside neuroimaging techniques to elucidate the neural correlates of consciousness during artistic engagement.
Cognitive Aesthetics
Cognitive aesthetics bridges psychology and neuroaesthetics by examining how mental processes such as perception, memory, and attention influence aesthetic experience. This interdisciplinary approach integrates neuroimaging findings with psychological theories to elucidate the cognitive mechanisms underlying art appreciation and beauty perception.
Art-evoked Brain States
Psychology explores how art-evoked brain states influence emotional and cognitive processes through subjective experience and behavioral responses. Neuroaesthetics utilizes neuroimaging techniques to map brain activity, identifying specific neural circuits involved in aesthetic perception and artistic appreciation.
Affective Neuroscience Mapping
Affective neuroscience mapping integrates emotional processing with brain activity to uncover the neural substrates influencing aesthetic experience, bridging psychology's behavioral analysis and neuroaesthetics' focus on neural mechanisms. This interdisciplinary approach utilizes advanced imaging techniques to correlate affective responses with specific brain regions, enhancing understanding of emotional engagement in art perception and cognitive appraisal.
Embodied Simulation Theory
Embodied Simulation Theory posits that the brain's mirror neuron system allows individuals to internally replicate observed actions and emotions, providing a neural basis for empathy and aesthetic experience. Neuroaesthetics applies this theory to explain how sensory-motor, affective, and cognitive processes interact during art perception, offering a more biologically grounded framework than traditional psychological approaches.
Brain-based Valuation
Brain-based valuation in neuroaesthetics involves neural mechanisms that assign subjective value to aesthetic experiences, primarily engaging the orbitofrontal cortex and reward circuits, which contrasts with psychology's broader behavioral and cognitive models of preference. While psychology examines aesthetic appreciation through perceptual, emotional, and cultural factors, neuroaesthetics provides a mechanistic understanding rooted in brain activity and valuation processes.
Neuroaesthetic Salience
Neuroaesthetic salience examines how specific neural mechanisms prioritize sensory input based on aesthetic value, distinguishing it from general psychological approaches that analyze behavior and cognition without focusing on underlying neural processes. This salience is pivotal in understanding how the brain selectively enhances perception of aesthetic stimuli, integrating sensory experience with neural reward circuits.
Psychological Hedonics
Psychological hedonics examines the subjective experience of pleasure and pain in cognitive and emotional processes, emphasizing affective responses to stimuli. Neuroaesthetics explores the neural mechanisms underlying aesthetic experiences, integrating brain imaging techniques to map how sensory inputs evoke hedonic evaluations in the cortex and limbic system.
Aesthetic Processing Network
The Aesthetic Processing Network, comprising interconnected brain regions such as the orbitofrontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, and insula, plays a critical role in neuroaesthetics by decoding and interpreting sensory input into aesthetic experiences. Unlike traditional psychology that focuses on subjective aesthetic preferences, neuroaesthetics employs neuroimaging techniques to map neural activity patterns underlying aesthetic appreciation and emotional engagement with art.
Neuropsychological Beauty Bias
Neuropsychological beauty bias reveals how neural mechanisms influence aesthetic judgments, demonstrating that brain regions such as the orbitofrontal cortex and amygdala play crucial roles in processing perceived beauty. While psychology broadly examines cognitive and emotional factors in aesthetic preference, neuroaesthetics narrows this focus to neural correlates and biases that shape subconscious attraction to visual stimuli.
Psychology vs Neuroaesthetics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com